Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 4.2Z: Correlation between "x" and "e to the power of x""
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
}} | }} | ||
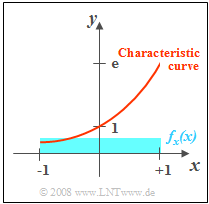
| − | [[File:EN_Sto_Z_4_2.png|right|frame|Given input PDF and characteristic curve]] | + | [[File:EN_Sto_Z_4_2.png|right|frame|Given input PDF $f_x(x)$ and characteristic curve $y = g(x)$]] |
| − | Let the random variable $x$ be uniformly distributed between $-1$ and $+1$. Thus | + | Let the random variable $x$ be uniformly distributed between $-1$ and $+1$. Thus, |
| − | *the mean $m_x = 0$, and | + | *the mean $m_x = 0$, and |
*the variance $\sigma_x^2 = 1/3$. | *the variance $\sigma_x^2 = 1/3$. | ||
| − | By the nonlinear characteristic $y = g(x) = {\rm e}^x$ the random | + | By the nonlinear characteristic $y = g(x) = {\rm e}^x$ the random quantity $y $ is formed. Thus, there is a fixed deterministic relationship between the two random variables $x$ and $y$. The random variable $y$ can only take values between $1/{\rm e}$ and ${\rm e}$. |
| − | For the probability density function, one obtains for this range according to the principle [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Exponentially_Distributed_Random_Variables#Transformation_of_random_variables|"Transformation of Random Variables"]]: | + | For the probability density function, one obtains for this range according to the principle [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Exponentially_Distributed_Random_Variables#Transformation_of_random_variables|"Transformation of Random Variables"]]: |
:$$f_y(y) = {\rm 1}/({\rm 2\it y}). $$ | :$$f_y(y) = {\rm 1}/({\rm 2\it y}). $$ | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
Hints: | Hints: | ||
*The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Two-Dimensional_Random_Variables|Two-Dimensional Random Variables]]. | *The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Two-Dimensional_Random_Variables|Two-Dimensional Random Variables]]. | ||
| − | *Reference is also made to the chapter [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Expected_Values_and_Moments|Expected Values and Moments]]. | + | *Reference is also made to the chapter [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Expected_Values_and_Moments|Expected Values and Moments]]. |
| − | + | *Consider that in the range $-1 ≤ x ≤ +1$ the exponential function can be approximated as follows: | |
| − | *Consider that in the | ||
:$$y={\rm e}^{x}\approx 1+ \frac{ x}{1!} + \frac{{ x}^{\rm 2}}{\rm 2!}+ \frac{{x}^{\rm 3}}{\rm 3!}+ \frac{{x}^{\rm 4}}{\rm 4!}.$$ | :$$y={\rm e}^{x}\approx 1+ \frac{ x}{1!} + \frac{{ x}^{\rm 2}}{\rm 2!}+ \frac{{x}^{\rm 3}}{\rm 3!}+ \frac{{x}^{\rm 4}}{\rm 4!}.$$ | ||
| Line 32: | Line 31: | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | {What is the mean value $m_y$ of the random | + | {What is the mean value $m_y$ of the random variable $y$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$m_y \ = \ $ { 1.175 3% } | $m_y \ = \ $ { 1.175 3% } | ||
| − | {Calculate the rms $\sigma_y$ of the random variable $y$. | + | {Calculate the rms value $\sigma_y$ of the random variable $y$. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$\sigma_y \ = \ $ { 0.658 3% } | $\sigma_y \ = \ $ { 0.658 3% } | ||
| − | {Which of the following statements are true regarding 2D PDF $f_{xy}(x, y)$? | + | {Which of the following statements are true regarding 2D–PDF $f_{xy}(x, y)$? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + Outside the curve $y = {\rm e}^x$ | + | + Outside the curve $y = {\rm e}^x$: ⇒ $f_{xy}(x, y)= 0$. |
| − | - For | + | - For all two-dimensional values $(x, {\rm e}^x)$ the PDF $f_{xy}(x, y)$ is constant. |
+ The PDF describes a "Dirac wall" along the curve $y = {\rm e}^x$. | + The PDF describes a "Dirac wall" along the curve $y = {\rm e}^x$. | ||
| − | + The height of the Dirac decreases from the lower left to the upper right. | + | + The height of the Dirac wall decreases from the lower left to the upper right. |
| − | {Calculate the joint moment $m_{xy}$ of the random variables $x$ and $y$, that is, the expected value of the product $x \cdot y$. | + | {Calculate the joint moment $m_{xy}$ of the random variables $x$ and $y$, that is, the expected value of the product $x \cdot y$. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$m_{xy}\ = \ $ { 0.367 3% } | $m_{xy}\ = \ $ { 0.367 3% } | ||
Revision as of 15:15, 7 February 2022
Let the random variable $x$ be uniformly distributed between $-1$ and $+1$. Thus,
- the mean $m_x = 0$, and
- the variance $\sigma_x^2 = 1/3$.
