Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 2.3Z: Asymmetrical Characteristic Operation"
m (Text replacement - "Category:Exercises for Linear and Time-Invariant Systems" to "Category:Linear and Time-Invariant Systems: Exercises") |
|||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Linear_and_Time_Invariant_Systems/Nonlinear_Distortion}} |
| − | }} | ||
| − | [[File:P_ID895__LZI_Z_2_3.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID895__LZI_Z_2_3.png|right|frame|System and signal examples]] |
| − | + | The cosine signal | |
:$$x(t) = A \cdot \cos(\omega_0 t)$$ | :$$x(t) = A \cdot \cos(\omega_0 t)$$ | ||
| − | + | is applied to the input of a system $S$ where $A = 0.5$ shall always hold for the amplitude. The system $S$ consists of | |
| − | * | + | *the addition of a direct (DC) component $C$, |
| − | * | + | *a nonlinearity with the characteristic curve |
:$$g(x) = \sin(x) \hspace{0.05cm} \approx x -{x^3}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{6} = g_3(x),$$ | :$$g(x) = \sin(x) \hspace{0.05cm} \approx x -{x^3}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{6} = g_3(x),$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *as well as an ideal high-pass filter that allows all frequencies to pass unaltered except for a direct (DC) signal $(f = 0)$. |
| − | + | The output signal of the overall system can generally be depicted as follows: | |
:$$y(t) = A_0 + A_1 \cdot \cos(\omega_0 t) + A_2 \cdot \cos(2\omega_0 t) + | :$$y(t) = A_0 + A_1 \cdot \cos(\omega_0 t) + A_2 \cdot \cos(2\omega_0 t) + | ||
A_3 \cdot \cos(3\omega_0 t) + \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...}$$ | A_3 \cdot \cos(3\omega_0 t) + \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...}$$ | ||
| − | + | The sinusoidal characteristic curve $g(x)$ is to be approximated by the cubic approximation $g_3(x)$ throughout the whole problem according to the above equation. | |
| − | + | This would result in exactly the same constellation as in [[Aufgaben:Exercise_2.3:_Sinusoidal_Characteristic|Exercise 2.3]] for $C = 0$ in whose subtask '''(2)''' the distortion factor was calculated: | |
*$K = K_{g3} \approx 1.08 \%$ für $A = 0.5$, | *$K = K_{g3} \approx 1.08 \%$ für $A = 0.5$, | ||
*$K = K_{g3} \approx 4.76 \%$ für $A = 1.0$. | *$K = K_{g3} \approx 4.76 \%$ für $A = 1.0$. | ||
| − | + | Considering the constants $A = C = 0.5$ the following holds for the input signal of the nonlinearity: | |
:$$x_{\rm C}(t) = C + A \cdot \cos(\omega_0 t) = {1}/{2} + {1}/{2}\cdot \cos(\omega_0 t).$$ | :$$x_{\rm C}(t) = C + A \cdot \cos(\omega_0 t) = {1}/{2} + {1}/{2}\cdot \cos(\omega_0 t).$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *So, the characteristic curve is operated asymmetrically with values between $0$ and $1$. |
| − | *In | + | *In the above graph, the signals $x_{\rm C}(t)$ and $y_{\rm C}(t)$ are plotted additionally directly before and after the characteristic curve $g(x)$ . |
| Line 39: | Line 38: | ||
| − | '' | + | ''Please note:'' |
| − | * | + | *The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Linear_and_Time_Invariant_Systems/Nonlinear_Distortion|Nonlinear Distortions]]. |
| − | * | + | *The following trigonometric relations are assumed to be known: |
:$$\cos^2(\alpha) = {1}/{2} + {1}/{2} | :$$\cos^2(\alpha) = {1}/{2} + {1}/{2} | ||
\cdot \cos(2\alpha)\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm} | \cdot \cos(2\alpha)\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm} | ||
| Line 49: | Line 48: | ||
| − | === | + | ===Questions=== |
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {Compute the output signal $y(t)$ considering the high-pass filter. What is the direct (DC) signal component $A_0$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$A_0 \ = \ $ { 0. } | $A_0 \ = \ $ { 0. } | ||
| − | { | + | {State the other Fourier coefficients of the signal $y(t)$ . |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$A_1 \ = \ $ { 0.422 3% } | $A_1 \ = \ $ { 0.422 3% } | ||
| Line 65: | Line 64: | ||
| − | { | + | {Compute the distortion factor of the overall system. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$K \ = \ $ { 7.51 3% } $\ \%$ | $K \ = \ $ { 7.51 3% } $\ \%$ | ||
