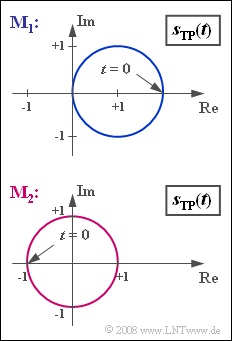
Exercise 3.1: Phase Modulation Locus Curve
The locus curve is generally understood as the plot of the equivalent low-pass signal $s_{\rm TP}(t)$ in the complex plane.
- The graph shows locus curves at the output of two modulators $\rm M_1$ and $\rm M_2$.
- The real and imaginary parts are each normalized to $1 \ \rm V$ in this graph.
Let the source signal be the same for both modulators:
$$ q(t) = A_{\rm N} \cdot \cos(2 \pi f_{\rm N} \cdot t),\hspace{1cm}
{\rm with}\hspace{0.2cm} A_{\rm N} = 2\,{\rm V},\hspace{0.2cm}f_{\rm N} = 5\,{\rm kHz}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
One of the two modulators implements phase modulation, which is characterized by the following equations:
- $$ s(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot \cos \hspace{-0.1cm} \big[\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t + \phi(t) \big]\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$ s_{\rm TP}(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot {\rm e}^{\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm j} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}\phi(t) }\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$ \phi(t) = K_{\rm PM} \cdot q(t)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The maximum value $ϕ(t)$ is called the modulation index $η$. Often $η$ is also called phase deviation in the literature.
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter Phase Modulation.
- Particular reference is made to the page Equivalent low-pass signal in phase modulation.
Questions
Solution
- Bewegt man sich auf dem Kreis in mathematisch positive Richtung, so liegt speziell eine OSB–AM vor, andernfalls eine USB–AM.
- Die Phasenfunktion $ϕ(t)$ als der Winkel eines Punktes $s_{\rm TP}(t)$ auf dem Kreis(bogen) bezogen auf den Koordinatenursprung kann Werte zwischen $±π/2$ annehmen und zeigt keinen Cosinusverlauf.
- Aber auch die Hüllkurve $a(t) = |s_{\rm TP}(t)|$ ist nicht cosinusförmig.
- Würde man beim Empfänger für $\rm M_1$ einen Hüllkurvendemodulator einsetzen, so käme es zu nichtlinearen Verzerrungen im Gegensatz zur ZSB–AM, deren Ortskurve eine horizontale Gerade ist.
(2) Hier handelt es sich um die Phasenmodulation ⇒ Antwort 3:
- Die Einhüllende $a(t) = A_{\rm T}$ ist konstant,
- während die Phase $ϕ(t)$ entsprechend dem Quellensignal $q(t)$ cosinusförmig verläuft.
(3) Bei der Phasenmodulation gilt:
- $$s_{\rm TP}(t) = A_{\rm T} \cdot {\rm e}^{\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm j} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}\phi(t) }\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Aus der Grafik kann man die Trägeramplitude $A_{\rm T}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 1 \ \rm V}$ als den Kreisradius ablesen.
(4) Das Quellensignal $q(t)$ ist zum Zeitpunkt $t = 0$ maximal und damit auch die Phasenfunktion:
- $$ \eta = \phi_{\rm max} = \phi( t =0) = \pi\hspace{0.15cm}\underline { = 3.1415} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Daraus erhält man für die Modulatorkonstante:
$$K_{\rm PM} = \frac{\eta}{A_{\rm N}} = \frac{\pi}{2\,{\rm V}}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 1.571\,{\rm V}^{-1}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(5) Man bewegt sich auf dem Kreis(bogen) im Uhrzeigersinn.
- Nach einem Viertel der Periodendauer $T_{\rm N} = 1/f_{\rm N} = 200 \ \rm µ s$ ist $ϕ(t) = 0$ und $s_{\rm TP}(t) = 1 \, \rm V$.
- Zur Zeit $t_1 = T_{\rm N}/2\hspace{0.15cm}\underline { = 100 \ \rm µ s}$ gilt $ϕ(t_1) = -π$ und $s_{\rm TP}(t_1) = -1 \, \rm V$.
- Danach bewegt man sich auf dem Kreisbogen entgegen dem Uhrzeigersinn.