Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 2.4: About the LZW Algorithm"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
}} | }} | ||
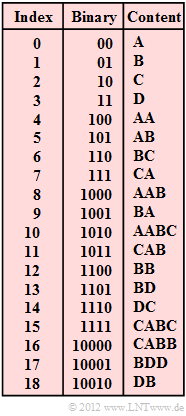
| − | [[File:EN_Inf_A_2_4.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:EN_Inf_A_2_4.png|right|frame|LZW Dictionary for Encoding/Decoding]] |
| − | + | The compression algorithm "LZW " – named after the inventors [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Abraham_Lempel Abraham Lempel], [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jacob_Ziv Jacob Ziv] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Terry_Welch Terry Welch] – works like "LZ78 " with a global dictionary. In this case, all possible characters – in the example <b>A</b>, <b>B</b>, <b>C</b>, <b>D</b> – are preassigned at the beginning and are successively expanded during encoding. | |
| − | + | During decoding, exactly the same dictionary is created, only the same entry with index $I$ is made one step later than during coding. To designate the decoding steps, we use the run variable $i$ here. | |
| − | + | Here are some more notes on LZW encoding and decoding: | |
| − | * | + | *During encoding, at each time $i$ , a search is made in the dictionary for the longest possible character string that matches the input string currently present. |
| − | * | + | *The dictionary index $I_i$ found is always transmitted in binary form. At the same time, $W(I_i) + Z$ is entered into the dictionary under the next free index. |
| − | * | + | *Here, $W(I_i)$ denotes a character or a character string, and $Z$ is the first character of the upcoming input string (i.e. also a character), which is no longer considered in $W(I_i)$ . |
| − | * | + | *With $M = 4$ possible characters, the first index $I_1$ is transmitted with two bits, the indices $I_2$, ... , $I_5$ with three bits, the next eight indices with four bits, then 16 indices with five bits, etc. The reason for this bit-saving measure can be found in the sample solution to this task. |
| − | + | After coding in the manner described here over $16$ coding steps, the following binary sequence of length $N_{\rm Bit} = 61$: | |
:$$\boldsymbol{\rm 00 \ 000 \ 001 \ 010 \ 100 \ 0001 \ 1000 \ 0111 \ 0001 \ 0001 \ 0011 \ 1011 \ 1011 \ 01101 \ 00011 \ 01001}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$\boldsymbol{\rm 00 \ 000 \ 001 \ 010 \ 100 \ 0001 \ 1000 \ 0111 \ 0001 \ 0001 \ 0011 \ 1011 \ 1011 \ 01101 \ 00011 \ 01001}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | The task of the decoder (more precisely: your task) is now, | |
| − | * | + | * to reconstruct from this binary sequence the indices $I_1$, ... , $I_{16}$ taking into account the different number of bits (description of the 16 decoding results by decimal numbers), |
| − | * | + | * then read out the corresponding characters or character sequences from the dictionary according to the indices and finally – with one step delay – generate the new dictionary entry. |
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
| − | '' | + | ''Hints:'' |
| − | * | + | *The task belongs to the chapter [[Information_Theory/Komprimierung_nach_Lempel,_Ziv_und_Welch|Compression according to Lempel, Ziv and Welch]]. |
*Insbesondere wird Bezug genommen auf die Seiten | *Insbesondere wird Bezug genommen auf die Seiten | ||
| − | :: [[Information_Theory/Komprimierung_nach_Lempel,_Ziv_und_Welch#LZ77_ | + | :: [[Information_Theory/Komprimierung_nach_Lempel,_Ziv_und_Welch#LZ77_-_the_basic_form_of_the_Lempel-Ziv_algorithms|LZ77 - the basic form of Lempel-Ziv algorithms]], |
| − | :: [[Information_Theory/Komprimierung_nach_Lempel,_Ziv_und_Welch#Lempel | + | :: [[Information_Theory/Komprimierung_nach_Lempel,_Ziv_und_Welch#Lempel-Ziv_coding_with_variable_index_bit_length|Lempel-Ziv coding with variable index bit length]], |
| − | :: [[Information_Theory/Komprimierung_nach_Lempel,_Ziv_und_Welch# | + | :: [[Information_Theory/Komprimierung_nach_Lempel,_Ziv_und_Welch#Decoding_of_the_LZW_algorithm|decoding of the LZW algorithm]]. |
| − | * | + | * [[Aufgaben:Aufgabe_2.3:_Zur_LZ78-Komprimierung|Task 2.3]] and [[Aufgaben:Aufgabe_2.3Z:_Zur_LZ77-Codierung|Task 2.3Z]] deal with other LZ methods in a similar way. |
| − | === | + | ===Questions=== |
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {Which indices are available for the first four steps $i=1$, ... , $i=4$ for decoding Enter all $I_i = I(i)$ as decimal numbers. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$I_1 \ = \ $ { 0. } | $I_1 \ = \ $ { 0. } | ||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
| − | { | + | {Continue the subdivision of the decoder input string to the end. Which indices result from the decoding steps $i=5$, ... , $i=8$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$I_5 \ = \ $ { 4 } | $I_5 \ = \ $ { 4 } | ||
Revision as of 19:16, 12 July 2021
The compression algorithm "LZW " – named after the inventors Abraham Lempel, Jacob Ziv and Terry Welch – works like "LZ78 " with a global dictionary. In this case, all possible characters – in the example A, B, C, D – are preassigned at the beginning and are successively expanded during encoding.
