Exercise 4.4Z: Supplement to Exercise 4.4
Der Informationstheoretiker "Robert G. Gallager" hat sich bereits 1963 mit folgender Fragestellung beschäftigt:
- Gegeben ist ein Zufallsvektor $\underline{x} = (x_1, \, x_2, \hspace{-0.04cm} \text{ ...} \hspace{0.08cm} , x_n)$ mit $n$ binären Elementen $x_i ∈ \{0, \, 1\}$.
- Bekannt sind alle Wahrscheinlichkeiten $p_i = {\rm Pr}(x_i = 1)$ und $q_i = {\rm Pr}(x_i = 0) = 1 - p_i$ mit Index $i = 1, \hspace{-0.04cm}\text{ ...} \hspace{0.08cm} ,\ n$.
- Gesucht ist die Wahrscheinlichkeit, dass die Anzahl der Einsen in diesem Vektor geradzahlig ist.
- Oder ausgedrückt mit dem "Hamming–Gewicht": Wie groß ist die Wahrscheinlichkeit ${\rm Pr}[w_{\rm H}(\underline{x}) {\rm \ ist \ gerade}]$?
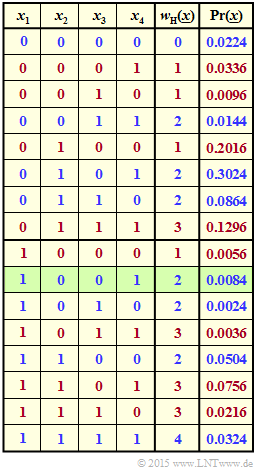
Die Grafik verdeutlicht die Aufgabenstellung für das Beispiel $n = 4$ sowie $p_1 = 0.2$, $p_2 = 0.9$, $p_3 = 0.3$ und $p_4 = 0.6$.
- Für die grün hinterlegte Zeile ⇒ $\underline{x} = (1, \, 0, \, 0, \, 1)$ gilt $w_{\rm H}(\underline{x}) = 2$ und
- $${\rm Pr}(\underline{x}) = p_1 \cdot q_2 \cdot q_3 \cdot p_4 = 0.0084.$$
- Blaue Schrift bedeutet "$w_{\rm H}(\underline{x})$ ist gerade". Rote Schrift steht für "$w_{\rm H}(\underline{x})$ ist ungerade".
- Die Wahrscheinlichkeit ${\rm Pr}[w_{\rm H}(\underline{x}) {\rm \ ist \ gerade}]$ ist die Summe der blauen Zahlen in der letzten Spalte.
- Die Summe der roten Zahlen ergibt ${\rm Pr}[w_{\rm H}(\underline{x}) {\rm \ ist \ ungerade}] = 1 - {\rm Pr}[w_{\rm H}(\underline{x}) {\rm \ ist \ gerade}]$.
Gallager hat das Problem in analytischer Weise gelöst:
- $$ {\rm Pr} \left [w_{\rm H}(\underline{x})\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm ist \hspace{0.15cm} gerade} \right ] \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} 1/2 \cdot [1 + \pi]\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $${\rm Pr} \left [w_{\rm H}(\underline{x})\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm ist \hspace{0.15cm} ungerade} \right ] \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} 1/2 \cdot [1 - \pi]\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Hierbei ist die folgende Hilfsgröße verwendet:
- $$\pi = \prod\limits_{i =1}^{n} \hspace{0.25cm}(1-2p_i) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Die Gleichung wendet man zum Beispiel an, um die extrinsischen $L$–Werte eines Single Parity–check Codes zu berechnen.
