Exercise 3.14: Error Probability Bounds
For the frequently used convolutional code with
- the code rate $R = 1/2$,
- the memory $m = 2$, and
- the transfer function matrix
- $${\boldsymbol{\rm G}}(D) = \big ( 1 + D + D^2\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.1cm} 1 + D^2 \hspace{0.05cm}\big ), $$
the "extended path weighting enumerator function" is:
- $$T_{\rm enh}(X, U) = \frac{UX^5}{1- 2 \hspace{0.05cm}U \hspace{-0.05cm}X} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
With the series expansion $1/(1 \, –x) = 1 + x + x^2 + \text{...} \ $ can also be written for this purpose:
- $$T_{\rm enh}(X, U) = U X^5 \cdot \left [ 1 + (2 \hspace{0.05cm}U \hspace{-0.05cm}X) + (2 \hspace{0.05cm}U\hspace{-0.05cm}X)^2 + (2 \hspace{0.05cm}U\hspace{-0.05cm}X)^3 +\text{...} \hspace{0.10cm} \right ] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The "simple path weighting enumerator function" $T(X)$ results from setting the second variable $U = 1$ .
Using these two functions, error probability bounds can be specified:
- The "burst error probability" is limited by the Bhattacharyya bound:
- $${\rm Pr(burst\:error)} \le {\rm Pr(Bhattacharyya)} = T(X = \beta) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- In contrast, the "bit error probability" is always less than $($or equal to$)$ the Viterbi bound:
- \[{\rm Pr(bit\:error)} \le {\rm Pr(Viterbi)} = \left [ \frac {\rm d}{ {\rm d}U}\hspace{0.2cm}T_{\rm enh}(X, U) \right ]_{\substack{X=\beta \\ U=1} } \hspace{0.05cm}.\]
Hints:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter "Distance Characteristics and Error Probability Barriers".
- The Bhattacharyya parameter for BSC is: $\beta = 2 \cdot \sqrt{\varepsilon \cdot (1- \varepsilon)}$.
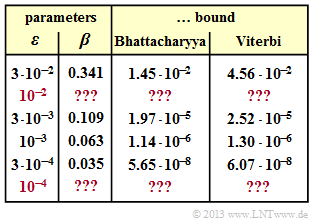
- In the table, for some values of the BSC parameter $\varepsilon$ are given:
- the Bhattacharyya parameter $\beta$,
- the Bhattacharyya bound ${\rm Pr}(\rm Bhattacharyya)$, and
- the Viterbi bound $\rm Pr(Viterbi)$.
- Throughout this exercise, you are to compute the corresponding quantities for $\varepsilon = 10^{-2}$ and $\varepsilon = 10^{-4}$.
- You can find the complete table in the sample solution.
Questions
Solution
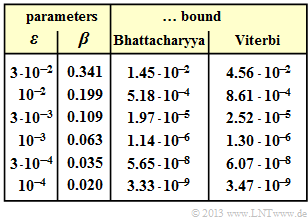
- $$\beta = 2 \cdot \sqrt{\varepsilon \cdot (1- \varepsilon)} = 2 \cdot \sqrt{0.01 \cdot 0.99} \hspace{0.2cm}\underline {\approx 0.199} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
For even smaller corruption probabilities $\varepsilon$ can be written approximately:
- $$\beta \approx 2 \cdot \sqrt{\varepsilon } \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \varepsilon = 10^{-4}\hspace{-0.1cm}: \hspace{0.2cm} \beta \hspace{0.2cm}\underline {\approx 0.02} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) It holds ${\rm Pr(Burst\:error)} ≤ {\rm Pr(Bhattacharyya)}$ with ${\rm Pr(Bhattacharyya)} = T(X = \beta)$.
