Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 5.7Z: Matched Filter - All Gaussian"
From LNTwww
m (Guenter verschob die Seite 5.7Z Mateched-Filter - alles gaussisch nach 5.7Z Matched-Filter - alles gaussisch) |
|||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Matched_Filter |
}} | }} | ||
| − | [[File:P_ID578__Sto_Z_5_7.png|right|]] | + | [[File:P_ID578__Sto_Z_5_7.png|right|frame|Given Gaussian pulse]] |
| − | + | At the input of a reception filter there is | |
| − | :$$g(t) = g_0 \cdot {\rm{e}}^{ - {\rm{\pi }}\left( {t/\Delta t_g } \right)^2 } .$ | + | *a Gaussian pulse $g(t)$ with amplitude $g_0$ and equivalent duration $\Delta t_g = 1\hspace{0.08cm} \rm ms$, |
| + | :$$g(t) = g_0 \cdot {\rm{e}}^{ - {\rm{\pi }}\left( {t/\Delta t_g } \right)^2 } ,$$ | ||
| + | *superimposed by white Gaussian noise with power density $N_0 = 10^{-4}\hspace{0.08cm} \rm V^2 \hspace{-0.1cm}/Hz$. | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | The pulse energy is $E_g = 0.01\hspace{0.08cm} \rm V^2 s$. Let the reception filter be an acausal Gaussian low-pass filter with frequency response | ||
:$$H_{\rm E} (f) = {\rm{e}}^{ - {\rm{\pi }}\left( {f/\Delta f_{\rm E} } \right)^2 } .$$ | :$$H_{\rm E} (f) = {\rm{e}}^{ - {\rm{\pi }}\left( {f/\Delta f_{\rm E} } \right)^2 } .$$ | ||
| − | + | The associated impulse response is thus: | |
:$$h_{\rm E} (t) = \Delta f_{\rm E} \cdot {\rm{e}}^{ - {\rm{\pi }}\left( {\Delta f_{\rm E} \hspace{0.03cm}\cdot \hspace{0.03cm}t} \right)^2 } .$$ | :$$h_{\rm E} (t) = \Delta f_{\rm E} \cdot {\rm{e}}^{ - {\rm{\pi }}\left( {\Delta f_{\rm E} \hspace{0.03cm}\cdot \hspace{0.03cm}t} \right)^2 } .$$ | ||
| − | + | The system-theoretical filter bandwidth $\Delta f_{\rm E}$ should be chosen so that the Gaussian low-pass filter is optimally matched to the input impulse $g(t)$. This is then referred to as a: "matched filter". | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| − | : | + | |
| + | |||
| + | Notes: | ||
| + | *The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Matched_Filter|Matched Filter]]. | ||
| + | *Use the following definite integral to solve: | ||
:$$\int_0^\infty {{\rm{e}}^{ - a^2 x^2 } {\rm{d}}x = \frac{{\sqrt {\rm{\pi }} }}{2a}} .$$ | :$$\int_0^\infty {{\rm{e}}^{ - a^2 x^2 } {\rm{d}}x = \frac{{\sqrt {\rm{\pi }} }}{2a}} .$$ | ||
| − | === | + | |
| + | |||
| + | ===Questions=== | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {Calculate the pulse amplitude. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $g_0$ | + | $g_0 \ = \ $ { 2.659 3% } $\ \rm V$ |
| − | { | + | {What is the maximum S/N ratio at the filter output in $\rm dB$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $10 | + | $10 \cdot \lg\ \rho_d(T_\text{D, opt}\hspace{-0.05cm}) \ = \ $ { 23 3% } $\ \rm dB$ |
| − | { | + | {At what filter bandwidth is this S/N ratio achieved? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $\Delta f_\text{E, opt}$ | + | $\Delta f_\text{E, opt}\ = \ $ { 1 3% } $\ \rm kHz$ |
