Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 3.2: GSM Services"
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
[[File:EN_Bei_A_3_2.png|right|frame|List of GSM services ]] | [[File:EN_Bei_A_3_2.png|right|frame|List of GSM services ]] | ||
| − | Any | + | Any "Public Land Mobile Network" $\rm (PLMN)$ must provide the fixed network infrastructure and so-called "interworking functions" $\rm (IWF)$. This is the only way to provide the desired services at the user interface. |
GSM services are divided into three categories: | GSM services are divided into three categories: | ||
| − | * | + | *Bearer services, |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | *Tele services, | ||
| − | + | *Supplementary services. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | Basis for data transmission are the '''bearer services''', where the maximum data rate is $\text{9.6 kbits/s}$. | ||
| − | + | '''Tele services''' are end-to-end services. The most important of these are: | |
| − | + | #the telephone service, | |
| − | + | #the fax service, | |
| − | + | #the short message service $\rm (SMS)$. | |
| + | Various '''supplementary services''' belong to each phase of GSM development: | ||
| + | #"call display", "call forwarding" and "caller ID" in phase 1, | ||
| + | #"call waiting", "hold" and "conference call" in phase 2, | ||
| + | #"GPRS", "HSCSD", "EDGE" in phase 2+. | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
| − | + | <u>Hint:</u> The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Examples_of_Communication_Systems/General_Description_of_GSM|"General Description of GSM"]]. | |
| − | Hint: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| Line 59: | Line 56: | ||
{Which statements are true for teleservices? | {Which statements are true for teleservices? | ||
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + Tele services are end-to-end services. |
| − | - A distinction is made between synchronous and asynchronous | + | - A distinction is made between synchronous and asynchronous tele services. |
+ Examples are the telephone, fax and SMS services. | + Examples are the telephone, fax and SMS services. | ||
| − | {Which | + | {Which supplementary services originate from GSM phase 2? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - Call Forwarding, | + | - "Call Forwarding", |
| − | + Call Waiting, | + | + "Call Waiting", |
| − | - General Packet Radio Service (GPRS), | + | - "General Packet Radio Service" $\rm (GPRS)$, |
| − | + Conference Call (CONF). | + | + "Conference Call" $\rm (CONF)$. |
| − | {What technology is used in | + | {What technology is used in "High Speed Circuit-Switched Data" $\rm (HSCSD)$? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
- Packet switching, | - Packet switching, | ||
Revision as of 17:51, 7 January 2023
Any "Public Land Mobile Network" $\rm (PLMN)$ must provide the fixed network infrastructure and so-called "interworking functions" $\rm (IWF)$. This is the only way to provide the desired services at the user interface.
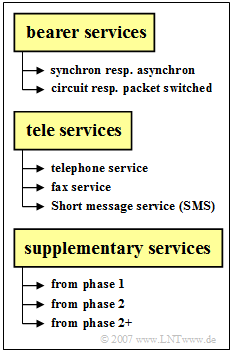
GSM services are divided into three categories:
- Bearer services,
- Tele services,
- Supplementary services.
Basis for data transmission are the bearer services, where the maximum data rate is $\text{9.6 kbits/s}$.
Tele services are end-to-end services. The most important of these are:
- the telephone service,
- the fax service,
- the short message service $\rm (SMS)$.
Various supplementary services belong to each phase of GSM development:
- "call display", "call forwarding" and "caller ID" in phase 1,
- "call waiting", "hold" and "conference call" in phase 2,
- "GPRS", "HSCSD", "EDGE" in phase 2+.
Hint: The exercise belongs to the chapter "General Description of GSM".
Questions
Solution
(1) Correct is the proposed solution 1:
- Carrier services form the basis for data transmission.
- They provide the technical means to transport data in a secured manner.
(2) Correct is the proposed solution 3:
- The maximum data rate for GSM data transmission is $9.6 \rm kbit/s$.
- There are synchronous and asynchronous as well as circuit-switched and packet-switched data transmission.
(3) Correct are proposed solutions 1 and 3:
- Proposition 2 is incorrect: The terms synchronous and asynchronous play a role only in connection with carrier services.
(4) Correct are the proposed solutions 2 and 4:
- In contrast, call forwarding belongs to GSM phase 1 and General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) to phase 2+.
(5) Correct is the proposed solution 2:
- High Speed Circuit-Switched Data (HSCSD) was introduced as a circuit-switched transmission technology.
- In contrast, General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) operates as packet-switched and Enhanced Data Rate for GSM Evolution (EDGE) can be described as circuit-switched data service.