Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 3.10Z: Maximum Likelihood Decoding of Convolutional Codes"
From LNTwww
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Channel_Coding/Decoding_of_Convolutional_Codes}} | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Channel_Coding/Decoding_of_Convolutional_Codes}} | ||
| − | [[File:P_ID2678__KC_Z_3_10.png|right|frame|Overall system model | + | [[File:P_ID2678__KC_Z_3_10.png|right|frame|Overall system model, given for this exercise]] |
| − | The Viterbi algorithm represents the best known realization form for the maximum likelihood decoding of a convolutional code. We assume the following model | + | The Viterbi algorithm represents the best known realization form for the maximum likelihood decoding of a convolutional code. We assume here the following model: |
| − | * The information sequence $\underline{u}$ is converted into the code sequence $\underline{x}$ by a convolutional code. It is valid $u_i ∈ \{0, \, 1\}$. In contrast, the code symbols are represented bipolar ⇒ $x_i ∈ \{–1, \, +1\}$. | + | * The information sequence $\underline{u}$ is converted into the code sequence $\underline{x}$ by a convolutional code. |
| − | * Let the channel be given by the [[Channel_Coding/Channel_Models_and_Decision_Structures#Binary_Symmetric_Channel_.E2.80. 93_BSC| | + | |
| − | * Given a | + | *It is valid $u_i ∈ \{0, \, 1\}$. In contrast, the code symbols are represented bipolar ⇒ $x_i ∈ \{–1, \, +1\}$. |
| + | |||
| + | * Let the channel be given by the models [[Channel_Coding/Channel_Models_and_Decision_Structures#Binary_Symmetric_Channel_.E2.80. 93_BSC|$\text{BSC}$]] ⇒ received values $y_i ∈ \{–1, \, +1\}$ or [[Channel_Coding/Channel_Models_and_Decision_Structures#AWGN_channel_at_Binary_Input| $\text{AWGN}$]] ⇒ $y_i$ real-valued. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Given a received sequence $\underline{y}$ the Viterbi algorithm decides for the sequence $\underline{z}$ according to | ||
:$$\underline{z} = {\rm arg} \max_{\underline{x}_{\hspace{0.03cm}i} \hspace{0.03cm} \in \hspace{0.05cm} \mathcal{C}} \hspace{0.1cm} {\rm Pr}( \underline{x}_{\hspace{0.03cm}i} |\hspace{0.05cm} \underline{y} ) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$\underline{z} = {\rm arg} \max_{\underline{x}_{\hspace{0.03cm}i} \hspace{0.03cm} \in \hspace{0.05cm} \mathcal{C}} \hspace{0.1cm} {\rm Pr}( \underline{x}_{\hspace{0.03cm}i} |\hspace{0.05cm} \underline{y} ) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | *This corresponds to the [[Channel_Coding/Channel_Models_and_Decision_Structures#Criteria_.C2.BBMaximum-a-posteriori.C2.AB_and_.C2.BBMaximum-Likelihood.C2.AB| "Maximum a posteriori"]] (MAP) criterion. If all information sequences $\underline{u}$ are equally likely, this transitions to the somewhat simpler [[Channel_Coding/Channel_Models_and_Decision_Structures#Criteria_.C2.BBMaximum-a-posteriori.C2.AB_and_.C2.BBMaximum-Likelihood.C2.AB| "Maximum likelihood criterion"]] : | + | *This corresponds to the [[Channel_Coding/Channel_Models_and_Decision_Structures#Criteria_.C2.BBMaximum-a-posteriori.C2.AB_and_.C2.BBMaximum-Likelihood.C2.AB| "Maximum a posteriori"]] $\rm (MAP)$ criterion. If all information sequences $\underline{u}$ are equally likely, this transitions to the somewhat simpler [[Channel_Coding/Channel_Models_and_Decision_Structures#Criteria_.C2.BBMaximum-a-posteriori.C2.AB_and_.C2.BBMaximum-Likelihood.C2.AB| "Maximum likelihood criterion"]] $\rm (ML)$: |
:$$\underline{z} = {\rm arg} \max_{\underline{x}_{\hspace{0.03cm}i} \hspace{0.05cm} \in \hspace{0.05cm} \mathcal{C}} \hspace{0.1cm} {\rm Pr}( \underline{y} \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} \underline{x}_{\hspace{0.03cm}i} ) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$\underline{z} = {\rm arg} \max_{\underline{x}_{\hspace{0.03cm}i} \hspace{0.05cm} \in \hspace{0.05cm} \mathcal{C}} \hspace{0.1cm} {\rm Pr}( \underline{y} \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} \underline{x}_{\hspace{0.03cm}i} ) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | *As a further result, the Viterbi | + | *As a further result, the Viterbi algorithm additionally outputs the sequence $\underline{v}$ as an estimate for the information sequence $\underline{u}$. |
| − | In this exercise, | + | In this exercise, you should determinethe relationship between the [[Channel_Coding/Objective_of_Channel_Coding#Important_definitions_for_block_coding| $\text{Hamming distance}$]] $d_{\rm H}(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y})$ and the [[Channel_Coding/Channel_Models_and_Decision_Structures#Maximum-likelihood_decision_at_the_AWGN_channel|$\text{Euclidean distance}$]] |
