Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 4.1Z: Log Likelihood Ratio at the BEC Model"
| (20 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Channel_Coding/Soft-in_Soft-Out_Decoder}} |
| − | [[File:P_ID2978__KC_Z_4_1.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID2978__KC_Z_4_1.png|right|frame|BEC channel model]] |
| − | + | We consider the so-called [[Channel_Coding/Channel_Models_and_Decision_Structures#Binary_Erasure_Channel_.E2.80.93_BEC| $\text{BEC channel }$]] ("binary erasure channel") with | |
| − | * | + | * the input variable $x ∈ \{+1, \, -1\}$, |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | * the output variable $y ∈ \{+1, \, -1, \, {\rm E}\}$, and | ||
| − | + | * the erasure probability $\lambda$. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Here $y = {\rm E}$ ("erasure") means that the initial value $y$ could neither be decided as "$+1$" nor as "$-1$". | |
| + | |||
| + | Also known are the input probabilities | ||
| + | :$${\rm Pr}(x = +1) = 3/4\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.5cm}{\rm Pr}(x = -1) = 1/4\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| + | |||
| + | The log likelihood ratio of the binary random variable $x$ is given by bipolar approach as follows: | ||
:$$L(x)={\rm ln} \hspace{0.15cm} \frac{{\rm Pr}(x = +1)}{{\rm Pr}(x = -1)}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$L(x)={\rm ln} \hspace{0.15cm} \frac{{\rm Pr}(x = +1)}{{\rm Pr}(x = -1)}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | Correspondingly, for the conditional log likelihood ratio in forward direction for all $y ∈ \{+1, \, -1, \, {\rm E}\}$: | |
:$$L(y\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}x) = | :$$L(y\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}x) = | ||
{\rm ln} \hspace{0.15cm} \frac{{\rm Pr}(y\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}x = +1)}{{\rm Pr}(y\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}x = -1)} \hspace{0.05cm}. $$ | {\rm ln} \hspace{0.15cm} \frac{{\rm Pr}(y\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}x = +1)}{{\rm Pr}(y\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}x = -1)} \hspace{0.05cm}. $$ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | |
| + | <u>Hints:</u> | ||
| + | * This exercise belongs to the chapter [[Channel_Coding/Soft-in_Soft-Out_Decoder| "Soft–in Soft–out Decoder"]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Reference is made in particular to the sections | ||
| + | :*[[Channel_Coding/Soft-in_Soft-Out_Decoder#Reliability_information_-_Log_Likelihood_Ratio| "Reliability Information – Log Likelihood Ratio"]], | ||
| + | :*[[Channel_Coding/Channel_Models_and_Decision_Structures#Binary_Erasure_Channel_.E2.80.93_BEC|"Binary Erasure Channel"]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Questions=== | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {What is the log likelihood ratio of the input variable $x$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $ | + | $L(x) \ = \ ${ 1.099 3% } |
| − | { | + | {What probability ${\rm Pr}(x = \, -1)$ corresponds to $L(x) = \, -2$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $ | + | ${\rm Pr}(x = \, -1) \ = \ ${ 0.881 3% } |
| − | { | + | {Calculate the conditional L–value $L(y = {\rm E}\hspace{0.05cm} |\hspace{0.05cm} x)$ in the forward direction. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $ | + | $L(y = {\rm E} \hspace{0.05cm} |\hspace{0.05cm} x) \ = \ ${ 0. } |
| − | { | + | {Which statements are true for the other two conditional log likelihood ratios? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + $L(y = +1 \hspace{0.05cm} |\hspace{0.05cm} x)$ is positive and infinite in magnitude. |
| − | - | + | + $L(y = \, -1 \hspace{0.05cm} |\hspace{0.05cm} x)$ is negative and infinite in magnitude. |
| + | - It holds $L(y = +1 \hspace{0.05cm} |\hspace{0.05cm} x) = L(y = \, -1 \hspace{0.05cm} |\hspace{0.05cm} x) = 0$. | ||
| − | { | + | {Under what conditions do the results from subtasks '''(3)''' and '''(4)''' hold? |
| − | |type=" | + | |type="()"} |
| − | + | - For $0 ≤ \lambda ≤ 1$. | |
| − | - | + | - For $0 < \lambda ≤ 1$. |
| + | - For $0 ≤ \lambda < 1$. | ||
