Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 4.5: Coaxial Cable - Impulse Response"
(Die Seite wurde neu angelegt: „ {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Lineare zeitinvariante Systeme/Koaxialkabel }} right| :Der Frequenzgang eines Koaxialkabels der Lä…“) |
|||
| (25 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Linear_and_Time_Invariant_Systems/Properties_of_Coaxial_Cables | |
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | [[File:P_ID1814__LZI_A_4_5.png|right|]] | + | [[File:P_ID1814__LZI_A_4_5.png|right|frame|Impulse response of a coaxial cable]] |
| − | : | + | The frequency response of a coaxial cable (German: "Koaxialkabel" ⇒ subscipt "K") of length $l$ can be represented by the following formula: |
:$$H_{\rm K}(f) = {\rm e}^{- \alpha_0 \hspace{0.05cm} \cdot \hspace{0.05cm} l} | :$$H_{\rm K}(f) = {\rm e}^{- \alpha_0 \hspace{0.05cm} \cdot \hspace{0.05cm} l} | ||
| − | \cdot | + | \cdot |
{\rm e}^{- (\alpha_1 + {\rm j} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm} \beta_1) \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot f \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}l} \cdot | {\rm e}^{- (\alpha_1 + {\rm j} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm} \beta_1) \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot f \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}l} \cdot | ||
| − | + | {\rm e}^{- (\alpha_2 + {\rm j} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm} \beta_2) \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \sqrt{f} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}l} | |
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | The first term of this equation is due to the ohmic losses, the second term to the transverse losses. Dominant, however, is the skin effect, which is expressed by the third term. | |
| − | + | With the coefficients valid for the "standard coaxial cable" $\text{(2.6 mm}$ core diameter, $\text{9.5 mm}$ outer diameter$)$ | |
:$$\alpha_2 = 0.2722 \hspace{0.15cm}\frac {\rm Np}{\rm km \cdot \sqrt{\rm MHz}} | :$$\alpha_2 = 0.2722 \hspace{0.15cm}\frac {\rm Np}{\rm km \cdot \sqrt{\rm MHz}} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}, | \hspace{0.05cm}, | ||
\hspace{0.2cm} \beta_2 = 0.2722 \hspace{0.15cm}\frac {\rm rad}{\rm km \cdot \sqrt{\rm | \hspace{0.2cm} \beta_2 = 0.2722 \hspace{0.15cm}\frac {\rm rad}{\rm km \cdot \sqrt{\rm | ||
MHz}}\hspace{0.05cm}$$ | MHz}}\hspace{0.05cm}$$ | ||
| − | + | this frequency response can also be represented as follows: | |
:$$H_{\rm K}(f) \approx {\rm e}^{- 0.2722 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}l/{\rm km} | :$$H_{\rm K}(f) \approx {\rm e}^{- 0.2722 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}l/{\rm km} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \sqrt{f/{\rm MHz}} } \cdot {\rm e}^{- {\rm j}\hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm} | \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \sqrt{f/{\rm MHz}} } \cdot {\rm e}^{- {\rm j}\hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm} | ||
| Line 23: | Line 22: | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \sqrt{f/{\rm MHz}}} | \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \sqrt{f/{\rm MHz}}} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | : | + | That means: |
| + | |||
| + | Attenuation curve ${a}_{\rm K}(f)$ and phase curve $b_{\rm K}(f)$ are identical except for the pseudo units "Np" and "rad", respectively. | ||
| + | |||
| − | + | If one defines the characteristic cable attenuation ${a}_{\rm *}$ at half the bit rate $($i.e., at $R/2)$ and normalizes the frequency to $R$, one can treat digital systems of different bit rate and length uniformly: | |
| − | :$${ | + | :$${a}_{\rm \star} = {a}_{\rm K}(f ={R}/{2}) |
\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}H_{\rm K}(f) = {\rm e}^{- | \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}H_{\rm K}(f) = {\rm e}^{- | ||
| − | { | + | {a}_{\rm \star} \cdot \sqrt{2f/R}}\cdot {\rm e}^{- {\rm j}\hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm} {a}_{\star} \cdot \sqrt{2f/R}}\hspace{0.4cm}{\rm with}\hspace{0.2cm}{a}_{\star}\hspace{0.2cm}{\rm in}\hspace{0.2cm}{\rm Np} |
