Exercise 4.6Z: Basics of Product Codes
From LNTwww
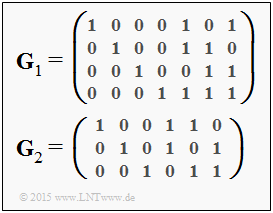
We consider here a product code according to the description on page "Basic structure of a product code". The two component codes $\mathcal{C}_1$ and $\mathcal{C}_2$ are defined by the generator matrices $\mathbf{G}_1$ and $\mathbf{G}_2$ given on the right.
Hints:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter "Basics of a Product Code".
- Reference is made in particular to the page "Basic structure of a product code".
- The two component codes are also covered in the "Exercise 4.6" .
Questions
Musterlösung
(1) Richtig sind die Aussagen 1, 2 und 4:
- Die Anzahl der Zeilen der Generatormatrix $\mathbf{G}_1$ gibt die Länge des Informationsblocks an ⇒ $k = 4$.
- Die Codewortlänge ist gleich der Anzahl der Spalten ⇒ $n=4$ ⇒ Coderate $R = k/n = 4/7$.
- Der Code ist systematisch, da die Generatormatrix $\mathbf{G}_1$ mit einer $4 × 4$–Diagonalmatrix beginnt.
- Es handelt sich um einen "normalen" Hammingcode.
- Für diesen gilt mit der Codewortlänge $n$ und der Anzahl der Prüfbits ⇒ $m = n - k$ der Zusammenhang $n = 2^m - 1$.
- Im vorliegenden Fall handelt es sich um den (normalen) Hammingcode $\rm (7, \ 4, \ 3)$.
- Der letzte Parameter in dieser Codebezeichnung gibt die minimale Distanz an ⇒ $d_{\rm min} = 3$.
(2) Richtig sind die Aussagen 2, 3 und 4:
- Es handelt sich um einen verkürzten Hammingcode mit dem Parameter $n = 6, \ k = 3$ und $d_{\rm min} = 3$, ebenfalls in systematischer Form.
- Die Coderate beträgt $R = 1/2$.
(3) Die Grundstruktur des Produktcodes ist auf der Seite Grundstruktur eines Produktcodes dargestellt.
- Man erkennt den Informationsblock mit $k = k_1 \cdot k_2 = 4 \cdot 3 \ \underline{= 12}$,
- Die Codewortlänge ist die Gesamtzahl aller Bit: $n = n_1 \cdot n_2 = 7 \cdot 6 \ \underline{= 42}$.
- Die Coderate ergibt sich somit zu $R = k/n = 12/42 = 2/7$.
- Oder: $R = R_1 \cdot R_2 = 4/7 \cdot 1/2 \ \underline{= 2/7} \approx 0.289$.
- Die freie Distanz beträgt $d = d_1 \cdot d_2 = 3 \cdot 3 \ \underline{= 9}$.