| + | + For $0 < \lambda < 1$. | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1)''' | + | '''(1)''' With the given symbol probabilities ${\rm Pr}(x = +1) = 3/4$ and ${\rm Pr}(x = -1) = 1/4$, we obtain: |
| − | '''(2)''' | + | :$$L(x)={\rm ln} \hspace{0.15cm} \frac{{\rm Pr}(x = +1)}{{\rm Pr}(x = -1)} |
| − | '''(3)''' | + | ={\rm ln} \hspace{0.15cm} \frac{3/4}{1/4}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 1.099}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ |
| − | '''(4)''' | + | |
| − | '''(5)''' | + | |
| + | '''(2)''' According to the definition | ||
| + | :$$L(x)={\rm ln} \hspace{0.15cm} \frac{{\rm Pr}(x = +1)}{{\rm Pr}(x = -1)}$$ | ||
| + | |||
| + | yields the following equation for $L(x) = \, -2$: | ||
| + | :$$\hspace{0.15cm} \frac{{\rm Pr}(x = +1)}{1-{\rm Pr}(x = +1)} \stackrel{!}{=}{\rm e}^{-2} \approx 0.135 \hspace{0.25cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.25cm} | ||
| + | 1.135 \cdot {\rm Pr}(x = +1)\stackrel{!}{=}0.135\hspace{0.3cm} | ||
| + | \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | ||
| + | {\rm Pr}(x = +1) = 0.119\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.4cm}{\rm Pr}(x = -1) | ||
| + | \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0.881}\hspace{0.05cm}. $$ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(3)''' For the conditional log likelihood ratio $L(y = {\rm E} \hspace{0.05cm} |\hspace{0.05cm} x)$ in the forward direction, valid for the BEC model: | ||
| + | :$$L(y = {\rm E}\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}x) = | ||
| + | {\rm ln} \hspace{0.15cm} \frac{{\rm Pr}(y= {\rm E}\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}x = +1)}{{\rm Pr}(y= {\rm E}\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}x = -1)} | ||
| + | = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.15cm} \frac{\lambda}{\lambda}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(4)''' Analogous to the sample solution of subtask '''(3)''', we obtain for $y = ±1$: | ||
| + | :$$L(y = +1\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}x) \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} | ||
| + | {\rm ln} \hspace{0.15cm} \frac{{\rm Pr}(y= +1\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}x = +1)}{{\rm Pr}(y= +1\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}x = -1)} | ||
| + | = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.15cm} \frac{1-\lambda}{0}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ \hspace{0.05cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.15cm}+\infty }\hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
| + | :$$L(y = -1\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}x) \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} | ||
| + | {\rm ln} \hspace{0.15cm} \frac{{\rm Pr}(y= -1\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}x = +1)}{{\rm Pr}(y= -1\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}x = -1)} | ||
| + | = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.15cm} \frac{0}{1-\lambda}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ \hspace{0.05cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.15cm}-\infty }\hspace{0.05cm}. $$ | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Accordingly, the <u>proposed solutions 1 and 2</u> are correct. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(5)''' Correct is the <u>last proposed solution</u>: | ||
| + | * For $\lambda = 0$ $($"ideal channel"$)$ ⇒ $L(y = {\rm E} \hspace{0.05cm} |\hspace{0.05cm} x) = \ln {(0/0)}$ ⇒ indefinite result. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * For $\lambda = 1$ $($complete erasure, $y ≡ {\rm E})$ ⇒ $L(y = +1 \hspace{0.05cm} |\hspace{0.05cm} x)$ and $L(y = \, -1 \hspace{0.05cm} |\hspace{0.05cm} x)$ are undefined. | ||
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Channel Coding: Exercises|^4.1 Soft–in Soft–out Decoder^]] |
Latest revision as of 17:18, 28 November 2022
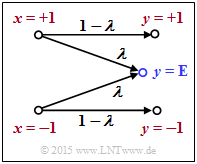
We consider the so-called $\text{BEC channel }$ ("binary erasure channel") with
- the input variable $x ∈ \{+1, \, -1\}$,
- the output variable $y ∈ \{+1, \, -1, \, {\rm E}\}$, and
- the erasure probability $\lambda$.
