Exercise 3.2Z: Components of the GSM System
From LNTwww
Revision as of 08:39, 30 June 2020 by Javier (talk | contribs) (Javier moved page Exercises:Exercise 3.2Z: Components of the GSM System to Exercise 3.2Z: Components of the GSM System)
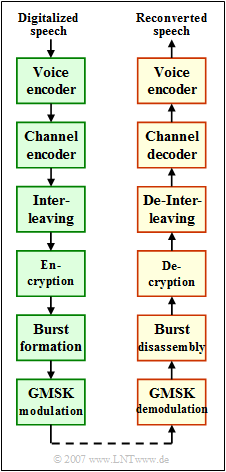
The diagram shows the entire transmission path of the GSM,
- On the left side the transmitter,
- on the right side the receiver.
The representation only refers to voice transmission. In GSM data transmission, only the uppermost block (speech encoder or decoder) is replaced by another channel encoder/decoder (concatenation of two channel codes).
This task deals with some basic properties of
- speech coder and speech decoder,
- Convolution encoder and convolution decoder,
- Interleaver and de-interleaver and
- Encryption and decryption.
Notes:
- The task belongs to the chapter Gemeinsamkeiten von GSM und UMTS.
- Reference is also made to the chapter Die Charakteristika von GSM.
Questionnaire
Sample Solution
(1) The answers 1 and 4 are correct:
- The goal of speech coding is to compress data and thus reduce redundancy.
- This is a typical task of source coding.
(2) The answers 2 and 3 are correct:
- Convolutional coding is a form of channel coding that enables the receiver (decoder) to detect and possibly correct errors.
- The channel coder adds (meaningful) redundancy to this, while the speech coder removes irrelevant redundancy.
- In many cases, both components are implemented together or at least closely coordinated
- This is called „common source– and channel coding”.
(3) Only the answer 2 is correct:
- The convolution decoder has big problems if the transmission errors do not occur statistically independent, but bundled.
- Task of Interleaver and De–interleaver is to break up such bundle errors and distribute them over a longer period of time.
- The redundancy is not changed by this procedure.
- In the AWGN–channel, bit errors occur statistically independently, so that interleaver and de–interleaver can be dispensed with.
(4) The answers 1 and 4 are correct:
- Encryption and decryption – the counterpart on the receiving side – serve only to protect user data against unauthorized access.
- They are not used for error correction and do not add redundancy.
- A distinction is made between symmetric and asymmetric encryption. GSM mainly uses the first variant.