During decoding, exactly the same dictionary is created, only the same entry with index $I$ is made one step later than during coding. To designate the decoding steps, we use the run variable $i$ here.
Here are some more notes on LZW encoding and decoding:
- During encoding, at each time $i$ , a search is made in the dictionary for the longest possible character string that matches the input string currently present.
- The dictionary index $I_i$ found is always transmitted in binary form. At the same time, $W(I_i) + Z$ is entered into the dictionary under the next free index.
- Here, $W(I_i)$ denotes a character or a character string, and $Z$ is the first character of the upcoming input string (i.e. also a character), which is no longer considered in $W(I_i)$ .
- With $M = 4$ possible characters, the first index $I_1$ is transmitted with two bits, the indices $I_2$, ... , $I_5$ with three bits, the next eight indices with four bits, then 16 indices with five bits, etc. The reason for this bit-saving measure can be found in the sample solution to this task.
After coding in the manner described here over $16$ coding steps, the following binary sequence of length $N_{\rm Bit} = 61$:
- $$\boldsymbol{\rm 00 \ 000 \ 001 \ 010 \ 100 \ 0001 \ 1000 \ 0111 \ 0001 \ 0001 \ 0011 \ 1011 \ 1011 \ 01101 \ 00011 \ 01001}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The task of the decoder (more precisely: your task) is now,
- to reconstruct from this binary sequence the indices $I_1$, ... , $I_{16}$ taking into account the different number of bits (description of the 16 decoding results by decimal numbers),
- then read out the corresponding characters or character sequences from the dictionary according to the indices and finally – with one step delay – generate the new dictionary entry.
Hints:
- The task belongs to the chapter Compression according to Lempel, Ziv and Welch.
- Insbesondere wird Bezug genommen auf die Seiten
Questions
Musterlösung
- Bereits zum Schritt $i = 2$ werden dagegen drei Bit benötigt. Hätte die Eingangsfolge mit AAA begonnen, so hätte die LZW–Codierung $I_2 = I(i = 2)$ den Dezimalwert $4$ ergeben. Dieser ist nicht mehr mit zwei Bit darstellbar und muss mit drei Bit codiert werden, ebenso wie $I_3$, $I_4$ und $I_5$.
- Der vorgegebene Eingabestring
- $$\boldsymbol{\rm 00 000 001 010 100 0001}\hspace{0.05cm}...$$
- ist deshalb vom Decoder wie folgt aufzuteilen:
- $$\boldsymbol{\rm 00 | 000 |001 |010 |100 |0001|}\hspace{0.05cm}...$$
- Die Decoderergebnisse der ersten vier Schritte lauten somit:
- $I_1 =$ 00 (binär) = 0 (dezimal) ⇒ A,
- $I_2 =$ 000 (binär) = 0 (dezimal) ⇒ A,
- $I_3 =$ 001 (binär) = 1 (dezimal) ⇒ B,
- $I_4 =$ 010 (binär) = 2 (dezimal) ⇒ C.
