Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 3.3: Noise at Channel Equalization"
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}\sqrt{2 f T}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}\sqrt{2 f T}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * Thus, the equation for the noise power density before the decision $($with $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.35)$ | + | * Thus, the equation for the noise power density $\rm (PSD)$ before the decision is $($with $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.35)$: |
:$${\it \Phi}_{d{\rm N}}(f) = {N_0}/{2} \cdot \frac{|H_{\rm G | :$${\it \Phi}_{d{\rm N}}(f) = {N_0}/{2} \cdot \frac{|H_{\rm G | ||
}(f)|^2}{|H_{\rm K}(f)|^2} = {N_0}/{2} \cdot {\rm exp}\left | }(f)|^2}{|H_{\rm K}(f)|^2} = {N_0}/{2} \cdot {\rm exp}\left | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
\right ] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \right ] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
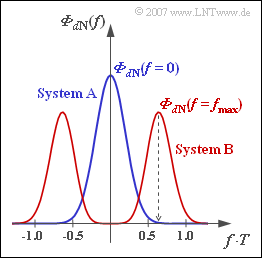
| − | + | *The noise PSD of system $\rm B$ is shown in red in the above graph and the noise PSD of system $\rm A$ is drawn in blue. | |
| − | For the system $\rm B$, the worst-case error probability | + | *For the system $\rm B$, the worst-case error probability |
:$$p_{\rm U} = {\rm Q} \left( \sqrt{\rho_{\rm U}} | :$$p_{\rm U} = {\rm Q} \left( \sqrt{\rho_{\rm U}} | ||
| − | \right) \hspace{0. | + | \right) \hspace{0.4cm}{\rm with} \hspace{0.4cm} \rho_{\rm U} = \frac{[\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})/2]^2}{ \sigma_d^2}$$ |
| − | was determined. The measurement resulted in $p_{\rm U} = 4 \cdot 10^{\rm -8}$, which corresponds to the signal-to-noise ratio $10 \cdot {\rm lg} \, \rho_{\rm U} = 14.8 \, {\rm dB}$. | + | :was determined. The measurement resulted in $p_{\rm U} = 4 \cdot 10^{\rm -8}$, which corresponds to the signal-to-noise ratio $10 \cdot {\rm lg} \, \rho_{\rm U} = 14.8 \, {\rm dB}$. |
| + | Notes: | ||
| + | *The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Digital_Signal_Transmission/Consideration_of_Channel_Distortion_and_Equalization|"Consideration of Channel Distortion and Equalization"]]. | ||
| − | + | * Use the [[Applets:Komplementäre_Gaußsche_Fehlerfunktionen|"Complementary Gaussian Error Functions"]] interaction module for numerical evaluation of the Q–function. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * Use the [[Applets:Komplementäre_Gaußsche_Fehlerfunktionen|"Complementary Gaussian Error Functions"]] interaction module for numerical evaluation of the Q function. | ||
| Line 50: | Line 49: | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | {What (normalized) noise rms value occurs in system $\rm B$? | + | {What (normalized) noise rms value occurs in system $\rm B$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$\sigma_d/s_0 \ = \ $ { 0.044 3% } | $\sigma_d/s_0 \ = \ $ { 0.044 3% } | ||
| − | {What noise rms value occurs for system $\rm A$ when it leads to exactly the same | + | {What noise rms value occurs for system $\rm A$ when it leads to exactly the same "worst-case error probability" as system $\rm B$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$\sigma_d/s_0 \ = \ $ { 0.044 3% } | $\sigma_d/s_0 \ = \ $ { 0.044 3% } | ||
| − | {By what attenuation factor $\alpha$ is system $\rm A$ equivalent to system $\rm B$ in terms of | + | {By what attenuation factor $\alpha$ is system $\rm A$ equivalent to system $\rm B$ in terms of worst-case error probability? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$20 \cdot {\rm lg} \ \alpha \ = \ $ { -70.967--66.833 } ${\ \rm dB}$ | $20 \cdot {\rm lg} \ \alpha \ = \ $ { -70.967--66.833 } ${\ \rm dB}$ | ||
| − | {What is the noise power density | + | {What is the noise power-spectral density normalized to $N_0/2$ $($at $f = 0)$ before the decision for system $\rm A$ and system $\rm B$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$\text{System A:}\hspace{0.4cm} {\it \Phi}_{d \rm N} (f = 0)/(N_0/2) \ = \ $ { 7.8 3% } $\ \cdot 10^6$ | $\text{System A:}\hspace{0.4cm} {\it \Phi}_{d \rm N} (f = 0)/(N_0/2) \ = \ $ { 7.8 3% } $\ \cdot 10^6$ | ||
Revision as of 12:10, 17 June 2022
We consider two different system variants, both using NRZ rectangular transmission pulses and are affected by AWGN noise.