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | *The corresponding $\rm dB$ value is greater by a factor of $8.686$. | |
| + | *For a binary system, $R = 1/T$ holds, so that the characteristic cable attenuation refers to the frequency $f = 1/(2T)$. | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | :$$h_{\rm K}(t) = \frac{ { | + | The [[Signal_Representation/Fourier_Transform_and_Its_Inverse#Fouriertransformation|Fourier transform]] of $H_{\rm K}(f)$ yields the impulse response $h_{\rm K}(t)$, which can be specified in closed-analytic form for a coaxial cable using the approximations described here. For a binary system holds: |
| − | {\rm | + | :$$h_{\rm K}(t) = \frac{ {a}_{\rm \star}/T}{ \sqrt{2 \pi^2 \cdot (t/T)^3}}\hspace{0.1cm} \cdot |
| − | \hspace{0.4cm}{\rm | + | {\rm e}^{ - {{a}_{\rm \star}^2}/(2 \hspace{0.05cm} \pi \cdot \hspace{0.05cm} t/T)} |
| + | \hspace{0.4cm}{\rm with}\hspace{0.2cm}{a}_{\rm \star}\hspace{0.2cm}{\rm in}\hspace{0.2cm}{\rm Np} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | Subtask '''(5)''' refers to the basic reception pulse $g_r(t) = g_s(t) \star h_{\rm K}(t)$, where the basic transmission pulse $g_s(t)$ is assumed to be a rectangle $($height $s_0$, duration $T)$. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | Notes: |
| + | *The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Linear_and_Time_Invariant_Systems/Eigenschaften_von_Koaxialkabeln|Properties of Coaxial Cables]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *You can use the (German language) interactive SWF applet [[Applets:Zeitverhalten_von_Kupferkabeln|"Zeitverhalten von Kupferkabeln"]] ⇒ "Time behavior of copper cables" to check your results. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Questions=== | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {What is the length $l$ of a standard coaxial cable if the characteristic cable attenuation is ${a}_{\rm \star} = 60 \ \rm dB$ for the bit rate $R = 140 \ \rm Mbit/s$ ? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $l$ | + | $l \ =\ $ { 3 3% } $\ \rm km$ |
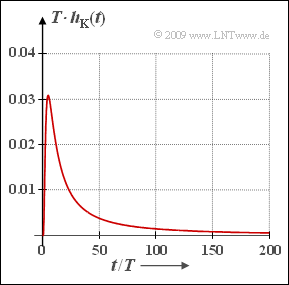
| − | { | + | {At which time $t_{\rm max}$ does $h_{\rm K}(t)$ have its maximum? Let ${a}_{\rm \star} = 60 \ \rm dB$. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $t_\ | + | $t_{\rm max} \ = \ $ { 5 3% } $\ \cdot T$ |
| − | { | + | {What is the maximum value of the impulse response? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $Max\ | + | ${\rm Max}\, \big [h_{\rm K}(t)\big ] \ = \ $ { 0.03 3% } $\ \cdot 1/T$ |
| − | { | + | {From which time $t_{\rm 5\%}$ is $h_{\rm K}(t)$ less than $5\%$ of the maximum? As an approximation, consider only the first term of the given formula. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $t_\ | + | $t_{\rm 5\%} \ = \ $ { 103.5 3% } $\ \cdot T$ |
| − | { | + | {Which statements are true for the basic reception pulse $g_r(t)$ ? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - | + | - $g_r(t)$ is twice as wide as $h_{\rm K}(t)$. |
| − | + | + | + It is approximated $g_r(t) = s_0 \cdot T \cdot h_{\rm K}(t)$. |
| − | - | + | - $g_r(t)$ can be approximated by a Gaussian pulse. |
| Line 77: | Line 86: | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | + | '''(1)''' The characteristic cable attenuation ${a}_{\rm \star} = 60 \ \rm dB$ corresponds approximately to $6.9\ \rm Np$. Therefore the following must hold: | |
| − | :$$\alpha_2 \cdot l \cdot | + | :$$\alpha_2 \cdot l \cdot {R}/{2} = 6.9\,\,{\rm |
Np} | Np} | ||
\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} l = \frac{6.9\,\,{\rm | \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} l = \frac{6.9\,\,{\rm | ||
| − | Np}}{0.2722 \,\, | + | Np}}{0.2722 \,\, {\rm Np}/({\rm km \cdot \sqrt{\rm MHz}}) |
\cdot \sqrt{70\,\,{\rm MHz}}}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ \approx 3\,\,{\rm km}} | \cdot \sqrt{70\,\,{\rm MHz}}}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ \approx 3\,\,{\rm km}} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | :$$x = \frac{ t}{ T}, \hspace{0.2cm} K_1 = \frac{ { | + | '''(2)''' With the substitutions |