Here $y = {\rm E}$ ("erasure") means that the initial value $y$ could neither be decided as "$+1$" nor as "$-1$".
Also known are the input probabilities
- $${\rm Pr}(x = +1) = 3/4\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.5cm}{\rm Pr}(x = -1) = 1/4\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The log likelihood ratio of the binary random variable $x$ is given by bipolar approach as follows:
- $$L(x)={\rm ln} \hspace{0.15cm} \frac{{\rm Pr}(x = +1)}{{\rm Pr}(x = -1)}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Correspondingly, for the conditional log likelihood ratio in forward direction for all $y ∈ \{+1, \, -1, \, {\rm E}\}$:
- $$L(y\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}x) = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.15cm} \frac{{\rm Pr}(y\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}x = +1)}{{\rm Pr}(y\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}x = -1)} \hspace{0.05cm}. $$
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter "Soft–in Soft–out Decoder".
- Reference is made in particular to the sections
Questions
Solution
- $$L(x)={\rm ln} \hspace{0.15cm} \frac{{\rm Pr}(x = +1)}{{\rm Pr}(x = -1)} ={\rm ln} \hspace{0.15cm} \frac{3/4}{1/4}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 1.099}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) According to the definition
- $$L(x)={\rm ln} \hspace{0.15cm} \frac{{\rm Pr}(x = +1)}{{\rm Pr}(x = -1)}$$
yields the following equation for $L(x) = \, -2$:
- $$\hspace{0.15cm} \frac{{\rm Pr}(x = +1)}{1-{\rm Pr}(x = +1)} \stackrel{!}{=}{\rm e}^{-2} \approx 0.135 \hspace{0.25cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.25cm} 1.135 \cdot {\rm Pr}(x = +1)\stackrel{!}{=}0.135\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm Pr}(x = +1) = 0.119\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.4cm}{\rm Pr}(x = -1) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0.881}\hspace{0.05cm}. $$
(3) For the conditional log likelihood ratio $L(y = {\rm E} \hspace{0.05cm} |\hspace{0.05cm} x)$ in the forward direction, valid for the BEC model:
- $$L(y = {\rm E}\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}x) = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.15cm} \frac{{\rm Pr}(y= {\rm E}\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}x = +1)}{{\rm Pr}(y= {\rm E}\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}x = -1)} = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.15cm} \frac{\lambda}{\lambda}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(4) Analogous to the sample solution of subtask (3), we obtain for $y = ±1$:
- $$L(y = +1\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}x) \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} {\rm ln} \hspace{0.15cm} \frac{{\rm Pr}(y= +1\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}x = +1)}{{\rm Pr}(y= +1\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}x = -1)} = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.15cm} \frac{1-\lambda}{0}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ \hspace{0.05cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.15cm}+\infty }\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$L(y = -1\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}x) \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} {\rm ln} \hspace{0.15cm} \frac{{\rm Pr}(y= -1\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}x = +1)}{{\rm Pr}(y= -1\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}x = -1)} = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.15cm} \frac{0}{1-\lambda}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ \hspace{0.05cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.15cm}-\infty }\hspace{0.05cm}. $$
- Accordingly, the proposed solutions 1 and 2 are correct.
(5) Correct is the last proposed solution:
- For $\lambda = 0$ $($"ideal channel"$)$ ⇒ $L(y = {\rm E} \hspace{0.05cm} |\hspace{0.05cm} x) = \ln {(0/0)}$ ⇒ indefinite result.
- For $\lambda = 1$ $($complete erasure, $y ≡ {\rm E})$ ⇒ $L(y = +1 \hspace{0.05cm} |\hspace{0.05cm} x)$ and $L(y = \, -1 \hspace{0.05cm} |\hspace{0.05cm} x)$ are undefined.