- To limit the noise power, in both cases a Gaussian low-pass filter
- $$H_{\rm G}(f) = {\rm exp}(- \pi \cdot \frac{f^2}{(2f_{\rm G})^2})$$
- with normalized cutoff frequency $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.35$ is used, so that both systems also have the same eye opening with $\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D} = 0) = 0.478 \cdot s_0$.
- The transmission energy $E_{\rm B} = s_0^2 \cdot T$ spent per bit is larger than the noise power density $N_0$ by a factor of $10^9$ ⇒ $10\cdot {\rm lg} \, E_{\rm B}/N_0 = 90 \, {\rm dB}$.
- The channel frequency response of system $\rm A$ is frequency-independent: $H_{\rm K}(f) = \alpha$. Accordingly, for the receiver filter $H_{\rm E}(f) = H_{\rm G}(f)/\alpha$ must be assumed, so that the following applies to the detection noise power:
- $$\sigma_d^2 = {N_0}/{2} \cdot \int_{-\infty}^{+\infty} |H_{\rm E}(f)|^2 \,{\rm d} f = \frac{N_0 \cdot f_{\rm G}}{\sqrt{2} \cdot \alpha^2} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- In contrast, system $\rm B$ assumes a coaxial cable with characteristic attenuation $($at half the bit rate$)$ $a_* = 80 \, {\rm dB}$ $($or $9.2 \, {\rm Np})$ so that the channel magnitude frequency response is:
- $$|H_{\rm K}(f)| = {\rm e}^{- 9.2 \hspace{0.05cm} \cdot \hspace{0.05cm}\sqrt{2 f T}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Thus, the equation for the noise power density $\rm (PSD)$ before the decision is $($with $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.35)$:
- $${\it \Phi}_{d{\rm N}}(f) = {N_0}/{2} \cdot \frac{|H_{\rm G }(f)|^2}{|H_{\rm K}(f)|^2} = {N_0}/{2} \cdot {\rm exp}\left [18.4 \cdot \sqrt{2 f T} - 2\pi \cdot \frac{(f \cdot T)^2}{(2 \cdot 0.35)^2} \right ] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The noise PSD of system $\rm B$ is shown in red in the above graph and the noise PSD of system $\rm A$ is drawn in blue.
- For the system $\rm B$, the worst-case error probability
- $$p_{\rm U} = {\rm Q} \left( \sqrt{\rho_{\rm U}} \right) \hspace{0.4cm}{\rm with} \hspace{0.4cm} \rho_{\rm U} = \frac{[\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})/2]^2}{ \sigma_d^2}$$
- was determined. The measurement resulted in $p_{\rm U} = 4 \cdot 10^{\rm -8}$, which corresponds to the signal-to-noise ratio $10 \cdot {\rm lg} \, \rho_{\rm U} = 14.8 \, {\rm dB}$.
Notes:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter "Consideration of Channel Distortion and Equalization".
- Use the "Complementary Gaussian Error Functions" interaction module for numerical evaluation of the Q–function.
