Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 4.1: Different Duplex Methods for UMTS"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Examples_of_Communication_Systems/General_Description_of_UMTS |
| − | |||
}} | }} | ||
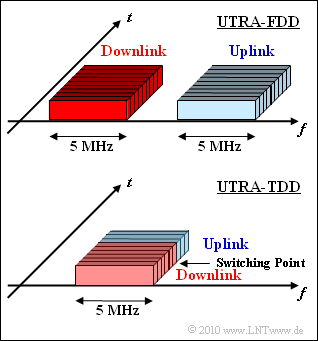
| − | [[File:P_ID1930__Bei_A_4_1.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID1930__Bei_A_4_1.png|right|frame|UTRA FDD and UTRA TDD]] |
| − | + | Planned in the early 1990s and available in Europe since 2004 $\rm UMTS$ (''Universal Mobile Telecommunications System'' ) is a so-called third-generation mobile communications system. | |
| − | + | It uses in both directions - ''uplink'' and ''downlink'' - the multiple access method [[Modulation_Methods/Tasks_and_Classification#FDMA.2C_TDMA.2C_and_CDMA|"CDMA"]] (''Code Division Multiple Access''). | |
| − | + | The standardization essentially provides for two different modes: | |
| − | *${\rm | + | *${\rm UTRA\:FDD}$ (''UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Frequency Division Duplex'' ) with twelve paired frequency bands for the uplink $(1920 - 1980 \ \ \rm MHz)$ and the downlink $(2110 - 2170 \ \ \rm MHz)$. |
| − | *${\rm | + | *${\rm UTRA\:TDD}$ (''UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Time Division Duplex'' ) provides four channels in the frequency band of $1900 - 1920 \ \rm MHz$ and another at $2020 - 2025 \ \rm MHz$. |
| − | + | There is currently no license for the band at $2010 - 2020 \ \rm MHz$ . However, this is also reserved for UTRA TDD. | |
| − | * | + | *The diagram shows schematically the frequency band assignments of UTRA FDD (top) and UTRA TDD (bottom). |
| − | * | + | *It can be seen that the two methods are quite different both in terms of multiple access and duplex implementation. |
| Line 28: | Line 27: | ||
| − | + | Hints: | |
| − | * | + | *This exercise belongs to the chapter [[Examples_of_Communication_Systems/General_Description_of_UMTS|"General Description of GSM"]]. |
| − | * | + | *Reference is made in particular to the page [[Examples_of_Communication_Systems/General_Description_of_UMTS#Full_duplex|"Full Duplex"]]. |
| − | === | + | ===Questions=== |
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {Which of the following statements are true? |
|type="()"} | |type="()"} | ||
| − | - UMTS | + | - UMTS is a second-generation mobile communications system. |
| − | + UMTS | + | + UMTS is a third-generation mobile communications system. |
| − | - UMTS | + | - UMTS is a fourth-generation mobile communications system. |
| − | { | + | {How are "uplink" and "downlink" separated in $\rm UTRA\:FDD$ ? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - | + | - The data is transmitted separately in time. |
| − | - | + | - The data is transmitted in the same frequency band. |
| − | + | + | + The data is transmitted in paired frequency bands. |
| − | { | + | {How are "uplink" and "downlink" separated for $\rm UTRA\:TDD$ ? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + The data are transmitted separately in time. |
| − | + | + | + The data is transmitted in the same frequency band. |
| − | - | + | - The data is transmitted in paired frequency bands. |
| − | { | + | {What is the total bandwidth allocated for $\rm UTRA\:FDD$ ? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$B_{\rm ges} \ = \ $ { 120 3% } $\ \rm MHz $ | $B_{\rm ges} \ = \ $ { 120 3% } $\ \rm MHz $ | ||
| − | { | + | {What bandwidth does each user occupy in $\rm UTRA\:FDD$ both uplink and downlink after bandspreading? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$B_{\rm user} \ = \ $ { 5 3% } $ \ \rm MHz $ | $B_{\rm user} \ = \ $ { 5 3% } $ \ \rm MHz $ | ||
| − | { | + | {What is the bandwidth of each user at $\rm UTRA\:TDD$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$B_{\rm user} \ = \ ${ 5 3% } $ \ \rm MHz $ | $B_{\rm user} \ = \ ${ 5 3% } $ \ \rm MHz $ | ||
| − | { | + | {which statements are true? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + In | + | + In Europe, only the $\rm FDD$ mode is used. |
| − | + | + | + The $\rm TDD$ mode is mainly suitable for asymmetric services. |
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
Revision as of 21:50, 29 January 2023
Planned in the early 1990s and available in Europe since 2004 $\rm UMTS$ (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System ) is a so-called third-generation mobile communications system.
