Exercise 4.6Z: Basics of Product Codes
From LNTwww
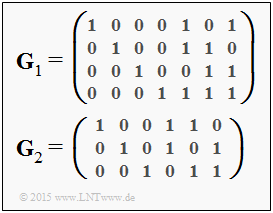
We consider here a product code according to the description on page "Basic structure of a Product Code". The two component codes $\mathcal{C}_1$ and $\mathcal{C}_2$ are defined by the generator matrices $\mathbf{G}_1$ and $\mathbf{G}_2$ given on the right.
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter "Basics of a Product Code".
- Reference is made in particular to the page "Basic structure of a product code".
- The two component codes are also covered in the "Exercise 4.6" .
Questions
Solution
(1) Correct are statements 1, 2 and 4:
- The number of rows of the generator matrix $\mathbf{G}_1$ indicates the length of the information block ⇒ $k = 4$.
- The codeword length is equal to the number of columns ⇒ $n=4$ ⇒ Code rate $R = k/n = 4/7$.
- The code is systematic because the generator matrix $\mathbf{G}_1$ starts with a $4 × 4$ diagonal matrix.
- This is a "normal" Hamming code.
- For this, with the codeword length $n$ and the number of check bits ⇒ $m = n - k$, the relation $n = 2^m - 1$ holds.
- In the present case, this is the (normal) Hamming code $\rm (7, \ 4, \ 3)$.
- The last parameter in this code label specifies the minimum distance ⇒ $d_{\rm min} = 3$.
(2) Correct statements 2, 3 and 4:
- This is a truncated Hamming code with parameter $n = 6, \ k = 3$ and $d_{\rm min} = 3$, also in systematic form.
- The code rate is $R = 1/2$.
(3) The basic structure of the product code is shown on the "Basic structure of a Product Code" page.
- You can see the information block with $k = k_1 \cdot k_2 = 4 \cdot 3 \ \underline{= 12}$,
- The codeword length is the total number of all bits: $n = n_1 \cdot n_2 = 7 \cdot 6 \ \underline{= 42}$.
- The code rate is thus given by $R = k/n = 12/42 = 2/7$.
- Or: $R = R_1 \cdot R_2 = 4/7 \cdot 1/2 \ \underline{= 2/7} \approx 0.289$.
- The free distance is $d = d_1 \cdot d_2 = 3 \cdot 3 \ \underline{= 9}$.