- For the considered convolutional code of rate 1/2, memory $m = 2$ and $\mathbf{G}(D) = (1 + D + D^2, \ 1 + D^2)$, the path weighting enumerator function is:
- $$T(X) = \frac{X^5 }{1- 2X} \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm Pr(Bhattacharyya)} = T(X = \beta) = \frac{\beta^5 }{1- 2\beta}$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}\varepsilon = 10^{-2}\hspace{-0.1cm}: \hspace{0.1cm} {\rm Pr(Bhattacharyya)} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} \frac{0.199^5 }{1- 2\cdot 0.199} \hspace{0.2cm}\underline {\approx 5.18 \cdot 10^{-4}}\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$\hspace{0.85cm} \varepsilon = 10^{-4}\hspace{-0.1cm}: \hspace{0.1cm} {\rm Pr(Bhattacharyya)} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} \frac{0.02^5 }{1- 2\cdot 0.02} \hspace{0.38cm}\underline {\approx 3.33 \cdot 10^{-9}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(3) To calculate the Viterbi bound, we assume the extended path weighting enumerator function:
- $$T_{\rm enh}(X, U) = \frac{U X^5}{1- 2UX} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The derivative of this function with respect to the input parameter $U$ is:
- $$\frac {\rm d}{{\rm d}U}\hspace{0.1cm}T_{\rm enh}(X, U) = \frac{(1- 2UX) \cdot X^5 - U X^5 \cdot (-2X)}{(1- 2UX)^2} = \frac{ X^5}{(1- 2UX)^2} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- This equation provides the Viterbi bound for $U = 1$ and $X = \beta$:
- $$\frac {\rm d}{{\rm d}U}\hspace{0.1cm}T_{\rm enh}(X, U) = \frac{(1- 2UX) \cdot X^5 - U X^5 \cdot (-2X)}{(1- 2UX)^2} = \frac{U X^5}{(1- 2UX)^2} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}\varepsilon = 10^{-2}\hspace{-0.1cm}: \hspace{0.1cm} {\rm Pr(Viterbi)} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} \frac{0.199^5 }{(1- 2\cdot 0.199)^2} = \hspace{0.2cm}\underline {\approx 8.61 \cdot 10^{-4}}\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$\hspace{0.85cm} \varepsilon = 10^{-4}\hspace{-0.1cm}: \hspace{0.1cm} {\rm Pr(Viterbi)} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} \frac{0.02^5 }{(1- 2\cdot 0.02)^2} = \hspace{0.2cm}\underline {\approx 3.47 \cdot 10^{-9}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- We check the result using the following approximation:
- $$T_{\rm enh}(X, U) = U X^5 + 2\hspace{0.05cm}U^2 X^6 + 4\hspace{0.05cm}U^3 X^7 + 8\hspace{0.05cm}U^4 X^8 + \text{...} $$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}\frac {\rm d}{{\rm d}U}\hspace{0.1cm}T_{\rm enh}(X, U) = X^5 + 4\hspace{0.05cm}U X^6 + 12\hspace{0.05cm}U^2 X^7 + 32\hspace{0.05cm}U^3 X^8 + \text{...} $$
- Setting $U = 1$ and $X = \beta$ we get again the Viterbi bound:
- $${\rm Pr(Viterbi)} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} \beta^5 + 4\hspace{0.05cm}\beta^6 + 12\hspace{0.05cm}\beta^7 + 32\hspace{0.05cm}\beta^8 +\text{...} = \beta^5 \cdot (1+ 4\hspace{0.05cm}\beta + 12\hspace{0.05cm}\beta^2 + 32\hspace{0.05cm}\beta^3 + ... )\hspace{0.05cm}. $$
- For $\varepsilon = 10^{–2} \ \Rightarrow \ \beta = 0.199$ is obtained by truncating the infinite sum after the $\beta^3$–term:
- $${\rm Pr(Viterbi)} \approx 3.12 \cdot 10^{-4} \cdot (1 + 0.796 + 0.475 + 0.252) = 7.87 \cdot 10^{-4} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The termination error – related to $8.61 \cdot 10^{–4}$ – here is about $8.6\%$. For $\varepsilon = 10^{–4} \ \Rightarrow \ \beta = 0.02$ the termination error is even smaller:
- $${\rm Pr(Viterbi)} \approx 3.20 \cdot 10^{-9} \cdot (1 + 0.086 + 0.0048 + 0.0003) = 3.47 \cdot 10^{-9} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(4) For $\beta = 0.5$ both bounds result in the value "infinite".
- For even larger $\beta$–values, the Bhattacharyya bound becomes negative and the result for the Viterbi bound is then also not applicable. It follows:
- $$\beta_0 = 2 \cdot \sqrt{\varepsilon_0 \cdot (1- \varepsilon_0)} = 0.5$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\varepsilon_0 \cdot (1- \varepsilon_0)} = 0.25^2 = 0.0625$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \varepsilon_0^2 - \varepsilon_0 + 0.0625 = 0$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \varepsilon_0 = 0.5 \cdot (1 - \sqrt{0.75}) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {\approx 0.067}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$