Exercise 2.12Z: Reed-Solomon Syndrome Calculation
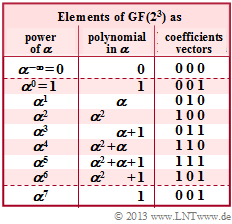
As in the "Exercise 2. 12" we consider the Reed–Solomon code $(7, \, 4, \, 4)_8$ based on the Galois field ${\rm GF}(q)$ with $q = 8 = 2^3$. The graph shows the corresponding conversion table.
Given are the possible code symbols in
- exponent representation $($powers of $\alpha)$
- polynomialrepresentation,
- coefficient vector representation.
Given is the received word $\underline{y} = (\alpha, \, 0, \, \alpha^3, \, 0, \, 1, \, \alpha, \, 0)$.
- Based on the syndrome $\underline {s} = (s_0, s_1, s_2) = \underline {y} \cdot { \boldsymbol{\rm H }}^{\rm T}$ it is to check whether individual symbols of the received vector $\underline{y}$ were corrupted during transmission.
- Given is the parity-check matrix $\mathbf{H}$ of the considered code and its transpose:
- $${ \boldsymbol{\rm H}} = \begin{pmatrix} 1 & \alpha^1 & \alpha^2 & \alpha^3 & \alpha^4 & \alpha^5 & \alpha^6\\ 1 & \alpha^2 & \alpha^4 & \alpha^6 & \alpha^1 & \alpha^{3} & \alpha^{5}\\ 1 & \alpha^3 & \alpha^6 & \alpha^2 & \alpha^{5} & \alpha^{1} & \alpha^{4} \end{pmatrix} \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.4cm} { \boldsymbol{\rm H}}^{\rm T} = \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 1 & 1 \\ \alpha^1 & \alpha^2 & \alpha^3 \\ \alpha^2 & \alpha^4 & \alpha^6 \\ \alpha^3 & \alpha^6 & \alpha^2 \\ \alpha^4 & \alpha^1 & \alpha^{5} \\ \alpha^5 & \alpha^{3} & \alpha^{1} \\ \alpha^6 & \alpha^{5} & \alpha^{4} \end{pmatrix} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Hints: This exercise refers to the section "Step (A): Evaluation of the syndrome in BDD" of the chapter "Error Correction according to Reed–Solomon Coding".
Questions
Solution
(1) The corresponding equation for syndrome calculation is:
- $$\underline {s} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} (s_0, s_1, s_2) = \begin{pmatrix} \alpha,0, \alpha^3,0, 1, \alpha,0 \end{pmatrix}\cdot \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 1 & 1 \\ \alpha^1 & \alpha^2 & \alpha^3 \\ \alpha^2 & \alpha^4 & \alpha^6 \\ \alpha^3 & \alpha^6 & \alpha^2 \\ \alpha^4 & \alpha^1 & \alpha^{5} \\ \alpha^5 & \alpha^{3} & \alpha^{1} \\ \alpha^6 & \alpha^{5} & \alpha^{4} \end{pmatrix} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The first element results in
- $$s_0 \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} \alpha \cdot 1 + \alpha^3 \cdot \alpha^2 + 1 \cdot \alpha^4 + \alpha \cdot \alpha^5= \alpha + \alpha^5 + \alpha^4+ \alpha^6$$
- $$\Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} s_0 \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} (\alpha) + (\alpha^2 + \alpha+ 1)+ (\alpha^2 + \alpha) + + (\alpha^2 + 1) = \alpha^2 + \alpha = \alpha^4\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Correct is the proposed solution 1.
(2) Correspondingly, for the second syndrome element, the proposed solution 2 applies accordingly:
- $$s_1 \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} \alpha \cdot 1 + \alpha^3 \cdot \alpha^4 + 1 \cdot \alpha^1 + \alpha \cdot \alpha^3= \alpha + \alpha^7 + \alpha+ \alpha^4= 1 + \alpha^4 = \alpha^2 + \alpha + 1 = \alpha^5 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(3) To calculate $s_2$, the received word must be multiplied by the last matrix column:
- $$s_2 \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} \alpha \cdot 1 + \alpha^3 \cdot \alpha^6 + 1 \cdot \alpha^5 + \alpha \cdot \alpha^1= \alpha + \alpha^2 + \alpha^5 + \alpha^2=\alpha^5 + \alpha = (\alpha^2 + \alpha + 1) + \alpha = \alpha^2 + 1 = \alpha^5 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Correct is the proposed solution 3.
(4) Due to the calculated syndrome $\underline{s} = (\alpha^4, \, \alpha^5, \, \alpha^6) ≠ 0$, the received word contains at least one symbol error ⇒ $r > 0$.
- The present Reed–Solomon–code $(7, \, 4, \, 4)_8 \ \Rightarrow \ d_{\rm min} = 4$ cannot correct more than $t = ⌊d_{\rm min}/2⌋ = 1$ errors.
- Since the received word can actually be decoded according to the specification ⇒ $\underline{r = 1}$.