Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 4.16: Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors"
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
[[File:P_ID671__Sto_A_4_16.png|right|frame|Three correlation matrices]] | [[File:P_ID671__Sto_A_4_16.png|right|frame|Three correlation matrices]] | ||
| − | Although the description of Gaussian random variables using vectors and matrices is actually only necessary and makes sense for more than $N = 2$ dimensions, here we restrict ourselves to the special case of two-dimensional random variables for simplicity. | + | Although the description of Gaussian random variables using vectors and matrices is actually only necessary and makes sense for more than $N = 2$ dimensions, here we restrict ourselves to the special case of two-dimensional random variables for simplicity. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
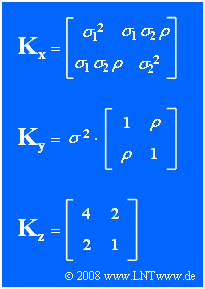
| + | In the graph above, the general correlation matrix $\mathbf{K_x}$ of the two-dimensional random variable $\mathbf{x} = (x_1, x_2)^{\rm T}$ is given, where $\sigma_1^2$ and $\sigma_2^2$ describe the variances of the individual components. $\rho$ denotes the correlation coefficient between the two components. | ||
| + | The random variables $\mathbf{y}$ and $\mathbf{z}$ give two special cases of $\mathbf{x}$ whose process parameters are to be determined from the correlation matrices $\mathbf{K_y}$ and $\mathbf{K_z}$ respectively. | ||
| Line 21: | Line 17: | ||
Hints: | Hints: | ||
*The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Generalization_to_N-Dimensional_Random_Variables|Generalization to N-Dimensional Random Variables]]. | *The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Generalization_to_N-Dimensional_Random_Variables|Generalization to N-Dimensional Random Variables]]. | ||
| − | *Some basics on the application of vectors and matrices can be found on the pages [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Generalization_to_N-Dimensional_Random_Variables#Basics_of_matrix_operations:_Determinant_of_a_matrix|Determinant of a Matrix]] and [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Generalization_to_N-Dimensional_Random_Variables#Basics_of_matrix_operations:_Inverse_of_a_matrix|Inverse of a Matrix]] . | + | *Some basics on the application of vectors and matrices can be found on the pages [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Generalization_to_N-Dimensional_Random_Variables#Basics_of_matrix_operations:_Determinant_of_a_matrix|Determinant of a Matrix]] and [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Generalization_to_N-Dimensional_Random_Variables#Basics_of_matrix_operations:_Inverse_of_a_matrix|Inverse of a Matrix]] . |
| − | * According to the page [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Two-Dimensional_Gaussian_Random_Variables#Contour_lines_for_correlated_random_variables|Contour lines for correlated random variables]] the angle $\alpha$ between the old and the new system is given by the following equation: | + | * According to the page [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Two-Dimensional_Gaussian_Random_Variables#Contour_lines_for_correlated_random_variables|"Contour lines for correlated random variables"]] the angle $\alpha$ between the old and the new system is given by the following equation: |
:$$\alpha = {1}/{2}\cdot \arctan (2 \cdot\rho \cdot | :$$\alpha = {1}/{2}\cdot \arctan (2 \cdot\rho \cdot | ||
\frac{\sigma_1\cdot\sigma_2}{\sigma_1^2 -\sigma_2^2}).$$ | \frac{\sigma_1\cdot\sigma_2}{\sigma_1^2 -\sigma_2^2}).$$ | ||
| − | *In particular, note: | + | *In particular, note: |
**A $2×2$-covariance matrix has two real eigenvalues $\lambda_1$ and $\lambda_2$. | **A $2×2$-covariance matrix has two real eigenvalues $\lambda_1$ and $\lambda_2$. | ||
**These two eigenvalues determine two eigenvectors $\xi_1$ and $\xi_2$. | **These two eigenvalues determine two eigenvectors $\xi_1$ and $\xi_2$. | ||
| Line 38: | Line 34: | ||
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
+ $\mathbf{K_y}$ describes all possible two-dimensional random variables with $\sigma_1 = \sigma_2 = \sigma$. | + $\mathbf{K_y}$ describes all possible two-dimensional random variables with $\sigma_1 = \sigma_2 = \sigma$. | ||
| − | + The value range of the parameter $\rho$ is $-1 \le \rho \le +1$. | + | + The value range of the parameter $\rho$ is $-1 \le \rho \le +1$. |
