Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 4.10: Signal Waveforms of the 16-QAM"
m |
m |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
}} | }} | ||
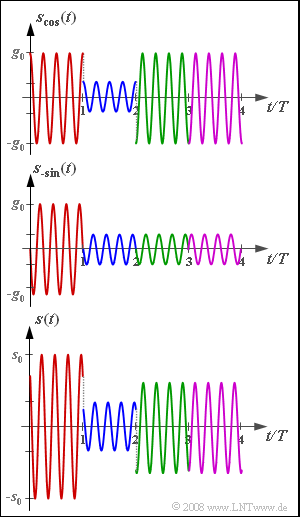
| − | [[File:P_ID1718__Mod_A_4_9.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID1718__Mod_A_4_9.png|right|frame|Signal waveforms of 16–QAM for <br>four typical symbols]] |
Let us consider the 16–QAM method according to the [[Modulation_Methods/Quadrature_Amplitude_Modulation#General_description_and_signal_space_allocation|block diagram]] in the theory section. | Let us consider the 16–QAM method according to the [[Modulation_Methods/Quadrature_Amplitude_Modulation#General_description_and_signal_space_allocation|block diagram]] in the theory section. | ||
Revision as of 19:20, 18 March 2022
Let us consider the 16–QAM method according to the block diagram in the theory section.
Very briefly, it can be described as follows:
- After serial-parallel conversion and subsequent signal space assignment, four bits of the binary redundancy-free source signal $q(t)$ at the input each result in a complex-valued amplitude coefficient
- $$a = a_{\rm I} +{\rm j} · a_{\rm Q}.$$
- With the basic rectangular transmission pulse $g_s(t)$ in the range from $0$ to $T$ and of height $g_0$ , after multiplication with the cosine function or minus-sine function in the given time interval, we obtain:
- $$s_{\rm cos}(t) = a_{\rm I}\cdot g_0 \cdot \cos(2 \pi f_{\rm T} t)\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$ s_{\rm -sin}(t) = -a_{\rm Q} \cdot g_0 \cdot \sin(2 \pi f_{\rm T} t)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The 16-QAM transmit signal is then the sum of these two component signals:
- $$s(t) = s_{\rm cos}(t)+ s_{\rm -sin}(t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The graph shows the signals $s_{\rm cos}(t)$, $s_{\rm –sin}(t)$ and $s(t)$ for four selected symbols. Using these, the amplitude coefficients are to be determined.
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter Quadrature Amplitude Modulation.
- The page Signal waveforms for 4–QAM is helpful for completing this exercise.
- The signal space allocation considered can be seen in the exercise page Aufgabe 4.10Z.
The color highlights also correspond.
- From question (6) onwards, use the parameter values $g_0 = 1 \ \rm V$ and $T = 1 \ \rm µ s$.
- Energy values are to be given in $\rm V^2s$ ; like this, they refer to the reference resistance
$R = 1 \ \rm \Omega$.
Questions
Solution
- $$ s_{\rm cos}(t)= a_{\rm I}\cdot g_0 \cdot \cos(2 \pi f_{\rm T} t)= g_0 \cdot \cos(2 \pi f_{\rm T} t)\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}a_{\rm I}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= +1} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Entsprechend erkennt man aus dem Quadratursignal ⇒ Imaginärteilteil :
- $$ s_{\rm -sin}(t)= -a_{\rm Q}\cdot g_0 \cdot \sin(2 \pi f_{\rm T} t)= -g_0 \cdot \sin(2 \pi f_{\rm T} t)\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}a_{\rm Q}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= +1} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) Die beiden Teilsignale haben jeweils die (maximale) Hüllkurve $g_0$, während $s_0$ das Sendesignal $s(t)$ charakterisiert.
- Wie aus der Signalraumzuordnung (siehe Aufgabe 4.10Z) hervorgeht, gilt:
- $${s_0}/{ g_0 }= \sqrt{2}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline { = 1.414} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(3) Die Amplitudenkoeffizienten $a_{\rm I}$ und $a_{\rm Q}$ haben die gleichen Vorzeichen wie bei der Teilaufgabe (1), aber mit kleinerem Betrag:
- $$a_{\rm I} = + 1/3\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= +0.333} \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.5cm}a_{\rm Q} = + 1/3\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= +0.333} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(4) Im dritten (grünen) Intervall erkennt man ein Minus–Cosinus–Signal mit der Amplitude $g_0$ und ein Minus–Sinus–Signal mit Amplitude $g_0/3$:
- $$a_{\rm I} = \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= -1} \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.5cm}a_{\rm Q} = + 1/3\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= +0.333} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Wie in der Teilaufgabe (4) der Aufgabe 4.10Z noch berechnet werden soll, ist hier der Betrag gleich $|a| =1.054$ und der Phasenwinkel ${\rm arc} \ a \approx 161^\circ$.
(5) Das violette Signal unterscheidet sich vom grünen Intervall nicht in der Inphasekomponente, sondern nur im Vorzeichen der Quadraturkomponente:
- $$a_{\rm I} = \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= -1} \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.5cm}a_{\rm Q} = - 1/3\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= -0.333} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(6) Die maximale Signalenergie tritt auf, wenn einer der vier äußeren Eckpunkte belegt ist. Dann gilt:
- $$ E_{\rm S, \hspace{0.05cm}max} = {1}/{2}\cdot s_0^2 \cdot T = {1}/{2}\cdot \left (\sqrt{2} \cdot g_0 \right )^2 \cdot T = g_0^2 \cdot T = (1\,{\rm V})^2 \cdot (1\,{\rm \mu s}) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 10^{-6}\,{\rm V^2s}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Die mittlere Signalenergie ist gleich dem Maximalwert, wenn nur die Eckpunkte der Signalraumzuordnung belegt sind und „innere Symbole” von der Codierung ausgeschlossen werden.
(7) Pro Symbol werden vier Bit übertragen. Daraus folgt:
- $$ E_{\rm B, \hspace{0.05cm}max} = {E_{\rm S, \hspace{0.05cm}max}}/{4}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 0.25 \cdot 10^{-6}\,{\rm V^2s}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(8) Die minimale Signalenergie ergibt sich bei einem der inneren Signalraumpunkte und ist um den Faktor $9$ kleiner als bei Teilaufgabe (7):
- $$E_{\rm B, \hspace{0.05cm}min} = \frac{E_{\rm B, \hspace{0.05cm}max}}{9} = \frac{g_0^2 \cdot T}{36} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline { \approx 0.028 \cdot 10^{-6}\,{\rm V^2s}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Im Theorieteil wird gezeigt, dass bei der 16–QAM für die mittlere Signalenergie pro Bit unter der Voraussetzung, dass alle Symbole gleichwahrscheinlich sind, näherungsweise gilt:
- $$E_{\rm B} \approx 0.139 · g_0^2 \cdot T = 0.035 \cdot 10^{-6}\,{\rm V^2s}.$$