| − | { | + | {Compute the maximum and the minimum value of the signal $y(t)$. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$y_\text{max} \ = \ $ { 0.386 3% } | $y_\text{max} \ = \ $ { 0.386 3% } | ||
| Line 79: | Line 78: | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1)''' | + | '''(1)''' Considering the cubic approximation $g_3(x)$ the following is obtained before the high-pass filter: |
:$$y_{\rm C}(t) = g_3\big[x_{\rm C}(t)\big] = \big[ C + A \cdot \cos(\omega_0 | :$$y_{\rm C}(t) = g_3\big[x_{\rm C}(t)\big] = \big[ C + A \cdot \cos(\omega_0 | ||
t)\big] - {1}/{6} \cdot \big[ C + A \cdot \cos(\omega_0 | t)\big] - {1}/{6} \cdot \big[ C + A \cdot \cos(\omega_0 | ||
| Line 91: | Line 90: | ||
t) + A^3 \cdot \cos^3(\omega_0 t)\big].$$ | t) + A^3 \cdot \cos^3(\omega_0 t)\big].$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *The signal $y_{\rm C}(t)$ contains a direct (DC) component $C - C^3/6$ which is no longer included in the signal $y(t)$ due to the high-pass filter: |
:$$\underline{ A_0 = 0}.$$ | :$$\underline{ A_0 = 0}.$$ | ||
| − | '''(2)''' | + | '''(2)''' Applying the given trigonometric relations the following coefficients with $A= C = 0.5$ are obtained: |
:$$A_1 = A - {1}/{6}\cdot 3 \cdot C^2 \cdot A - {1}/{6} \cdot {3}/{4}\cdot | :$$A_1 = A - {1}/{6}\cdot 3 \cdot C^2 \cdot A - {1}/{6} \cdot {3}/{4}\cdot | ||
A^3 = {1}/{2} - {1}/{16} - {1}/{64} = {27}/{64} | A^3 = {1}/{2} - {1}/{16} - {1}/{64} = {27}/{64} | ||
| Line 104: | Line 103: | ||
A^3 = - {1}/{192} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{\approx -0.005}.$$ | A^3 = - {1}/{192} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{\approx -0.005}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *Higher order terms do not occur. Thus, $\underline{A_4 = 0}$ holds. |
| − | '''(3)''' | + | '''(3)''' In this task, the higher order distortion factors are $K_2 = 2/27 \approx 7.41\%$ and $K_3 = 1/81 \approx 1.23\%$. |
| − | * | + | *Thereby, the following is obtained for the overall distortion factor: |
:$$K = \sqrt{K_2^2 + K_3^2} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{\approx7.51 \%}.$$ | :$$K = \sqrt{K_2^2 + K_3^2} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{\approx7.51 \%}.$$ | ||
| − | '''(4)''' | + | '''(4)''' The maximum value occurs at time $t = 0$ and at multiples of $T$ : |
:$$y_{\rm max}= y(t=0) = A_1 + A_2 + A_3 = 0.422 -0.031 -0.005 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= | :$$y_{\rm max}= y(t=0) = A_1 + A_2 + A_3 = 0.422 -0.031 -0.005 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= | ||
0.386}.$$ | 0.386}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *The minimum values are located exactly in the middle between two maxima and it holds that: |
:$$y_{\rm min}= - A_1 + A_2 - A_3 = -0.422 -0.031 +0.005\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = | :$$y_{\rm min}= - A_1 + A_2 - A_3 = -0.422 -0.031 +0.005\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = | ||
-0.448}.$$ | -0.448}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *The signal $y(t)$ is shifted downward by $0.448$ compared to the signal drawn in the sketch on the information page. |
| − | * | + | *This signal value is obtained from the following equation considering $A = C = 1/2$: |
:$$C - \frac{C \cdot A^2}{4}- \frac{C^3}{6} = {1}/{2} - {1}/{32}- {1}/{48} = 0.448.$$ | :$$C - \frac{C \cdot A^2}{4}- \frac{C^3}{6} = {1}/{2} - {1}/{32}- {1}/{48} = 0.448.$$ | ||
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
| Line 129: | Line 128: | ||
| − | [[Category:Linear and Time-Invariant Systems: Exercises|^2.2 | + | [[Category:Linear and Time-Invariant Systems: Exercises|^2.2 Nonlinear Distortions^]] |
Latest revision as of 15:50, 29 September 2021
The cosine signal
- $$x(t) = A \cdot \cos(\omega_0 t)$$
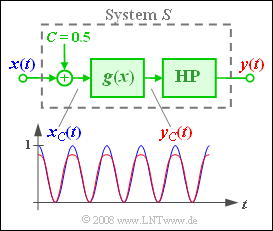
is applied to the input of a system $S$ where $A = 0.5$ shall always hold for the amplitude. The system $S$ consists of
- the addition of a direct (DC) component $C$,
- a nonlinearity with the characteristic curve
- $$g(x) = \sin(x) \hspace{0.05cm} \approx x -{x^3}\hspace{-0.1cm}/{6} = g_3(x),$$
- as well as an ideal high-pass filter that allows all frequencies to pass unaltered except for a direct (DC) signal $(f = 0)$.
