Exercise 1.2: A Simple Binary Channel Code
From LNTwww
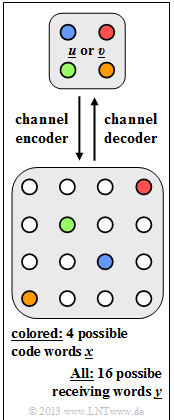
The graph illustrates the channel coding considered here $\mathcal{C}$:
- There are four possible information blocks $\underline{u} = (u_{1}, u_{2}, \text{...}\hspace{0.05cm} , u_{k})$.
- Each information block $\underline{u}$ is uniquely assigned (recognizable by the same color) to the codeword $\underline{x}= (x_{1}, x_{2}, \text{...}\hspace{0.05cm} , x_{n})$ .
- Due to decoding errors $(0 → 1, \ 1 → 0)$ there are more than 4, namely 16 different receive words $\underline{y} = (y_{1}, y_{2}, \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm} , y_{n})$.
From subtask (4) we consider the following mapping:
- $$\underline{u_0} = (0, 0) \leftrightarrow (0, 0, 0, 0) = \underline{x_0}\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$\underline{u_1} = (0, 1) \leftrightarrow (0, 1, 0, 1) = \underline{x_1}\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$\underline{u_2} = (1, 0) \leftrightarrow (1, 0, 1, 0) = \underline{x_2}\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$\underline{u_3} = (1, 1) \leftrightarrow (1, 1, 1, 1) = \underline{x_3}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter Obective of Channel Coding
- Reference is made in particular to the pages
Questions
Solution
(1) The code size here is given to $|\mathcal{C}| = 4$.
- In general, $|\mathcal{C}|= 2^k$.
- From this follows $\underline{ k = 2}$.
(2) Each codeword $\underline{x}$ is uniquely associated with an information block $\underline{u}$.
- By corruptions of single of the total $n$ bits of a codeword $\underline{x}$ the receive words $\underline{y}$ result.
- From the number $(16 = 2^4$) of possible receive words follows $\underline{ n = 4}$.
(3) The code rate is by definition $R = k/n$.
- Using the above results, we obtain $\underline{R = 0.5}$.
(4) Correct Yes:
- A systematic code is characterized by the fact that in each case the first $k$ bits of the code words are identical to the information block.
(5) The Hamming weight of a binary code is equal to the algebraic sum $x_1 + x_2 + \text{...} + x_n$ over all code word elements. Thus:
- $$w_{\rm H}(\underline{x}_0) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 0} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm}w_{\rm H}(\underline{x}_1) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 2} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm} w_{\rm H}(\underline{x}_2) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 2}\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm}w_{\rm H}(\underline{x}_3) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 4}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(6) The Hamming distance between two codewords here can only take the values $2$ and $4$:
- $$d_{\rm H}(\underline{x}_0, \hspace{0.05cm}\underline{x}_1) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 2}\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm} d_{\rm H}(\underline{x}_0, \hspace{0.05cm}\underline{x}_2) = 2\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm} d_{\rm H}(\underline{x}_0, \hspace{0.05cm}\underline{x}_3) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 4}\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$ d_{\rm H}(\underline{x}_1, \hspace{0.05cm}\underline{x}_2) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 4}\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm} d_{\rm H}(\underline{x}_1, \hspace{0.05cm}\underline{x}_3) = 2\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm} d_{\rm H}(\underline{x}_2, \hspace{0.05cm}\underline{x}_3) = 2\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(7) From the result of subtask (6) it follows $d_{\rm min}(\mathcal{C}) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 2}$.
- Generally, for this quantity:
- $$d_{\rm min}(\mathcal{C}) = \min_{\substack{\underline{x},\hspace{0.05cm}\underline{x}' \hspace{0.05cm}\in \hspace{0.05cm} \mathcal{C} \ {\underline{x}} \hspace{0.05cm}\ne \hspace{0.05cm} \underline{x}'}}\hspace{0.1cm}d_{\rm H}(\underline{x}, \hspace{0.05cm}\underline{x}')\hspace{0.05cm}.$$