Exercise 4.2Z: Mixed Random Variables
One speaks of a "mixed random variable", if the random variable contains discrete components in addition to a continuous component.
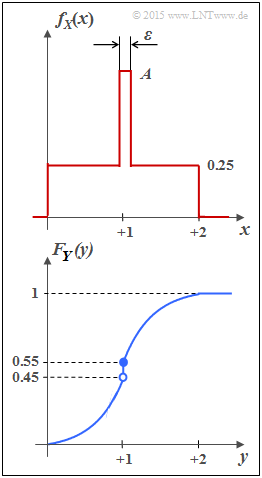
- For example, the random variable $Y$ with cumulative distribution function $F_Y(y)$ as shown in the sketch below has both a continuous and a discrete component.
- The probability density function $f_Y(y)$ is obtained from $F_Y(y)$ by differentiation.
- The jump at $y= 1$ in the CDF thus becomes a "Dirac" in the probability density function.
- In subtask (4) the differential entropy $h(Y)$ of $Y$ is to be determined (in bit), assuming the following equation:
- $$h(Y) = \hspace{0.1cm} - \hspace{-0.45cm} \int\limits_{{\rm supp}\hspace{0.03cm}(\hspace{-0.03cm}f_Y)} \hspace{-0.35cm} f_Y(y) \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \big[ f_Y(y) \big] \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm d}y \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
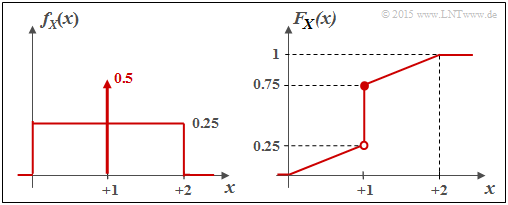
- In subtask (2), calculate the differential entropy $h(X)$ of the random variable $X$ whose PDF $f_X(x)$ is sketched above. If one performs a suitable boundary transition, the random variable $X$ also becomes a mixed random variable.
Hints:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter Differential Entropy.
- Further information on mixed random variables can be found in the chapter Cumulative Distribution Function of the book "Theory of Stochastic Signals".
Questions
Solution
- $$f_X(x) \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm d}x = 0.25 \cdot 2 + (A - 0.25) \cdot \varepsilon \stackrel{!}{=} 1 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm}(A - 0.25) \cdot \varepsilon \stackrel{!}{=} 0.5 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} A = 0.5/\varepsilon +0.25\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) The differential entropy (in "bit") is given as follows:
- $$h(X) = \hspace{0.1cm} \hspace{-0.45cm} \int\limits_{{\rm supp}(f_X)} \hspace{-0.35cm} f_X(x) \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1}{f_X(x)} \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm d}x \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
We now divide the integral into three partial integrals:
- $$h(X) = \hspace{-0.25cm} \int\limits_{0}^{1-\varepsilon/2} \hspace{-0.15cm} 0.25 \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1}{0.25} \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm d}x + \hspace{-0.25cm}\int\limits_{1+\varepsilon/2}^{2} \hspace{-0.15cm} 0.25 \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1}{0.25} \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm d}x + \hspace{-0.25cm}\int\limits_{1-\varepsilon/2}^{1+\varepsilon/2} \hspace{-0.15cm} \big [0.5/\varepsilon + 0.25 \big ] \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1}{0.5/\varepsilon + 0.25} \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm d}x $$
- $$ \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} h(X) = 2 \cdot 0.25 \cdot 2 \cdot (2-\varepsilon) - (0.5 + 0.25 \cdot \varepsilon) \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm}(0.5/\varepsilon +0.25) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
In particular, one obtains
- for $\varepsilon = 0.1$:
- $$h(X) =1.9 - 0.525 \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm}(5.25) = 1.9 - 1.256 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0.644\,{\rm bit}} \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- for $\varepsilon = 0.01$:
- $$h(X) =1.99 - 0.5025 \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm}(50.25)= 1.99 - 2.84 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= -0.850\,{\rm bit}} \hspace{0.05cm}$$
- for $\varepsilon = 0.001$:
- $$h(X) =1.999 - 0.50025 \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm}(500.25) = 1.999 - 8.967 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= -6.968\,{\rm bit}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(3) All the proposed solutions $1$ are correct:
- After the boundary transition $\varepsilon → 0$ we obtain for the differential entropy
- $$h(X) = \lim\limits_{\varepsilon \hspace{0.05cm}\rightarrow \hspace{0.05cm} 0} \hspace{0.1cm}\big[(2-\varepsilon) - (0.5 + 0.25 \cdot \varepsilon) \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm}(0.5/\varepsilon +0.25)\big] = 2\,{\rm bit} - 0.5 \cdot \lim\limits_{\varepsilon \hspace{0.05cm}\rightarrow \hspace{0.05cm} 0}\hspace{0.1cm}{\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm}(0.5/\varepsilon) \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} - \infty \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The probability density function (PDF) in this case is given by.
- $$f_X(x) = \left\{ \begin{array}{c} 0.25 + 0.5 \cdot \delta (x-1) \\ 0 \\ \end{array} \right. \begin{array}{*{20}c} {\rm{f\ddot{u}r}} \hspace{0.1cm} 0 \le x \le 2, \\ {\rm sonst} \\ \end{array} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Consequently, it is a "mixed" random variable with
- a stochastic, uniformly distributed part in the range $0 \le x \le 2$, and
- a discrete component at $x = 1$ with probability $0.5$.
The graph shows the PDF $f_X(x)$ on the left and the CDF $F_X(x)$ on the right.
(4) The correct solutions are 2, 3 and 5.
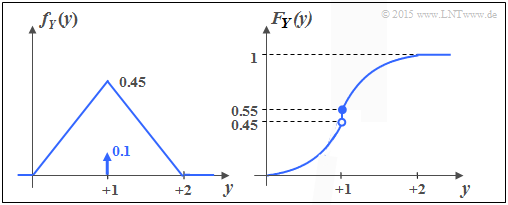
The lower graph shows the PDF and the CDF of the random variable $Y$. You can see:
- Like $X$ , $Y$ contains a continuous and a discrete part.
- The discrete part occurs with probability ${\rm Pr}(Y = 1) = 0.1$.
- Since $F_Y(y)= {\rm Pr}(Y \le y)$ holds, the right-hand side limit is:
- $$F_Y(y = 1) = 0.55.$$
- The continuous component is not uniformly distributed; rather, there is a triangular PDF.
- The last proposition is also correct: $h(Y) = h(X) = - \infty$.
Because: For every random quantity with a discrete part – and it is also extremely small, the differential entropy is equal minus infinity..