The output signal of the overall system can generally be depicted as follows:
- $$y(t) = A_0 + A_1 \cdot \cos(\omega_0 t) + A_2 \cdot \cos(2\omega_0 t) + A_3 \cdot \cos(3\omega_0 t) + \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...}$$
The sinusoidal characteristic curve $g(x)$ is to be approximated by the cubic approximation $g_3(x)$ throughout the whole problem according to the above equation.
This would result in exactly the same constellation as in Exercise 2.3 for $C = 0$ in whose subtask (2) the distortion factor was calculated:
- $K = K_{g3} \approx 1.08 \%$ für $A = 0.5$,
- $K = K_{g3} \approx 4.76 \%$ für $A = 1.0$.
Considering the constants $A = C = 0.5$ the following holds for the input signal of the nonlinearity:
- $$x_{\rm C}(t) = C + A \cdot \cos(\omega_0 t) = {1}/{2} + {1}/{2}\cdot \cos(\omega_0 t).$$
- So, the characteristic curve is operated asymmetrically with values between $0$ and $1$.
- In the above graph, the signals $x_{\rm C}(t)$ and $y_{\rm C}(t)$ are plotted additionally directly before and after the characteristic curve $g(x)$ .
Please note:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter Nonlinear Distortions.
- The following trigonometric relations are assumed to be known:
- $$\cos^2(\alpha) = {1}/{2} + {1}/{2} \cdot \cos(2\alpha)\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm} \cos^3(\alpha) = {3}/{4} \cdot \cos(\alpha) + {1}/{4} \cdot \cos(3\alpha) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Questions
Solution
- $$y_{\rm C}(t) = g_3\big[x_{\rm C}(t)\big] = \big[ C + A \cdot \cos(\omega_0 t)\big] - {1}/{6} \cdot \big[ C + A \cdot \cos(\omega_0 t)\big]^3 $$
- $$\Rightarrow \; y_{\rm C}(t) = C + A \cdot \cos(\omega_0 t) - {1}/{6} \cdot \big[ C^3 + 3 \cdot C^2 \cdot A \cdot \cos(\omega_0 t) + \hspace{0.09cm}3 \cdot C \cdot A^2 \cdot \cos^2(\omega_0 t) + A^3 \cdot \cos^3(\omega_0 t)\big].$$
- The signal $y_{\rm C}(t)$ contains a direct (DC) component $C - C^3/6$ which is no longer included in the signal $y(t)$ due to the high-pass filter:
- $$\underline{ A_0 = 0}.$$
(2) Applying the given trigonometric relations the following coefficients with $A= C = 0.5$ are obtained:
- $$A_1 = A - {1}/{6}\cdot 3 \cdot C^2 \cdot A - {1}/{6} \cdot {3}/{4}\cdot A^3 = {1}/{2} - {1}/{16} - {1}/{64} = {27}/{64} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ \approx 0.422},$$
- $$A_2 = - {1}/{6}\cdot 3 \cdot {1}/{2}\cdot C \cdot A^2 = - \frac{1}{32} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{\approx -0.031},$$
- $$A_3 = - {1}/{6}\cdot \frac{1}{4}\cdot A^3 = - {1}/{192} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{\approx -0.005}.$$
- Higher order terms do not occur. Thus, $\underline{A_4 = 0}$ holds.
(3) In this task, the higher order distortion factors are $K_2 = 2/27 \approx 7.41\%$ and $K_3 = 1/81 \approx 1.23\%$.
- Thereby, the following is obtained for the overall distortion factor:
- $$K = \sqrt{K_2^2 + K_3^2} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{\approx7.51 \%}.$$
(4) The maximum value occurs at time $t = 0$ and at multiples of $T$ :
- $$y_{\rm max}= y(t=0) = A_1 + A_2 + A_3 = 0.422 -0.031 -0.005 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0.386}.$$
- The minimum values are located exactly in the middle between two maxima and it holds that:
- $$y_{\rm min}= - A_1 + A_2 - A_3 = -0.422 -0.031 +0.005\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = -0.448}.$$
- The signal $y(t)$ is shifted downward by $0.448$ compared to the signal drawn in the sketch on the information page.
- This signal value is obtained from the following equation considering $A = C = 1/2$:
- $$C - \frac{C \cdot A^2}{4}- \frac{C^3}{6} = {1}/{2} - {1}/{32}- {1}/{48} = 0.448.$$