Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 1.1Z: ISDN Connection"
From LNTwww
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
===Solutions=== | ===Solutions=== | ||
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1)''' The <first two statements</u> are correct: | + | '''(1)''' The <u>first two statements</u> are correct: |
*Das Sprachsignal ${q(t)}$ muss zunächst in ein elektrisches Signal gewandelt und anschließend für die Übertragung aufbereitet werden. | *Das Sprachsignal ${q(t)}$ muss zunächst in ein elektrisches Signal gewandelt und anschließend für die Übertragung aufbereitet werden. | ||
*Bei ISDN ist das Sendesignal ${s(t)}$ digital. | *Bei ISDN ist das Sendesignal ${s(t)}$ digital. | ||
Revision as of 14:19, 8 August 2020
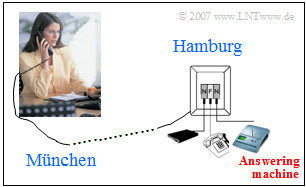
We consider the scenario shown in the picture:
A woman from Munich dials a number in Hamburg with her ISDN phone. However, she cannot reach the person she wants to talk to, so she leaves him a message on tape.
The distortion-free connection is fully described by
- a damping factor $\alpha$,
- a term $\tau$, and
- the current signal-to-noise ratio (SNR)
Notes: The task shall establish a relation between this real scenario and the functional units of a general message transmission system mentioned in Theorieteil .
Questions
Solutions
(1) The first two statements are correct:
- Das Sprachsignal ${q(t)}$ muss zunächst in ein elektrisches Signal gewandelt und anschließend für die Übertragung aufbereitet werden.
- Bei ISDN ist das Sendesignal ${s(t)}$ digital.
(2) Richtig sind die Lösungsvorschläge 3 und 4:
- Das Empfangssignal ${r(t)}$ ist aufgrund des unvermeidbaren thermischen Rauschens stets analog.
- Die Nachrichtensinke ist der Anrufbeantworter.
- Bei einem idealen Übertragungssystem müsste $v(t) = {q(t)}$ gelten.
- Aufgrund des additiven Rauschterms ${n(t)}$, der Dämpfung $\alpha$ und der Laufzeit $\tau$ gilt jedoch hier:
- $$v(t) = \alpha \cdot q ( t - \tau) + n(t).$$
- Es handelt sich nach unseren Definitionen um ein verzerrungsfreies System.