Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 2.5: "Binomial" or "Poisson"?"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Poisson_Distribution |
}} | }} | ||
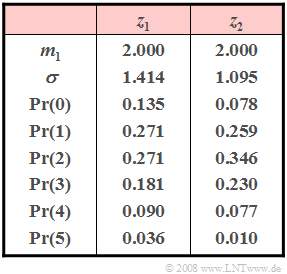
| − | [[File:P_ID104__Sto_A_2_5_neu.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID104__Sto_A_2_5_neu.png|right|frame|characteristics of $z_1$ and $z_2$]] |
| − | + | Consider two discrete random sizes $z_1$ and $z_2$ that can take (at least) all integer values between $0$ and $5$ (including these limits). The probabilities of these random sizes are given in the adjacent table. However, one of the two random variables is not limited to the given range of values. | |
| − | + | Furthermore it is known that | |
| − | * | + | * one of the variables is binomially distributed, and |
| − | * | + | * the other describes a Poisson distribution. |
| − | + | However, it is not known which of the two variables$(z_1$ or $z_2)$ is binomially distributed and which is Poisson distributed. | |
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
| − | + | Hints: | |
| − | * | + | *This exercise belongs to the chapter [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Poisson_Distribution|Poisson distribution]]. |
| − | * | + | *But also refers to the previous chapter [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Binomial_Distribution|binomial distribution]]. |
| − | * | + | *To check your results you can use the interactive applet [[Applets:Binomial-_und_Poissonverteilung_(Applet)|Binomial and Poisson distribution]] . |
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
| − | === | + | ===Questions=== |
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {Find out from the probabilities, means, and dispersions whether $z_1$ or $z_2$ is Poisson distributed. |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + $z_1$ | + | + $z_1$ is Poisson distributed and $z_2$ is binomially distributed. |
| − | - $z_1$ | + | - $z_1$ is binomially distributed and $z_2$ is Poisson distributed. |
| − | { | + | {What rate $\lambda$ does the Poisson distribution exhibit? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $\lambda \ = \ $ | + | $\lambda \ = \ $ { 2 3% } |
| − | { | + | {The values of the Poisson distribution are not limited to the range $0$, ... , $5$ . <br>What are the probabilities that the Poisson distributed size is exactly equal to $6$ or is greater than $6$ ? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
${\rm Pr}(z_{\rm Poisson} = 6) \ = \ $ { 0.012 3% } | ${\rm Pr}(z_{\rm Poisson} = 6) \ = \ $ { 0.012 3% } | ||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
| − | { | + | {Now consider the binomial distribution. Give its characteristic probability $p$ . |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$p \ = \ $ { 0.4 3% } | $p \ = \ $ { 0.4 3% } | ||
| − | { | + | {What is the size of the parameter $I$ of the binomial distribution? Check your result using the probability $\rm Pr(0)$. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$I \ = \ $ { 5 3% } | $I \ = \ $ { 5 3% } | ||
| − | |||
Revision as of 23:37, 15 December 2021
Consider two discrete random sizes $z_1$ and $z_2$ that can take (at least) all integer values between $0$ and $5$ (including these limits). The probabilities of these random sizes are given in the adjacent table. However, one of the two random variables is not limited to the given range of values.
Furthermore it is known that
- one of the variables is binomially distributed, and
- the other describes a Poisson distribution.
However, it is not known which of the two variables$(z_1$ or $z_2)$ is binomially distributed and which is Poisson distributed.
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter Poisson distribution.
- But also refers to the previous chapter binomial distribution.
- To check your results you can use the interactive applet Binomial and Poisson distribution .
Questions
Musterlösung
- Bei der Poissonverteilung sind Mittelwert $m_1$ und Varianz $\sigma^2$ gleich.
- Die Zufallsgröße $z_1$ erfüllt diese Bedingung im Gegensatz zur Zufallsgröße $z_2$.
(2) Bei der Poissonverteilung ist zudem der Mittelwert gleich der Rate. Deshalb muss $\underline{\lambda = 2}$ gelten.
(3) Die entsprechende Wahrscheinlichkeit lautet mit $z_{\rm Poisson} = z_1$:
- $${\rm Pr}(z_1 = 6)=\frac{2^6}{6!}\cdot e^{-2}\hspace{0.15cm} \underline{\approx 0.012}$$
- $${\rm Pr}(z_1 > 6)=1 -{\rm Pr}(0) -{\rm Pr}(1) - \ \text{...} \ - {\rm Pr}(6)\hspace{0.15cm} \underline{\approx 0.004}.$$
(4) Für die Varianz der Binomialverteilung gilt:
- $$\sigma^{2}= I\cdot p\cdot (1- p)= m_{\rm 1}\cdot ( 1- p).$$
- Die charakteristische Wahrscheinlichkeit der Binomialverteilung ergibt sich aus der Varianz $\sigma^2 = 1.095$ und dem Mittelwert $m_1 = 2$ gemäß der Gleichung:
- $$ 1- p = \frac{\sigma^{2}}{m_1}= \frac{1.2}{2} = 0.6\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} p \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{= 0.4}.$$
(5) Aus dem Mittelwert $m_1 = 2$ folgt weiterhin $\underline{I= 5}.$
- Die Wahrscheinlichkeit für den Wert "0" müsste mit diesen Parametern wie folgt lauten:
- $${\rm Pr}(z_2 = 0)=\left({5 \atop {0}}\right)\cdot p^{\rm 0}\cdot (1 - p)^{\rm 5-0}=0.6^5=0.078.$$
- Das bedeutet: Unsere Ergebnisse sind richtig.