| − | K_2 = \frac{ { | + | :$$x = \frac{ t}{ T}, \hspace{0.2cm} K_1 = \frac{ {a}_{\rm \star}/T}{\sqrt{2 \pi^2 }}, \hspace{0.2cm} |
| − | + | K_2 = \frac{ {a}_{\rm \star}^2}{2 \pi}$$ | |
| + | the impulse response can be described as follows: | ||
:$$h_{\rm K}(x) = K_1 \cdot x^{-3/2}\cdot {\rm e}^{-K_2/x} | :$$h_{\rm K}(x) = K_1 \cdot x^{-3/2}\cdot {\rm e}^{-K_2/x} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | *By setting the derivative to zero: | |
| − | :$$- | + | :$$- {3}/{2} \cdot K_1 \cdot x^{-5/2}\cdot {\rm e}^{-K_2/x}+ K_1 \cdot x^{-3/2}\cdot {\rm |
e}^{-K_2/x}\cdot (-K_2) \cdot (-x^{-2})= 0 | e}^{-K_2/x}\cdot (-K_2) \cdot (-x^{-2})= 0 | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | :$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | + | :$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {3}/{2} \cdot x^{-5/2} = K_2 \cdot |
x^{-7/2} \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | x^{-7/2} \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | ||
| − | x_{\rm max} = | + | x_{\rm max} = {2}/{3} \cdot K_2 = \frac{{a}_{\rm \star}^2}{3 \pi} |
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | *This results in the following for $60 \ \rm dB$ cable attenuation $({a}_{\rm \star} \approx 6.9 \ \rm Np)$: | |
| − | :$$x_{\rm max} = { t_{\rm max}}/{ T}= { 6.9^2}/{(3\pi)}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ \approx 5 }\hspace{0.05cm} | + | :$$x_{\rm max} = { t_{\rm max}}/{ T}= { 6.9^2}/{(3\pi)}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ \approx 5 }\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ |
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
| − | + | '''(3)''' Substituting the result into the given equation, we get (for simplicity, we use "${a}$"instead of "${a}_{\rm \star}$"): | |
| − | :$$h_{\rm K}(t_{\rm max}) = \frac{1}{T} \cdot \frac{ { | + | :$$h_{\rm K}(t_{\rm max}) = \frac{1}{T} \cdot \frac{ {a}}{ \sqrt{2 \pi^2 \cdot {{a}^6}/{(3\pi)^3}}}\hspace{0.1cm} \cdot |
| − | {\rm exp} \left[ - \frac{{ | + | {\rm exp} \left[ - \frac{{a}^2}{2\pi} \cdot |
| − | \frac{3\pi}{{\rm a}^2}\hspace{0.1cm}\right] | + | \frac{3\pi}{{\rm a}^2}\hspace{0.1cm}\right] |
| − | = \frac{1}{T} \cdot \frac{1}{{ | + | = \frac{1}{T} \cdot \frac{1}{{a}^2}\cdot |
\sqrt{\frac{27 \pi | \sqrt{\frac{27 \pi | ||
| − | }{2}} \cdot {\rm e}^{-3/2} \approx \frac{1}{T} \cdot \frac{1.453}{{ | + | }{2}} \cdot {\rm e}^{-3/2} \approx \frac{1}{T} \cdot \frac{1.453}{{a}^2} |
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | *With $a = 6.9$ we obtain the final result: | |
| − | :$${\rm Max}[h_{\rm K}(t)] = \frac{1.453}{{6.9\,}^2} \cdot {1}/{T}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{\approx 0.03 \cdot {1}/{T}} | + | :$${\rm Max}\,[h_{\rm K}(t)] = \frac{1.453}{{6.9\,}^2} \cdot {1}/{T}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{\approx 0.03 \cdot {1}/{T}} |
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | :$$\frac{ { | + | '''(4)''' Using the result from '''(3)''' , the appropriate equation of determination is: |
| − | \hspace{0.15cm}{= 0.0015 \cdot {1}/{T}} | + | :$$\frac{ {a}/T}{ \sqrt{2 \pi^2 \cdot (t_{5\%}/T)^3}}= 0.05 \cdot 0.03 {1}/{T} |
| − | + | \hspace{0.15cm}{= 0.0015 \cdot {1}/{T}} | |
| + | \hspace{0.2cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.2cm} (t_{5\%}/T)^{3/2} = \frac{a}{\sqrt{2} \cdot \pi \cdot | ||
0.0015}\approx 1036 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow | 0.0015}\approx 1036 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow | ||
\hspace{0.3cm} | \hspace{0.3cm} | ||
\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{t_{5\%}/T \approx 103.5} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{t_{5\%}/T \approx 103.5} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | *This value is a bit too large, because the second term ${\rm e}^{-0.05}\approx 0.95$ was neglected. | |
| + | *The exact calculation gives $t_{\rm 5\%}/T \approx 97$. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| − | + | '''(5)''' <u>The second solution</u> is correct: | |