By the nonlinear characteristic $y = g(x) = {\rm e}^x$ the random quantity $y $ is formed. Thus, there is a fixed deterministic relationship between the two random variables $x$ and $y$. The random variable $y$ can only take values between $1/{\rm e}$ and ${\rm e}$.
For the probability density function, one obtains for this range according to the principle "Transformation of Random Variables":
- $$f_y(y) = {\rm 1}/({\rm 2\it y}). $$
Hints:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter Two-Dimensional Random Variables.
- Reference is also made to the chapter Expected Values and Moments.
- Consider that in the range $-1 ≤ x ≤ +1$ the exponential function can be approximated as follows:
- $$y={\rm e}^{x}\approx 1+ \frac{ x}{1!} + \frac{{ x}^{\rm 2}}{\rm 2!}+ \frac{{x}^{\rm 3}}{\rm 3!}+ \frac{{x}^{\rm 4}}{\rm 4!}.$$
Questions
Solution
- A second calculation possibility is based directly on the calculation rules for expected values:
- $$m_y={\rm E}\big[ y\big] = \int_{-\infty}^{+\infty}g(x) \cdot f_x(x)\,\, {\rm d}x = {1}/{2}\cdot\int_{-1}^{1}{\rm e}^{ x}\,\,{\rm d}x=\rm {1}/{2}\cdot(e-e^{-1}) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 1.175}.$$
(2) For the quadratic mean of the random variable $y$ holds:
- $$m_{2 y} = {\rm E}\big[ y^{\rm 2}\big] = {\rm E}[{\rm e}^{ 2 x}]= {1}/{2}\cdot\int_{-1}^{+1}{\rm e}^{2 x} \,\,{\rm d}x = {1}/{4}\cdot({\rm e}^{2}-{\rm e}^{-2}) = 1.813.$$
- From this we obtain by Steiner's theorem:
- $$\sigma_y^{\rm 2} = m_{ 2 y}- m_{ y}^2 = {1}/{4}\cdot({\rm e}^{2}-{\rm e}^{-2})-{1}/{4}\cdot( {\rm e}^{2}-2+{\rm e}^{-2})={1}/{2}\cdot(1-{\rm e}^{-2})=0.432 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}\sigma_y \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0.658}.$$
(3) Correct are the proposed solutions 1, 3 and 4:
- Outside the curve $y = {\rm e}^x$ the PDF is of course zero.
- Since the volume under the 2D PDF is equal to $1$ , the PDF values for the infinitely narrow region are infinite $y = {\rm e}^x$ .
- This means that the PDF describes a curved Dirac wall.
- Due to the decay of the PDF $f_y(y)$ with increasing $y$ the height of this Dirac wall decreases continuously from $(-1, 1/{\rm e})$ to $(+1, {\rm e})$ .
(4) For the joint moment holds:
- $$m_{xy} = {\rm E}\big[ x\cdot y \big] = {\rm E}\big[ x\cdot {\rm e}^{x} \big].$$
- With the series expansion given, the approximation follows:
- $$m_{xy} \approx {\rm E}\big[x\big] + {\rm E}\big[x^{\rm 2}\big] + \frac{1}{2} \cdot {\rm E}\big[ x^{\rm 3}\big] + \frac{1}{6} \cdot {\rm E}\big[ x^{\rm 4}\big]+ \frac{1}{24} \cdot {\rm E}\big[ x^{\rm 5}\big].$$
- Because of the symmetry of the random variable $x$ holds for all odd values of $k$: $\rm E\big[\it x^{k}\rm \big] =\rm 0.$ Furthermore:
- $${\rm E}\big[ x^{\rm 2}\big] = \sigma_{x}^{\rm 2}= \frac{1}{3}, \hspace{0.5cm} {\rm E}\big[ x^{\rm 4}\big] = \frac{1}{2}\int_{-1}^{+1} x^{\rm 4} \,\,{\rm d}x = \rm\frac{1}{5}\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}{\it m_{xy}} = \rm\frac{1}{3} + \frac{1}{6}\cdot\frac{1}{5} = \frac{11}{30}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{\approx 0.367}.$$
(5) Because $m_x = 0$ holds $\mu_{xy} = m_{xy}$. Thus, for the correlation coefficient:
- $$\it \rho_{xy} = \frac{\mu_{xy}}{\sigma_x \cdot \sigma_y}=\rm\frac{0.367}{0.577 \cdot 0.658}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ \approx 0.967}.$$
- Between $x$ and $y$ there is indeed a definite deterministic relation.
- But since there are also nonlinear bindings in this, the correlation coefficient $ \rho_{xy} \ne 1$.