:$$d_{\rm E}(\underline{x} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{y}) = | :$$d_{\rm E}(\underline{x} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{y}) = | ||
| − | \sqrt{\sum_{i=1}^{L} \hspace{0.2cm}(x_i - y_i)^2}\hspace{0.05cm}$$ | + | \sqrt{\sum_{i=1}^{L} \hspace{0.2cm}(x_i - y_i)^2}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ |
| − | + | Then, the above maximum likelihood criterion is to be formulated with | |
* the Hamming distance $d_{\rm H}(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y})$, | * the Hamming distance $d_{\rm H}(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y})$, | ||
| − | * the Euclidean distance $d_{\rm E}(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y})$, and | + | |
| − | * the [[Channel_Coding/Decoding_of_Convolutional_Codes#Relationship_between_Hamming_distance_and_correlation| | + | * the Euclidean distance $d_{\rm E}(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y})$, and |
| + | |||
| + | * the [[Channel_Coding/Decoding_of_Convolutional_Codes#Relationship_between_Hamming_distance_and_correlation|$\text{correlation value}$]] $〈 x \cdot y 〉$. | ||
| + | |||
| Line 29: | Line 36: | ||
| + | <u>Hints:</u> | ||
| + | * This exercise refers to the chapter [[Channel_Coding/Decoding_of_Convolutional_Codes| "Decoding of Convolutional Codes"]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Reference is made in particular to the section [[Channel_Coding/Decoding_of_Convolutional_Codes#Viterbi_algorithm_based_on_correlation_and_metrics|"Viterbi algorithm – based on correlation and metrics"]]. | ||
| − | + | * For simplicity, "tilde" and "apostrophe" are omitted. | |
| − | * | + | |
| − | + | * For more information on this topic, see the following sections in this book: | |
| − | |||
| − | * For more information on this topic, see the following | ||
** [[Channel_Coding/Channel_Models_and_Decision_Structures#Criteria_.C2.BBMaximum-a-posteriori.C2.AB_and_.C2.BBMaximum-Likelihood.C2.AB| "MAP and ML criterion"]], | ** [[Channel_Coding/Channel_Models_and_Decision_Structures#Criteria_.C2.BBMaximum-a-posteriori.C2.AB_and_.C2.BBMaximum-Likelihood.C2.AB| "MAP and ML criterion"]], | ||
| + | |||
** [[Channel_Coding/Channel_Models_and_Decision_Structures#Maximum-likelihood_decision_at_the_BSC_channel| "ML decision at the BSC channel"]], | ** [[Channel_Coding/Channel_Models_and_Decision_Structures#Maximum-likelihood_decision_at_the_BSC_channel| "ML decision at the BSC channel"]], | ||
| + | |||
** [[Channel_Coding/Channel_Models_and_Decision_Structures#Maximum-likelihood_decision_at_the_AWGN_channel| "ML decision at the AWGN channel"]], | ** [[Channel_Coding/Channel_Models_and_Decision_Structures#Maximum-likelihood_decision_at_the_AWGN_channel| "ML decision at the AWGN channel"]], | ||
| + | |||
** [[Channel_Coding/Decoding_of_Linear_Block_Codes#Block_diagram_and_requirements| "Decoding linear block codes"]]. | ** [[Channel_Coding/Decoding_of_Linear_Block_Codes#Block_diagram_and_requirements| "Decoding linear block codes"]]. | ||
| Line 44: | Line 56: | ||
===Questions=== | ===Questions=== | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | {How are $d_{\rm H}(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y})$ and $d_{\rm E}(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y})$ related in the BSC | + | {How are $d_{\rm H}(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y})$ and $d_{\rm E}(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y})$ related in the BSC model? |
|type="()"} | |type="()"} | ||
- $d_{\rm H}(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y}) = d_{\rm E}(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y})$ is valid. | - $d_{\rm H}(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y}) = d_{\rm E}(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y})$ is valid. | ||
| Line 50: | Line 62: | ||
+ $d_{\rm H}(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y}) = d_{\rm E}^2(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y})/4$ is valid. | + $d_{\rm H}(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y}) = d_{\rm E}^2(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y})/4$ is valid. | ||
| − | {Which of the equations describe the | + | {Which of the equations describe the maximum likelihood decoding in the BSC model? The minimization/maximization refers alwaysto all $\underline{x} ∈\mathcal{ C}$. |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