| + | *In general: | ||
:$$g_r(t) = g_s(t) \star h_{\rm K}(t) = s_0 \cdot | :$$g_r(t) = g_s(t) \star h_{\rm K}(t) = s_0 \cdot | ||
| − | \ | + | \int_{t-T/2}^{t+T/2} h_{\rm K}(\tau) \,{\rm d} \tau .$$ |
| − | + | *Since the channel pulse response $h_{\rm K}(t)$ changes only insignificantly within a symbol duration, it can also be written: | |
| − | :$$g_r(t) = h_{\rm K}(t) \cdot s_0 \cdot T .$$ | + | :$$g_r(t) = h_{\rm K}(t) \cdot s_0 \cdot T.$$ |
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Linear and Time-Invariant Systems: Exercises|^4.2 Coaxial Cable^]] |
Latest revision as of 10:42, 18 November 2021
The frequency response of a coaxial cable (German: "Koaxialkabel" ⇒ subscipt "K") of length $l$ can be represented by the following formula:
- $$H_{\rm K}(f) = {\rm e}^{- \alpha_0 \hspace{0.05cm} \cdot \hspace{0.05cm} l} \cdot {\rm e}^{- (\alpha_1 + {\rm j} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm} \beta_1) \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot f \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}l} \cdot {\rm e}^{- (\alpha_2 + {\rm j} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm} \beta_2) \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \sqrt{f} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}l} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The first term of this equation is due to the ohmic losses, the second term to the transverse losses. Dominant, however, is the skin effect, which is expressed by the third term.
With the coefficients valid for the "standard coaxial cable" $\text{(2.6 mm}$ core diameter, $\text{9.5 mm}$ outer diameter$)$
- $$\alpha_2 = 0.2722 \hspace{0.15cm}\frac {\rm Np}{\rm km \cdot \sqrt{\rm MHz}} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm} \beta_2 = 0.2722 \hspace{0.15cm}\frac {\rm rad}{\rm km \cdot \sqrt{\rm MHz}}\hspace{0.05cm}$$
this frequency response can also be represented as follows:
- $$H_{\rm K}(f) \approx {\rm e}^{- 0.2722 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}l/{\rm km} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \sqrt{f/{\rm MHz}} } \cdot {\rm e}^{- {\rm j}\hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm} 0.2722 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}l/{\rm km} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \sqrt{f/{\rm MHz}}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
That means:
Attenuation curve ${a}_{\rm K}(f)$ and phase curve $b_{\rm K}(f)$ are identical except for the pseudo units "Np" and "rad", respectively.
If one defines the characteristic cable attenuation ${a}_{\rm *}$ at half the bit rate $($i.e., at $R/2)$ and normalizes the frequency to $R$, one can treat digital systems of different bit rate and length uniformly:
- $${a}_{\rm \star} = {a}_{\rm K}(f ={R}/{2}) \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}H_{\rm K}(f) = {\rm e}^{- {a}_{\rm \star} \cdot \sqrt{2f/R}}\cdot {\rm e}^{- {\rm j}\hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm} {a}_{\star} \cdot \sqrt{2f/R}}\hspace{0.4cm}{\rm with}\hspace{0.2cm}{a}_{\star}\hspace{0.2cm}{\rm in}\hspace{0.2cm}{\rm Np} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The corresponding $\rm dB$ value is greater by a factor of $8.686$.
- For a binary system, $R = 1/T$ holds, so that the characteristic cable attenuation refers to the frequency $f = 1/(2T)$.
The Fourier transform of $H_{\rm K}(f)$ yields the impulse response $h_{\rm K}(t)$, which can be specified in closed-analytic form for a coaxial cable using the approximations described here. For a binary system holds:
- $$h_{\rm K}(t) = \frac{ {a}_{\rm \star}/T}{ \sqrt{2 \pi^2 \cdot (t/T)^3}}\hspace{0.1cm} \cdot {\rm e}^{ - {{a}_{\rm \star}^2}/(2 \hspace{0.05cm} \pi \cdot \hspace{0.05cm} t/T)} \hspace{0.4cm}{\rm with}\hspace{0.2cm}{a}_{\rm \star}\hspace{0.2cm}{\rm in}\hspace{0.2cm}{\rm Np} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Subtask (5) refers to the basic reception pulse $g_r(t) = g_s(t) \star h_{\rm K}(t)$, where the basic transmission pulse $g_s(t)$ is assumed to be a rectangle $($height $s_0$, duration $T)$.
