Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 2.5: Half-Wave Rectification"
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {Calculate the Fourier coefficients of the signal $v(t)$. What is the value of the coefficient $A_2$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$v(t)$: $A_2\ = \ $ { -0.67--0.66 } | $v(t)$: $A_2\ = \ $ { -0.67--0.66 } | ||
| − | { | + | {Calculate the Fourier coefficients of the signal $w(t)$. What is the value of the coefficient $B_1$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$w(t)$: $B_1\ = \ $ { 1.571 3% } | $w(t)$: $B_1\ = \ $ { 1.571 3% } | ||
| − | { | + | {How can $x(t)$ be composed of $v(t)$ and $w(t)$ ? Give the corresponding Fourier coefficients of the signal $x(t)$ in particular |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$x(t)$: $A_0\ = \ $ { 0.5 3% } | $x(t)$: $A_0\ = \ $ { 0.5 3% } | ||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
'''(1)''' Auch das verschobene Signal $v(t)$ ist gerade und alle Sinuskoeffizienten sind dementsprechend Null. | '''(1)''' Auch das verschobene Signal $v(t)$ ist gerade und alle Sinuskoeffizienten sind dementsprechend Null. | ||
Revision as of 20:41, 16 January 2021
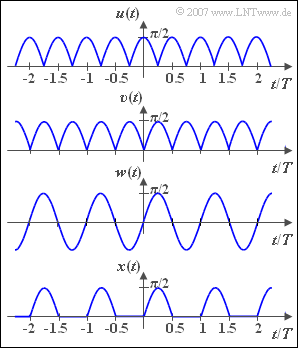
We are looking for the Fourier coefficients of the signal $x(t)$, sketched below, which results from the one-way rectification of the sinusoidal signal $w(t)$ with amplitude $\pi /2$ .
The Fourier series representation of the signal $u(t)$ sketched above is assumed to be known. This was already determined in Aufgabe 2.4 . Taking into account the amplitude $\pi /2$ the following applies:
- $$u(t)=1+\frac{2}{3} \cdot \cos(\omega_1t)-\frac{2}{15}\cdot \cos(2\omega_1t)+\frac{2}{35}\cdot \cos(3\omega_1t)-\dots$$
It should be noted:
- The fundamental angular frequency is denoted by $\omega_1$ . But since the period of the signals $u(t)$ and $v(t)$ is $T/2$ , $\omega_1 = 2\pi /(T/2) = 4 \pi /T$.
- Because in this task the signals $u(t)$, $w(t)$ and $x(t)$ are to be related to each other, the signal $u(t)$ must also be represented with the period duration $T$ of the signal $x(t)$ .
- With $\omega_0 = 2\pi /T = \omega_1/2$ the same applies:
- $$u(t)=1+\frac{2}{3} \cdot \cos(2\omega_0t)-\frac{2}{15} \cdot \cos(4\omega_0t)+\frac{2}{35} \cdot \cos(6\omega_0t)-\dots$$
For the Fourier coefficients this means:
- The DC coefficient results in $A_0 = 1$,
- All sine coefficients are $B_n = 0$,
- The cosine coefficients with odd $n = 1, \ 3, \ 5, \dots$ are all $0$,
- The cosine coefficients with even $n = 2, \ 4, \ 6, \dots$ are not equal to $0$ :
- $$A_n=(-1)^{\hspace{0.01cm}n/2+1}\frac{2}{n^2-1}.$$
This results in the following numerical values:
- $$A_1=A_3=A_5=\dots=0,$$
- $$A_2=2/3; \;A_4=-2/15;\;A_6=2/35;\;A_8=-2/63.$$
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter Fourierreihe.
- You can find a compact summary of the topic in the two learning videos
Questions
Solution
- Am Gleichsignalkoeffizienten ändert sich ebenfalls nichts: $A_0 = 1$.
- Aus den Signalverläufen ist zu erkennen, dass $v(t) = u(t - T/4)$ gilt:
- $$v(t)=1+\frac{2}{3}\cdot \cos(2\omega_0(t-\frac{T}{4}))-\frac{2}{15}\cdot \cos(4\omega_0(t-\frac{T}{4}))+\frac{2}{35}\cdot \cos(6\omega_0(t-\frac{T}{4}))-\dots$$
- Die Cosinusterme können nun mit $\omega_0 \cdot T = 2 \pi$ umgeformt werden:
- $$\cos(2\omega_0(t-\frac{T}{4}))=\cos(2\omega_0t-\pi)=-\cos(2\omega_0t),$$
- $$\cos(4\omega_0(t-\frac{T}{4}))=\cos(4\omega_0t-2\pi)=\cos(4\omega_0t),$$
- $$\cos(6\omega_0(t-\frac{T}{4}))=\cos(6\omega_0t-3\pi)=-\cos(6\omega_0t).$$
- Damit erhält man für die Fourierreihe:
- $$v(t)=1-{2}/{3}\cdot \cos(2\omega_0t)-{2}/{15}\cdot \cos(4\omega_0t)-{2}/{35}\cdot \cos(6\omega_0t)-\dots$$
- bzw. für die Cosinuskoeffizienten mit geradzahligem $n$:
- $$A_n=\frac{-2}{n^2-1}\hspace{0.5cm}\Rightarrow\hspace{0.5cm}A_2=-\hspace{-0.05cm}2/3 \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{= -\hspace{-0.05cm}0.667}.$$
(2) Wegen $w(t) = \pi /2 \cdot \sin(\omega_0 t)$ sind alle Fourierkoeffizienten außer $B_1 = \pi /2 \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{=1.571}$ gleich Null.
(3) Aus der grafischen Darstellung erkennt man den Zusammenhang $x(t)={1}/{2} \cdot \big [v(t)+w(t) \big].$ Das bedeutet:
- $$x(t)=\frac{1}{2}+\frac{\pi}{4}\cdot \sin(\omega_0 t)-\frac{1}{3}\cdot \cos(2\omega_0 t)-\frac{1}{15}\cdot \cos(4\omega_0 t)-\frac{1}{35}\cdot \cos(6\omega_0 t)-\ldots$$
- Die gesuchten Fourierkoeffizienten sind somit:
- $$A_0 \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{=0.5},\hspace{1cm} B_1 = \pi /4 \hspace{0.1cm}\underline{= 0.785},\hspace{1cm} A_2\hspace{0.1cm}\underline{ = -0.333}.$$