Wie bereits in der "Aufgabe A4.4" dargelegt, lautet nämlich der extrinsische $L$–Wert mit dem Hamming–Gewicht $w_{\rm H}$ der verkürzten Folge $\underline{x}^{(-i)}$:
- $$L_{\rm E}(i) = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.15cm}\frac{{\rm Pr} \left [w_{\rm H}(\underline{x}^{(-i)})\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm ist \hspace{0.15cm} gerade} \hspace{0.05cm} | \hspace{0.05cm}\underline{y} \hspace{0.05cm}\right ]}{{\rm Pr} \left [w_{\rm H}(\underline{x}^{(-i)})\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm ist \hspace{0.15cm} ungerade} \hspace{0.05cm} | \hspace{0.05cm}\underline{y} \hspace{0.05cm}\right ]} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Hierbei ist berücksichtigt, dass man für $L_{\rm E}(i)$ nur die anderen Symbole $(j ≠ i)$ heranziehen darf:
- $$\underline{x}^{(-i)} = \big ( \hspace{0.03cm}x_1, \hspace{-0.04cm} \text{ ...} \hspace{0.08cm} , \hspace{0.03cm} x_{i-1}, \hspace{0.43cm} x_{i+1}, \hspace{-0.04cm} \text{ ...} \hspace{0.08cm} , x_{n} \hspace{0.03cm} \big )\hspace{0.03cm}. $$
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter "Soft–in Soft–out Decoder".
- Reference is made in particular to the page "For calculating the extrinsic $L$–values".
- The exercise is intended as a supplement to "Exercise 4.4" .
Questions
Solution
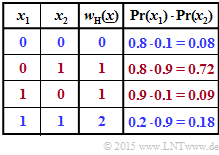
(1) According to the adjacent table applies:
- $${\rm Pr} \left [w_{\rm H}(\underline{x})\hspace{0.10cm}{\rm is \hspace{0.10cm} even}\right ] = {\rm Pr} \left [w_{\rm H} = 0 \right] + {\rm Pr} \left [w_{\rm H} = 2 \right] \hspace{0.05cm}. $$
With the probabilities
- $$p_1 = {\rm Pr} (x_1 = 1) \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} 0.2\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm}q_1 = {\rm Pr} (x_1 = 0) = 0.8\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$p_2 = {\rm Pr} (x_2 = 1) \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} 0.9\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm}q_2 = {\rm Pr} (x_2 = 0) = 0.1$$
one obtains:
- $${\rm Pr} \left [w_{\rm H}(\underline{x}) = 0\right] \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} {\rm Pr} \left [(x_1 = 0)\cap (x_2 = 0) \right] = q_1 \cdot q_2 = 0.8 \cdot 0.1 = 0.08 \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $${\rm Pr} \left [w_{\rm H}(\underline{x}) = 2\right] \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} {\rm Pr} \left [(x_1 = 1)\cap (x_2 = 1) \right] = p_1 \cdot p_2 = 0.2 \cdot 0.9 = 0.18$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm Pr} \left [w_{\rm H}(\underline{x})\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm ist \hspace{0.15cm} gerade}\right] = 0.8 + 0.18 \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{= 0.26} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The Gallager's equation provides for the same set of parameters:
- $${\rm Pr} \left [w_{\rm H}(\underline{x})\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm ist \hspace{0.15cm} gerade}\right] \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} 0.5 + 0.5 \cdot \prod\limits_{i =1}^{2} \hspace{0.25cm}(1-2\cdot p_i) = 0.5 + 0.5 \cdot (1 - 2 \cdot 0.2)\cdot (1 - 2 \cdot 0.9) = 0.26 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The equation given by Gallager 1963 was hereby verified for $n = 2$.