(2) Berücksichtigt man, dass
- für $i = 1$ zwei Bit verwendet werden,
- für $2 ≤ i ≤ 5$ drei Bit,
- für $6 ≤ i ≤ 19$ vier Bit,
- für $14 ≤ i ≤ 29$ fünf Bit,
so kommt man vom "kontinuierlichen Decoder–Eingangsstring"
- $$\boldsymbol{\rm 00 000 001 010 100 0001 1000 0111 0001 0001 0011 1011 1011 01101 00011 01001}$$
zum "eingeteilten Decoder–Eingabestring" $($bezeichnet mit $I_1$, ... , $I_{16})$:
- $$\boldsymbol{\rm 00 |000 |001 |010 |100 |0001 |1000 |0111 | 0001 |0001 |0011 |1011 |1011 |01101 |00011 |01001} \hspace{0.1cm}.$$
Damit lauten die gesuchten Ergebnisse für die Decodierschritte $i = 5$, ... , $i = 8$:
- $I_5 =$ 100 (binär) = 4 (dezimal) ⇒ AA,
- $I_6 =$ 0001 (binär) = 1 (dezimal) ⇒ B,
- $I_7 =$ 1000 (binär) = 8 (dezimal) ⇒ AAB,
- $I_8 =$ 0111 (binär) = 7 (dezimal) ⇒ CA.
(3) Richtig is tdie Aussage 2.
- Man erhält folgende Decodierergebnisse (in verkürzter Form):
- $I_{9} = 1$ ⇒ B, $\hspace{0.5cm}I_{10} = 1$ ⇒ B,$\hspace{0.5cm}I_{11} = 3$ ⇒ D,$\hspace{0.5cm}I_{12} = 11$ ⇒ CAB,
- $I_{13} = 11$ ⇒ CAB,$\hspace{0.5cm}I_{14} = 13$ ⇒ BD,$\hspace{0.5cm}I_{15} = 3$ ⇒ D,$\hspace{0.5cm}I_{16} = 9$ ⇒ BA.
(4) Richtig sind die Aussagen 1 und 4. Begründung:
- Der neu ankommende Index ist $18$ (dezimal) und im Wörterbuch wird unter dem Index $I = 18$ der Eintrag DB gefunden.
- Zum Decodierschritt $i = 17$ wird in das Wörterbuch die Zeile $I = 19$ eingetragen.
- Der Eintrag BAD setzt sich zusammen aus dem Decodierergebnis aus Schritt $i = 16$ $($BA$)$ und dem ersten Zeichen $($D$)$ des neuen Ergebnisses DB.
(5) Richtig ist hier nur die Aussage 1:
- Für die erste Phrase genügen zwei Bit.
- Für die Phrasen $I_2$, ... , $I_5$ benötigt man drei Bit.
- Für die Phrasen $I_6$, ... , $I_{13}$ benötigt man vier Bit.
- Für die Phrasen $I_{14}$, ... , $I_{29}$ benötigt man fünf Bit.
- Für die Phrasen $I_{30}$, ... , $I_{58}$ benötigt man sechs Bit.
- Damit erhält man für die gesamte Bitanzahl:
- $$N_{\rm Bit} = 1 \cdot 2 + 4 \cdot 3 + 8 \cdot 4 + 16 \cdot 5 + 29 \cdot 6 = 300 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Mit einheitlicher Bitlänge (sechs Bit für jeden Index) wären $58 · 6 = 348$ Bit (also mehr) erforderlich ⇒ die Aussage 2 ist prinzipiell falsch.
Nun zur dritten Aussage, die ebenfalls nicht zutrifft:
- Bei der uncodierten Übertragung von $N = 150$ Zeichen aus der Symbolmenge $\{$ A, \ B, \ C, \ D $\}$ würde man genau $300$ Bit benötigen. Mit LZW benötigt man sicher mehr Bit, wenn die Quelle redundanzfrei ist (Zeichen gleichwahrscheinlich und statistisch unabhängig).
- Bei redundanter Quelle mit (beispielsweise) $H = 1.6$ bit/Quellensymbol kann man die Bitanzahl auf $N_{\rm Bit} = N \cdot H$ begrenzen, vorausgesetzt, es handelt sich um eine sehr große Datei $(N \to \infty)$.
- Bei einer eher kleinen Datei – wie hier lediglich mit $N = 150$ Bit – ist keine Aussage möglich, ob die Bitanzahl $N_{\rm Bit}$ kleiner, gleich oder größer als $150 · 1.6 = 240$ sein wird.
- Auch $N_{\rm Bit} > 300$ ist durchaus möglich. Dann sollte man auf die "Lempel–Ziv–Komprimierung" besser verzichten.