Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 3.12: Path Weighting Function"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Channel_Coding/Distance_Characteristics_and_Error_Probability_Barriers}} | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Channel_Coding/Distance_Characteristics_and_Error_Probability_Barriers}} | ||
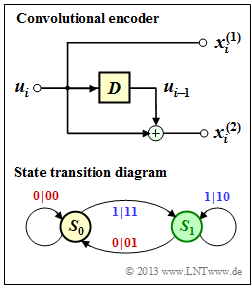
| − | [[File:EN_KC_A_3_12.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:EN_KC_A_3_12.png|right|frame|$m = 1$ convolutional encoder and state transition diagram]] |
| − | In [[Aufgaben:Exercise_3.6:_State_Transition_Diagram| | + | In [[Aufgaben:Exercise_3.6:_State_Transition_Diagram|$\text{Exercise 3.6}$]] the state transition diagram for the drawn convolutional encoder with properties |
* Rate $R = 1/2$, | * Rate $R = 1/2$, | ||
| + | |||
* memory $m = 1$, | * memory $m = 1$, | ||
| + | |||
* transfer function matrix $\mathbf{G}(D) = (1, \, D)$ | * transfer function matrix $\mathbf{G}(D) = (1, \, D)$ | ||
| − | which is shown on the right. | + | was constructed which is shown on the right. |
| + | |||
| + | Now, from this state transition diagram | ||
| + | * the path weighting enumerator function $T(X)$, and | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* the extended path weighting enumerator function $T_{\rm enh}(X, \, U)$ | * the extended path weighting enumerator function $T_{\rm enh}(X, \, U)$ | ||
| − | be determined, where $X$ and $U$ are dummy variables. | + | can be determined, where $X$ and $U$ are dummy variables. The method is explained in detail in the [[Channel_Coding/Distance_Characteristics_and_Error_Probability_Barriers#Path_weighting_enumerator_function_from_state_transition_diagram|"Theory part"]]. |
| − | |||
| − | The | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | Finally, from $T(X)$ the [[Channel_Coding/Distance_Characteristics_and_Error_Probability_Barriers#Free_distance_vs._minimum_distance|"free distance"]] $d_{\rm F}$ has to be determined. | ||
| + | Hints: | ||
| + | * This exercise belongs to the chapter [[Channel_Coding/Distance_Characteristics_and_Error_Probability_Boundss| "Distance Characteristics and Error Probability Bounds"]]. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* Consider the series expansion in the solution | * Consider the series expansion in the solution | ||
:$$\frac{1}{1-x} = 1 + x + x^2 + x^3 + \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...}\hspace{0.1cm}.$$ | :$$\frac{1}{1-x} = 1 + x + x^2 + x^3 + \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...}\hspace{0.1cm}.$$ | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
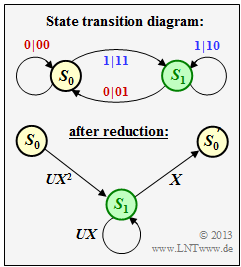
+ The state $S_0$ must be split into $S_0$ and $S_0\hspace{0.01cm}'$. | + The state $S_0$ must be split into $S_0$ and $S_0\hspace{0.01cm}'$. | ||
| − | - The state $S_1$ must be split into $S_0$ and $S_0\hspace{0.01cm}'$. | + | - The state $S_1$ must be split into $S_0$ and $S_0\hspace{0.01cm}'$. |
| − | + The transition from $S_0$ to $S_1$ must be labeled $U\hspace{-0.05cm}X^2$. | + | + The transition from $S_0$ to $S_1$ must be labeled $U\hspace{-0.05cm}X^2$. |
| − | + The transition from $S_1$ to $S_1$ is to be labeled $U\hspace{-0.05cm}X$. | + | + The transition from $S_1$ to $S_1$ is to be labeled $U\hspace{-0.05cm}X$. |
| − | + The transition from $S_1$ to $S_0\hspace{0.01cm}'$ shall be labeled $X$. | + | + The transition from $S_1$ to $S_0\hspace{0.01cm}'$ shall be labeled $X$. |
{What equations apply to the extended path weighting enumerator function $T_{\rm enh}(X, \, U)$? | {What equations apply to the extended path weighting enumerator function $T_{\rm enh}(X, \, U)$? | ||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