It uses in both directions - uplink and downlink - the multiple access method "CDMA" (Code Division Multiple Access).
The standardization essentially provides for two different modes:
- ${\rm UTRA\:FDD}$ (UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Frequency Division Duplex ) with twelve paired frequency bands for the uplink $(1920 - 1980 \ \ \rm MHz)$ and the downlink $(2110 - 2170 \ \ \rm MHz)$.
- ${\rm UTRA\:TDD}$ (UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Time Division Duplex ) provides four channels in the frequency band of $1900 - 1920 \ \rm MHz$ and another at $2020 - 2025 \ \rm MHz$.
There is currently no license for the band at $2010 - 2020 \ \rm MHz$ . However, this is also reserved for UTRA TDD.
- The diagram shows schematically the frequency band assignments of UTRA FDD (top) and UTRA TDD (bottom).
- It can be seen that the two methods are quite different both in terms of multiple access and duplex implementation.
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter "General Description of GSM".
- Reference is made in particular to the page "Full Duplex".
Questions
Solution
(1) Richtig ist die Aussage 2:
- Ein Vertreter der zweiten Mobilfunkgeneration ist GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications), das bereits seit Anfang der 1990er Jahre verfügbar ist und auf dem Modulationsverfahren GMSK (Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying) basiert.
- Dagegen verwendet UMTS als Vielfachzugriffsverfahren CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access).
- Das Mobilfunksystem der vierten Generation ist LTE (Long Term Evolution), das auf dem OFDM–Verfahren (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplex) beruht. Die LTE–Einführung begann Anfang der 2010er Jahre.
(2) Aus der Grafik auf der Angabenseite erkennt man, dass für $\rm UTRA–FDD$ die letzte Aussage zutrifft.
(3) Richtig sind die Aussagen 1 und 2:
- Gemäß der unteren Grafik erfolgt bei $\rm UTRA–FDD$ die Übertragung von Uplink und Downlink im gleichen Frequenzband.
- Die Trennung geschieht per Zeitmultiplex.
(4) Laut Angabe belegen Uplink und Downlink jeweils $60 \ {\rm MHz} \ \Rightarrow \ B_{\rm ges}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 120 \ \rm MHz}$.
(5) Es gilt jeweils $B_{\rm user} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 5 \ \rm MHz}$, sowohl im Uplink als auch im Downlink.
- Dieser Wert ergibt sich, wenn man die jeweilige gesamte Bandbreite für Uplink und Downlink $(60 \ \rm MHz)$ durch die Anzahl der Kanäle $(12)$ dividiert.
(6) Hier gilt wiederum $B_{\rm user} \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{= 5 \ \rm MHz}$, wobei aber nun diese Bandbreite per TDMA zwischen Uplink und Downlink aufgeteilt werden muss.
(7) Beide Aussagen sind richtig:
- Es ist nicht geplant, den $\rm TDD$–Modus in Europa anzubieten.
- Bei asymmetrischem Dienst ist das Datenvolumen im Downlink deutlich größer als im Uplink. Hier würde $\rm TDD$–Modus Sinn machen.
Beispiele: Surfen und Downloads im Internet.