Notes:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter Properties of Coaxial Cables.
- You can use the (German language) interactive SWF applet "Zeitverhalten von Kupferkabeln" ⇒ "Time behavior of copper cables" to check your results.
Questions
Solution
- $$\alpha_2 \cdot l \cdot {R}/{2} = 6.9\,\,{\rm Np} \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} l = \frac{6.9\,\,{\rm Np}}{0.2722 \,\, {\rm Np}/({\rm km \cdot \sqrt{\rm MHz}}) \cdot \sqrt{70\,\,{\rm MHz}}}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ \approx 3\,\,{\rm km}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) With the substitutions
- $$x = \frac{ t}{ T}, \hspace{0.2cm} K_1 = \frac{ {a}_{\rm \star}/T}{\sqrt{2 \pi^2 }}, \hspace{0.2cm} K_2 = \frac{ {a}_{\rm \star}^2}{2 \pi}$$
the impulse response can be described as follows:
- $$h_{\rm K}(x) = K_1 \cdot x^{-3/2}\cdot {\rm e}^{-K_2/x} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- By setting the derivative to zero:
- $$- {3}/{2} \cdot K_1 \cdot x^{-5/2}\cdot {\rm e}^{-K_2/x}+ K_1 \cdot x^{-3/2}\cdot {\rm e}^{-K_2/x}\cdot (-K_2) \cdot (-x^{-2})= 0 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {3}/{2} \cdot x^{-5/2} = K_2 \cdot x^{-7/2} \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} x_{\rm max} = {2}/{3} \cdot K_2 = \frac{{a}_{\rm \star}^2}{3 \pi} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- This results in the following for $60 \ \rm dB$ cable attenuation $({a}_{\rm \star} \approx 6.9 \ \rm Np)$:
- $$x_{\rm max} = { t_{\rm max}}/{ T}= { 6.9^2}/{(3\pi)}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ \approx 5 }\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(3) Substituting the result into the given equation, we get (for simplicity, we use "${a}$"instead of "${a}_{\rm \star}$"):
- $$h_{\rm K}(t_{\rm max}) = \frac{1}{T} \cdot \frac{ {a}}{ \sqrt{2 \pi^2 \cdot {{a}^6}/{(3\pi)^3}}}\hspace{0.1cm} \cdot {\rm exp} \left[ - \frac{{a}^2}{2\pi} \cdot \frac{3\pi}{{\rm a}^2}\hspace{0.1cm}\right] = \frac{1}{T} \cdot \frac{1}{{a}^2}\cdot \sqrt{\frac{27 \pi }{2}} \cdot {\rm e}^{-3/2} \approx \frac{1}{T} \cdot \frac{1.453}{{a}^2} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- With $a = 6.9$ we obtain the final result:
- $${\rm Max}\,[h_{\rm K}(t)] = \frac{1.453}{{6.9\,}^2} \cdot {1}/{T}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{\approx 0.03 \cdot {1}/{T}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(4) Using the result from (3) , the appropriate equation of determination is:
- $$\frac{ {a}/T}{ \sqrt{2 \pi^2 \cdot (t_{5\%}/T)^3}}= 0.05 \cdot 0.03 {1}/{T} \hspace{0.15cm}{= 0.0015 \cdot {1}/{T}} \hspace{0.2cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.2cm} (t_{5\%}/T)^{3/2} = \frac{a}{\sqrt{2} \cdot \pi \cdot 0.0015}\approx 1036 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{t_{5\%}/T \approx 103.5} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- This value is a bit too large, because the second term ${\rm e}^{-0.05}\approx 0.95$ was neglected.
- The exact calculation gives $t_{\rm 5\%}/T \approx 97$.
(5) The second solution is correct:
- In general:
- $$g_r(t) = g_s(t) \star h_{\rm K}(t) = s_0 \cdot \int_{t-T/2}^{t+T/2} h_{\rm K}(\tau) \,{\rm d} \tau .$$
- Since the channel pulse response $h_{\rm K}(t)$ changes only insignificantly within a symbol duration, it can also be written:
- $$g_r(t) = h_{\rm K}(t) \cdot s_0 \cdot T.$$