Questions
Solution
- $$\sqrt{\rho_{\rm U}} = \frac{\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})/2}{ \sigma_d}\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \sigma_d = \frac{0.478 \cdot s_0/2}{ \sqrt{30.2}} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline { \approx 0.044 \cdot s_0 }\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) With the same error probability $p_{\rm U}$ (and thus the same $\rho_{\rm U}$), $\sigma_d$ must have exactly the same value as calculated in subtask (1), since the eye opening also remains the same ⇒ $\sigma_d/s_0 \underline{= 0.044}.$
(3) According to the specification section:
- $$\alpha^2 = \frac{N_0 \cdot f_{\rm G}}{\sqrt{2} \cdot \sigma_d^2} = \frac{10^{-9} \cdot s_0^2 \cdot T \cdot f_{\rm G}}{\sqrt{2} \cdot \sigma_d^2} = 10^{-9} \cdot \frac{ f_{\rm G} \cdot T}{\sqrt{2} \cdot (\sigma_d/s_0)^2}\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \alpha^2 = 10^{-9} \cdot \frac{ 0.35}{\sqrt{2} \cdot 0.044^2} \approx 1.28 \cdot 10^{-7} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Expressed in ${\rm dB}$, one thus obtains
- $$20 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.1cm}\alpha = 10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.1cm}\alpha^2 = -70\,{\rm dB}\hspace{0.1cm}+\hspace{0.1cm}10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.1cm}1.28\hspace{0.15cm}\underline { = -68.9\,{\rm dB}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(4) For system $\rm B$, because $H_{\rm E}(f = 0) = 1$, the normalized value is equal to $1$, that means, it is ${\it \Phi}_{d \rm N}(f = 0) = N_0/2$.
In contrast, for system $\rm A$, this value is larger by $1/\alpha^2$ due to the components of the frequency-independent cable attenuation $\alpha$:
- $${\rm System}\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm A:}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{{\it \Phi}_{d{\rm N}}(f = 0)}{N_0/2} = \frac{1}{\alpha^2} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 7.8 \cdot 10^{6}} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{1.05cm}{\rm System\hspace{0.15cm}B}: \frac{{\it \Phi}_{d \rm N}(f = 0)}{N_0/2} \, \underline {= 1}.$$
(5) ${\it \Phi}_{d \rm N}(f)$ is maximal if the exponent
- $$18.4 \cdot \sqrt{2 f T} - 2\pi \cdot \frac{(f \cdot T)^2}{0.49}$$
has the maximum value. Thus, with $x = f \cdot T$, the optimization function is:
- $$y(x) = 26.022 \cdot \sqrt{x} - 12.823 \cdot x^2 \approx 26 \cdot \sqrt{x} - 13 \cdot x^2 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \frac{{\rm d}y}{{\rm d}x} = \frac{26} {2\cdot \sqrt{x}} - 13 \cdot 2 \cdot x = 0$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \frac{1} { \sqrt{x}} = 2 \cdot x \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}\frac{1} { x} = 4 \cdot x^2 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} x^3 = 0.25 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} x \approx 0.63 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
This gives $f_{\rm max} \cdot T\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 0.63}$.
(6) With $x_{\rm max} = 0.63$ we get the function value
- $$y(x_{\rm max}) \approx 26 \cdot \sqrt{0.63} - 13 \cdot 0.63^2 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 15.477}.$$
It follows:
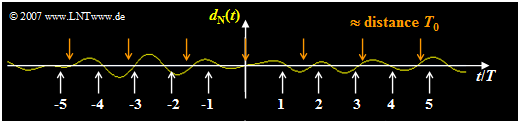
- The noise power density at the (normalized) frequency $f \cdot T \approx 0.63$ is larger than at the frequency $e^{\rm 15.5} \underline{\approx 5.4 \cdot 10^6}$ by a factor of $f = 0$.
- Thus, periodic components with period $T_0 \approx 1.6 \cdot T$ predominate in the noise component $d_{\rm N}(t)$.
- The graph shows a simulation and confirms this result.