+ $T_{\rm enh}(X, \, U) = UX^3 + U^2X^4 + U^3X^5 + \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...}\hspace{0.1cm}$ | + $T_{\rm enh}(X, \, U) = UX^3 + U^2X^4 + U^3X^5 + \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...}\hspace{0.1cm}$ | ||
| − | {What equations apply to the "simple | + | {What equations apply to the "simple path weighting enumerator function" $T(X)$? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
+ $T(X) = X^3/(1 \, –X)$, | + $T(X) = X^3/(1 \, –X)$, | ||
+ $T(X) = X^3 + X^4 + X^5 +\hspace{0.05cm}\text{...}\hspace{0.1cm}$ | + $T(X) = X^3 + X^4 + X^5 +\hspace{0.05cm}\text{...}\hspace{0.1cm}$ | ||
| − | {What is the free distance of the code | + | {What is the free distance of the considered code? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$d_{\rm F} \ = \ ${ 3 } | $d_{\rm F} \ = \ ${ 3 } | ||
Revision as of 16:55, 22 November 2022
In $\text{Exercise 3.6}$ the state transition diagram for the drawn convolutional encoder with properties
- Rate $R = 1/2$,
- memory $m = 1$,
- transfer function matrix $\mathbf{G}(D) = (1, \, D)$
was constructed which is shown on the right.
Now, from this state transition diagram
- the path weighting enumerator function $T(X)$, and
- the extended path weighting enumerator function $T_{\rm enh}(X, \, U)$
can be determined, where $X$ and $U$ are dummy variables. The method is explained in detail in the "Theory part".
Finally, from $T(X)$ the "free distance" $d_{\rm F}$ has to be determined.
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter "Distance Characteristics and Error Probability Bounds".
- Consider the series expansion in the solution
- $$\frac{1}{1-x} = 1 + x + x^2 + x^3 + \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...}\hspace{0.1cm}.$$
Questions
Solution
(1) From the adjacent graph, one can see that proposed solutions 1, 3, 4, and 5 are correct:
- The state $S_0$ must be split into a start state $S_0$ and a final state ${S_0}'$.
- The reason for this is that for the following calculation of the path weighting enumerator function $T(X, \, U)$ all transitions from $S_0$ to $S_0$ must be excluded.
- Each code symbol $x ∈ \{0, \, 1\}$ is represented by $X^x$, where $X$ is a dummy variable with respect to the output sequence: $x = 0 \ \Rightarrow \ X^0 = 1, \ x = 1 \ \Rightarrow \ X^1 = X. $ It further follows $(00) \ \Rightarrow \ 1, \ (01) \ \Rightarrow \ X, \ (10) \ \Rightarrow \ X, \ (11) \ \Rightarrow \ X^2$.
- For a blue transition in the original diagram – this represents $u_i = 1$ – add the factor $U$ in the modified diagram.
(2) Richtig sind die Lösungsvorschläge 2 und 3:
- The reduced diagram is a "ring" according to the listing in the "Theory section". It follows:
- $$T_{\rm enh}(X, U) = \frac{A(X, U) \cdot B(X, U)}{1- C(X, U)} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- With $A(X, \, U) = UX^2, \ B(X, \, U) = X, \ C(X, \, U) = UX$ one obtains with the given series expansion:
- $$T_{\rm enh}(X, U) = \frac{U \hspace{0.05cm} X^3}{1- U \hspace{0.05cm} X} = U \hspace{0.05cm} X^3 \cdot \left [ 1 + (U \hspace{0.05cm} X) + (U \hspace{0.05cm} X)^2 +\text{...} \hspace{0.10cm} \right ] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(3) One gets from the extended path weighting enumerator function to $T(X)$ by setting the formal parameter $U = 1$. So both proposed solutions are correct.
(4) The free distance $d_{\rm F}$ can be read from the path weighting enumerator function $T(X)$ as the lowest exponent of the dummy variable $X$ ⇒ $d_{\rm F} \ \underline{= 3}$.