| − | - The value range of the parameter $\rho$ is $0 < \rho < 1$. | + | - The value range of the parameter $\rho$ is $0 < \rho < 1$. |
| Line 48: | Line 44: | ||
| − | {Give the eigenvalues of $\mathbf{K_y}$ under the condition $\sigma = 1$ and $0 < \rho < 1$ What values result for $\rho = 0.5 $, assuming $\lambda_1 \ge \lambda_2$ | + | {Give the eigenvalues of $\mathbf{K_y}$ under the condition $\sigma = 1$ and $0 < \rho < 1$ What values result for $\rho = 0.5 $, assuming $\lambda_1 \ge \lambda_2$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$\lambda_1 \ = \ $ { 1.5 3% } $\ (\lambda_1 \ge \lambda_2)$ | $\lambda_1 \ = \ $ { 1.5 3% } $\ (\lambda_1 \ge \lambda_2)$ | ||
| Line 56: | Line 52: | ||
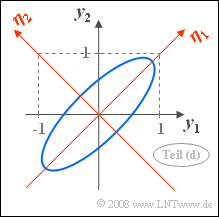
{Calculate the corresponding eigenvectors $\mathbf{\eta_1}$ and $\mathbf{\eta_2}$. Which of the following statements are true? | {Calculate the corresponding eigenvectors $\mathbf{\eta_1}$ and $\mathbf{\eta_2}$. Which of the following statements are true? | ||
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + $\mathbf{\eta_1}$ and $\mathbf{\eta_2}$ lie in the direction of the ellipse | + | + $\mathbf{\eta_1}$ and $\mathbf{\eta_2}$ lie in the direction of the ellipse main axes. |
| − | + The new coordinates are rotated by $45^\circ$ | + | + The new coordinates are rotated by $45^\circ$. |
| − | - The | + | - The standard deviations with respect to the new system are $\lambda_1$ and $\lambda_2$. |
| − | {What are the characteristics of the random variable | + | {What are the characteristics of the random variable $\mathbf{z}$ specified by $\mathbf{K_z}$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$\sigma_1 = \ $ { 2 3% } | $\sigma_1 = \ $ { 2 3% } | ||
Revision as of 14:22, 29 March 2022
Although the description of Gaussian random variables using vectors and matrices is actually only necessary and makes sense for more than $N = 2$ dimensions, here we restrict ourselves to the special case of two-dimensional random variables for simplicity.
In the graph above, the general correlation matrix $\mathbf{K_x}$ of the two-dimensional random variable $\mathbf{x} = (x_1, x_2)^{\rm T}$ is given, where $\sigma_1^2$ and $\sigma_2^2$ describe the variances of the individual components. $\rho$ denotes the correlation coefficient between the two components.
The random variables $\mathbf{y}$ and $\mathbf{z}$ give two special cases of $\mathbf{x}$ whose process parameters are to be determined from the correlation matrices $\mathbf{K_y}$ and $\mathbf{K_z}$ respectively.
Hints:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter Generalization to N-Dimensional Random Variables.
- Some basics on the application of vectors and matrices can be found on the pages Determinant of a Matrix and Inverse of a Matrix .
- According to the page "Contour lines for correlated random variables" the angle $\alpha$ between the old and the new system is given by the following equation:
- $$\alpha = {1}/{2}\cdot \arctan (2 \cdot\rho \cdot \frac{\sigma_1\cdot\sigma_2}{\sigma_1^2 -\sigma_2^2}).$$
- In particular, note:
- A $2×2$-covariance matrix has two real eigenvalues $\lambda_1$ and $\lambda_2$.
- These two eigenvalues determine two eigenvectors $\xi_1$ and $\xi_2$.
- These span a new coordinate system in the direction of the principal axes of the old system.
Questions
Solution
- $\mathbf{K_y}$ is indeed the most general correlation matrix of a 2D random variable with $\sigma_1 = \sigma_2 = \sigma$.
- The parameter $\rho$ specifies the correlation coefficient. This can take all values between $\pm 1$ including these marginal values.
(2) In this case, the governing equation is:
- $${\rm det}\left[ \begin{array}{cc} 1- \lambda & 0 \ 0 & 1- \lambda \end{array} \right] = 0 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} (1- \lambda)^2 = 0\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{\lambda_{1/2} =1}.$$
(3) With positive $\rho$ the governing equation of the eigenvalues is:
- $$(1- \lambda)^2 -\rho^2 = 0\hspace{0.5cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.5cm}\lambda^2 - 2\lambda + 1 - \rho^2 = 0\hspace{0.5cm}\Rightarrow\hspace{0.5cm}\lambda_{1/2} =1 \pm \rho.$$
- For $\rho= 0.5$ one gets $\underline{\lambda_{1} =1.5}$ and $\underline{\lambda_{2} =0.5}$.
- By the way, the equation holds in the whole domain of definition $-1 \le \rho \le +1$.
- For $\rho = 0$ is $\lambda_1 = \lambda_2 = +1$ ⇒ see subtask (2)'.
- For $\rho = \pm 1$ this gives $\lambda_1 = 2$ and $\lambda_2 = 0$.