+ $\underline{z} = \arg \min {d_{\rm H}(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y})}$, | + $\underline{z} = \arg \min {d_{\rm H}(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y})}$, | ||
| Line 56: | Line 68: | ||
+ $\underline{z} = \arg \min {d_{\rm E}^2(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y})}$, | + $\underline{z} = \arg \min {d_{\rm E}^2(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y})}$, | ||
| − | {Which equation describes the | + | {Which equation describes the maximum likelihood decision in the BSC model? |
|type="()"} | |type="()"} | ||
- $\underline{z} = \arg \min 〈 \underline{x} \cdot \underline{y} 〉$, | - $\underline{z} = \arg \min 〈 \underline{x} \cdot \underline{y} 〉$, | ||
+ $\underline{z} = \arg \max 〈 \underline{x} \cdot \underline{y} 〉$. | + $\underline{z} = \arg \max 〈 \underline{x} \cdot \underline{y} 〉$. | ||
| − | {What equations apply to the | + | {What equations apply to the maximum likelihood decision in the AWGN model? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
- $\underline{z} = \arg \min {d_{\rm H}(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y})}$, | - $\underline{z} = \arg \min {d_{\rm H}(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y})}$, | ||
Revision as of 15:50, 18 November 2022
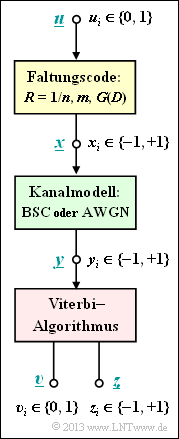
The Viterbi algorithm represents the best known realization form for the maximum likelihood decoding of a convolutional code. We assume here the following model:
- The information sequence $\underline{u}$ is converted into the code sequence $\underline{x}$ by a convolutional code.
- It is valid $u_i ∈ \{0, \, 1\}$. In contrast, the code symbols are represented bipolar ⇒ $x_i ∈ \{–1, \, +1\}$.
- Let the channel be given by the models $\text{BSC}$ ⇒ received values $y_i ∈ \{–1, \, +1\}$ or $\text{AWGN}$ ⇒ $y_i$ real-valued.
- Given a received sequence $\underline{y}$ the Viterbi algorithm decides for the sequence $\underline{z}$ according to
- $$\underline{z} = {\rm arg} \max_{\underline{x}_{\hspace{0.03cm}i} \hspace{0.03cm} \in \hspace{0.05cm} \mathcal{C}} \hspace{0.1cm} {\rm Pr}( \underline{x}_{\hspace{0.03cm}i} |\hspace{0.05cm} \underline{y} ) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- This corresponds to the "Maximum a posteriori" $\rm (MAP)$ criterion. If all information sequences $\underline{u}$ are equally likely, this transitions to the somewhat simpler "Maximum likelihood criterion" $\rm (ML)$:
- $$\underline{z} = {\rm arg} \max_{\underline{x}_{\hspace{0.03cm}i} \hspace{0.05cm} \in \hspace{0.05cm} \mathcal{C}} \hspace{0.1cm} {\rm Pr}( \underline{y} \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} \underline{x}_{\hspace{0.03cm}i} ) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- As a further result, the Viterbi algorithm additionally outputs the sequence $\underline{v}$ as an estimate for the information sequence $\underline{u}$.
In this exercise, you should determinethe relationship between the $\text{Hamming distance}$ $d_{\rm H}(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y})$ and the $\text{Euclidean distance}$
- $$d_{\rm E}(\underline{x} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{y}) = \sqrt{\sum_{i=1}^{L} \hspace{0.2cm}(x_i - y_i)^2}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Then, the above maximum likelihood criterion is to be formulated with
- the Hamming distance $d_{\rm H}(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y})$,
- the Euclidean distance $d_{\rm E}(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y})$, and
- the $\text{correlation value}$ $〈 x \cdot y 〉$.
Hints:
- This exercise refers to the chapter "Decoding of Convolutional Codes".
- Reference is made in particular to the section "Viterbi algorithm – based on correlation and metrics".
- For simplicity, "tilde" and "apostrophe" are omitted.
- For more information on this topic, see the following sections in this book:
Questions
Solution
(1) Correct is the proposed solution 3:
- Let the two binary sequences be $\underline{x}$ and $\underline{y}$ with $x_i ∈ \{-1, \, +1\}, \ y_i ∈ \{-1, \, +1\}$. Let the sequence length be $L$ in each case.
- The Hamming distance $d_{\rm H}(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y})$ gives the number of bits in which $\underline{x}$ and $\underline{y}$ differ, for which thus $x_i \, - y_i = ±2$ ⇒ $ (x_i \, - y_i)^2 = 4$ holds.