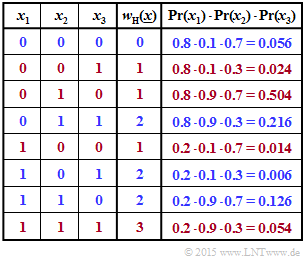
(2) In the second table, the four combinations with an even number of ones are marked in blue. The probabilities of occurrence of each combination are given in the last column. Thus, the result is:
- $$ {\rm Pr} \left [w_{\rm H}(\underline{x})\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm ist \hspace{0.15cm} gerade}\right] = 0.056 + 0.216 + 0.006 + 0.126 \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{= 0.404} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The red rows provide the complementary event:
- $$ {\rm Pr} \left [w_{\rm H}(\underline{x})\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm ist \hspace{0.15cm} ungerade}\right] = 0.024 + 0.504 + 0.014 + 0.054= 0.596 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The Gallager's equation again gives the exact same result, although it should be noted that this equation is valid for all $n$ and all arbitrary probabilities:
- $${\rm Pr} \left [w_{\rm H}(\underline{x})\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm is \hspace{0.15cm} even}\right] \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} 0.5 + 0.5 \cdot \prod\limits_{i =1}^{3} \hspace{0.25cm}(1-2\cdot p_i) $$
- $$\Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm}{\rm Pr} \left [w_{\rm H}(\underline{x})\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm is \hspace{0.15cm} even}\right] \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} 0.5 + 0.5 \cdot (+0.6) \cdot (-0.8) \cdot (+0.4) = 0.404 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(3) According to the specification page applies:
- $$\pi = \prod\limits_{i =1}^{4} \hspace{0.25cm}(1-2\cdot p_i) \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} (1 - 2 \cdot 0.2) \cdot (1 - 2 \cdot 0.9) \cdot (1 - 2 \cdot 0.3) \cdot (1 - 2 \cdot 0.6) $$
- $$\Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm}\pi = \prod\limits_{i =1}^{4} \hspace{0.25cm}(1-2\cdot p_i) \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm}(+0.6) \cdot (-0.8) \cdot (+0.4) \cdot (-0.2) = 0.0384 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
From this can be calculated:
- $${\rm Pr}({\rm blue}) = {\rm Pr} \left [w_{\rm H}(\underline{x})\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm is \hspace{0.15cm} even}\right] \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} 0.5 + 0.5 \cdot \pi = 0.5 + 0.5 \cdot 0.0384\hspace{0.15cm} \underline{= 0.5192}\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $${\rm Pr}({\rm red}) = {\rm Pr} \left [w_{\rm H}(\underline{x})\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm is \hspace{0.15cm} uneven}\right] \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} 0.5 - 0.5 \cdot \pi = 0.5 - 0.5 \cdot 0.0384\hspace{0.15cm} \underline{= 0.4808}\hspace{0.05cm}. $$
If you add up the blue and red probabilities on the information page, you get exactly the values calculated here.
For the quotient we get:
- $$Q = \frac{{\rm Pr} \left [w_{\rm H}(\underline{x})\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm ist \hspace{0.15cm} gerade}\right]} { {\rm Pr} \left [w_{\rm H}(\underline{x})\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm ist \hspace{0.15cm} ungerade}\right]} = \frac{0.5192}{0.4808}\hspace{0.15cm} \underline{= 1.0799} \hspace{0.05cm}. $$
(4) For the single parity–check code, the extrinsic $L$ value with respect to the $i$th bit was specified as follows:
- $$L_{\rm E}(i) = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.15cm}\frac{{\rm Pr} \left [w_{\rm H}(\underline{x}^{(-i)})\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm ist \hspace{0.15cm} gerade} \hspace{0.05cm} | \hspace{0.05cm}\underline{y} \hspace{0.05cm}\right ]}{{\rm Pr} \left [w_{\rm H}(\underline{x}^{(-i)})\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm ist \hspace{0.15cm} ungerade} \hspace{0.05cm} | \hspace{0.05cm}\underline{y} \hspace{0.05cm}\right ]} \hspace{0.05cm},$$
or:
- $$L_{\rm E}(i) = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.15cm}\frac{1+\prod_{j \ne i} \hspace{0.25cm}(1-2\cdot p_j)}{1-\prod_{j \ne i} \hspace{0.25cm}(1-2\cdot p_j)} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
At $\text{SPC (5, 4, 2}$) ⇒ $n = 5$, this product for $i = 5$ results from the following four factors:
- $$\pi = \prod\limits_{j = 1, \hspace{0.05cm}2, \hspace{0.05cm}3, \hspace{0.05cm}4} \hspace{0.05cm}(1-2\cdot p_j) = (1-2\cdot p_1) \cdot (1-2\cdot p_2) \cdot (1-2\cdot p_3) \cdot (1-2\cdot p_4) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The comparison with the subtask (3) shows that $L_{\rm E}(i = 5) = \ln {Q} = \ln {(1.0799)} \ \underline{\approx 0.077}$.
(5) Correct is proposed solution 3 because the result for $L_{\rm E}(i = 5)$ is independent of $p_5$.