(4) The eigenvectors are obtained by substituting the eigenvalues $\lambda_1$ and $\lambda_2$ into the correlation matrix:
- $$\left[ \begin{array}{cc} 1- (1+\rho) & \rho \\ \rho & 1- (1+\rho) \end{array} \right]\cdot{\boldsymbol{\eta_1}} = \left[ \begin{array}{cc} -\rho & \rho \\ \rho & -\rho \end{array} \right]\cdot \left[ \begin{array}{c} \eta_{11} \\ \eta_{12} \end{array} \right]=0$$
- $$\Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm}-\rho \cdot \eta_{11} + \rho \cdot \eta_{12} = 0\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm}\eta_{11}= {\rm const} \cdot \eta_{12}\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm}{\boldsymbol{\eta_1}}= {\rm const}\cdot \left[ \begin{array}{c} 1 \\ 1 \end{array} \right];$$
- $$\left[ \begin{array}{cc} 1- (1-\rho) & \rho \\ \rho & 1- (1-\rho) \end{array} \right]\cdot{\boldsymbol{\eta_2}} = \left[ \begin{array}{cc} \rho & \rho \\ \rho & \rho \end{array} \right]\cdot \left[ \begin{array}{c} \eta_{21} \\ \eta_{22} \end{array} \right]=0$$
- $$\Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm}\rho \cdot \eta_{21} + \rho \cdot \eta_{22} = 0\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm}\eta_{21}= -{\rm const} \cdot \eta_{22}\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm}{\boldsymbol{\eta_2}}= {\rm const}\cdot \left[ \begin{array}{c} -1 \\ 1 \end{array} \right].$$
Putting this into what is called orthonormal form, the following holds:
- $${\boldsymbol{\eta_1}}= \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\cdot \left[ \begin{array}{c} 1 \\ 1 \end{array} \right],\hspace{0.5cm} {\boldsymbol{\eta_2}}= \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\cdot \left[ \begin{array}{c} -1 \\ 1 \end{array} \right].$$
The sketch illustrates the result:
- The coordinate system defined by $\mathbf{\eta_1}$ and $\mathbf{\eta_2}$ is actually in the direction of the principal axes of the original system.
- With $\sigma_1 = \sigma_2$ almost always results $($exception: $\rho= 0)$ the angle of rotation $\alpha = 45^\circ$.
- This also follows from the equation given in the theory section:
- $$\alpha = {1}/{2}\cdot \arctan (2 \cdot\rho \cdot \frac{\sigma_1\cdot\sigma_2}{\sigma_1^2 -\sigma_2^2})= {1}/{2}\cdot \arctan (\infty)\hspace{0.3cm}\rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm}\alpha = 45^\circ.$$
- The eigenvalues $\lambda_1$ and $\lambda_2$ do not denote the scatter with respect to the new axes, but the variances.
Thus, correct are the proposed solutions 1 and 2.
(5) By comparing the matrices $\mathbf{K_x}$ and $\mathbf{K_z}$ we get.
- $\sigma_{1}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ =2}$,
- $\sigma_{2}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ =1}$,
- $\rho = 2/(\sigma_{1} \cdot \sigma_{2})\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ =1}$.
(6) According to the now familiar scheme:
- $$(4- \lambda) \cdot (1- \lambda) -4 = 0\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}\lambda^2 - 5\lambda = 0\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{\lambda_{1} =5,\hspace{0.1cm} \lambda_{2} =0}.$$
(7) According to the equation given on the specification sheet:
- $$\alpha ={1}/{2}\cdot \arctan (2 \cdot 1 \cdot \frac{2 \cdot 1}{2^2 -1^2})= {1}/{2}\cdot \arctan ({4}/{3}) = 26.56^\circ.$$
The same result is obtained using the eigenvector:
- $$\left[ \begin{array}{cc} 4-5 & 2 \\ 2 & 1-5 \end{array} \right]\cdot \left[ \begin{array}{c} \zeta_{11} \\ \zeta_{12} \end{array} \right]=0 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm}-\zeta_{11}= 2\zeta_{12}=0\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm}\zeta_{12}={\zeta_{11}}/{2}$$
- $$\Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm}\alpha = \arctan ({\zeta_{12}}/{\zeta_{11}}) = \arctan(0.5) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 26.56^\circ}.$$
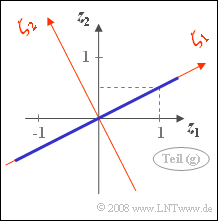
The accompanying sketch shows the joint PDF of the random variable $\mathbf{z}$:
- Because $\rho = 1$ all values lie on the correlation line with coordinates $z_1$ and $z_2 = z_1/2$.
- By rotating by the angle $\alpha = \arctan(0.5) = 26.56^\circ$ a new coordinate system is formed.
- The variance along the axis $\mathbf{\zeta_1}$ is $\lambda_1 = 5$ $($scatter $\sigma_1 = \sqrt{5} = 2.236)$,
- while in the direction orthogonal to it $\mathbf{\zeta_2}$ the random variable is not extended $(\lambda_2 = \sigma_2 = 0)$.