- Equal symbols $(x_i = y_i)$ do not contribute to the Hamming–distance and give $(x_i \, – y_i)^2 = 0$. According to the solution 3, we can therefore write:
- $$ d_{\rm H}(\underline{x} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{y}) = \frac{1}{4} \cdot \sum_{i=1}^{L} \hspace{0.2cm}(x_i - y_i)^2= \frac{1}{4} \cdot d_{\rm E}^2(\underline{x} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{y})\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) All proposed solutions are correct:
- In the BSC model, it is common practice to select the code word $\underline{x}$ with the smallest Hamming distance $d_{\rm H}(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y})$ for the given received vector $\underline{y}$:
- $$\underline{z} = {\rm arg} \min_{\underline{x} \hspace{0.05cm} \in \hspace{0.05cm} \mathcal{C}} \hspace{0.1cm} d_{\rm H}(\underline{x} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{y})\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- But according to the subtask (1) also applies:
- $$\underline{z} = {\rm arg} \min_{\underline{x} \hspace{0.05cm} \in \hspace{0.05cm} \mathcal{C}} \hspace{0.1cm} d_{\rm E}^{\hspace{0.15cm}2}(\underline{x} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{y})/4 \hspace{0.2cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.2cm} \underline{z} = {\rm arg} \min_{\underline{x} \hspace{0.05cm} \in \hspace{0.05cm} \mathcal{C}} \hspace{0.1cm} d_{\rm E}^{\hspace{0.15cm}2}(\underline{x} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{y}) \hspace{0.2cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.2cm} \underline{z} = {\rm arg} \min_{\underline{x} \hspace{0.05cm} \in \hspace{0.05cm} \mathcal{C}} \hspace{0.1cm} d_{\rm E}(\underline{x} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{y}) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The factor $1/4$ does not matter for the minimization. Since $d_{\rm E}(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y}) ≥ 0$, it does not matter whether the minimization is done with respect to $d_{\rm E}(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y})$ or $d_{\rm E}^2(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y})$.
(3) Correct is the proposed solution 2:
- The square of the Euclidean distance can be expressed as follows:
- $$d_{\rm E}^{\hspace{0.15cm}2}(\underline{x} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{y}) = \sum_{i=1}^{L} \hspace{0.2cm}(x_i - y_i)^2 = \hspace{0.1cm}\sum_{i=1}^{L} \hspace{0.1cm} x_i^{\hspace{0.15cm}2} \hspace{0.1cm}+ \hspace{0.1cm}\sum_{i=1}^{L} \hspace{0.1cm} y_i^{\hspace{0.15cm}2} \hspace{0.1cm}-2 \cdot \sum_{i=1}^{L} \hspace{0.1cm} x_i \cdot y_i \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The first two summands are each equal to $L$ and need not be considered for minimization.
- For the last expression in this equation, $–2 \cdot 〈 \underline{x}, \, \underline{y} 〉$ can be written.
- Due to the negative sign, minimization becomes maximization ⇒ answer 2.
(4) Correct are proposed solutions 2 and 3:
- For the AWGN channel, unlike the BSC, no Hamming distance can be specified.
- Based on the equation
- $$d_{\rm E}^{\hspace{0.15cm}2}(\underline{x} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{y}) = \hspace{0.1cm}\sum_{i=1}^{L} \hspace{0.1cm} x_i^{\hspace{0.15cm}2} \hspace{0.1cm}+ \hspace{0.1cm}\sum_{i=1}^{L} \hspace{0.1cm} y_i^{\hspace{0.15cm}2} \hspace{0.1cm}-2 \cdot \sum_{i=1}^{L} \hspace{0.1cm} x_i \cdot y_i$$
- the same statements apply for the first and last summands as for the BSC model – see subtask (3).
- For the middle summand, $y_i = x_i + n_i$ and $x_i ∈ \{–1, \, +1\}$ hold:
- $$\sum_{i=1}^{L} \hspace{0.1cm} y_i^{\hspace{0.15cm}2} = \hspace{0.1cm}\sum_{i=1}^{L} \hspace{0.1cm} x_i^{\hspace{0.15cm}2} \hspace{0.1cm}+ \hspace{0.1cm}\sum_{i=1}^{L} \hspace{0.1cm} n_i^{\hspace{0.15cm}2} \hspace{0.1cm}+2 \cdot \sum_{i=1}^{L} \hspace{0.1cm} x_i \cdot n_i \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The first summand again gives $L$, the second is proportional to the noise power, and the last term vanishes since $\underline{x}$ and $\underline{n}$ are uncorrelated.
- So for minimizing $d_{\rm E}(\underline{x}, \, \underline{y})$, the sum over $y_i^2$ need not be considered since there is no relation to the code sequences $\underline{x}$.