| − | { | + | {Which of the following statements are true if the filter bandwidth $\Delta f_{\rm E}$ is smaller than calculated in subtask '''(3)'''? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + The signal component $d_{\rm S}(T_\text{D, opt}\hspace{-0.05cm})$ is smaller than with matching. |
| − | - | + | - The noise power $\sigma_d^2$ is larger than with matching. |
| − | + | + | + The S/N ratio is smaller than calculated in subtask '''(2)'''. |
| Line 47: | Line 58: | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | + | '''(1)''' For the energy of an pulse $g(t)$ applies in general, or for this example: | |
| − | :$$E_g = \int_{ - \infty }^{ + \infty } {g(t) | + | :$$E_g = \int_{ - \infty }^{ + \infty } {g^2(t) \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm{d}}t} = g^2_0 \cdot \int_{ - \infty }^{ + \infty } {{\rm{e}}^{ - 2{\rm{\pi }}\left( {t/\Delta t_g } \right)^2 } \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm{d}}t} .$$ |
| − | + | *This equation can be transformed as follows: | |
:$$E_g = 2 \cdot g_0 ^2 \cdot \int_0^\infty {{\rm{e}}^{ - \left( {\sqrt {2 \rm{\pi }} /\Delta t_g } \right)^2 \cdot \hspace{0.05cm} t^2 }\hspace{0.1cm} {\rm{d}}t} .$$ | :$$E_g = 2 \cdot g_0 ^2 \cdot \int_0^\infty {{\rm{e}}^{ - \left( {\sqrt {2 \rm{\pi }} /\Delta t_g } \right)^2 \cdot \hspace{0.05cm} t^2 }\hspace{0.1cm} {\rm{d}}t} .$$ | ||
| − | + | *With $a = (2\pi)^{1/2}\cdot 1/\Delta t_g$ and the formula given, the following relationship holds: | |
:$$E_g = 2 \cdot g_0 ^2 \cdot \frac{{\sqrt {\rm{\pi }} }}{2a} = \sqrt 2 \cdot g_0 ^2 \cdot \Delta t_g .$$ | :$$E_g = 2 \cdot g_0 ^2 \cdot \frac{{\sqrt {\rm{\pi }} }}{2a} = \sqrt 2 \cdot g_0 ^2 \cdot \Delta t_g .$$ | ||
| − | + | *Solving this equation for $g_0$, the final result is: | |
:$$g_0 = \sqrt {\frac{E_g }{\Delta t_g \cdot \sqrt 2 }} = \sqrt {\frac{{0.01\;{\rm{V}}^{\rm{2}} {\rm{s}}}}{{0.001\;{\rm{s}} \cdot 1.414}}} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline { = 2.659\;{\rm{V}}}.$$ | :$$g_0 = \sqrt {\frac{E_g }{\Delta t_g \cdot \sqrt 2 }} = \sqrt {\frac{{0.01\;{\rm{V}}^{\rm{2}} {\rm{s}}}}{{0.001\;{\rm{s}} \cdot 1.414}}} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline { = 2.659\;{\rm{V}}}.$$ | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''(2)''' Assuming a matched filter, the S/N ratio at the output is: | ||
:$$\rho _{d} ( {T_{{\rm{D,}}\,{\rm{opt}}} } ) = \frac{2 \cdot E_g }{N_0 } = \frac{{2 \cdot 10^{ - 2} \;{\rm{V}}^{\rm{2}} {\rm{s}}}}{{10^{ - 4} \;{\rm{V}}^{\rm{2}} {\rm{/Hz}}}} = 200.$$ | :$$\rho _{d} ( {T_{{\rm{D,}}\,{\rm{opt}}} } ) = \frac{2 \cdot E_g }{N_0 } = \frac{{2 \cdot 10^{ - 2} \;{\rm{V}}^{\rm{2}} {\rm{s}}}}{{10^{ - 4} \;{\rm{V}}^{\rm{2}} {\rm{/Hz}}}} = 200.$$ | ||
| − | : | + | *In logarithmic representation, the following result is obtained: |
:$$10 \cdot \lg \rho _{d} ( {T_{{\rm{D,}}\,{\rm{opt}}} } ) = 10 \cdot \lg \left( {200} \right) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 23\;{\rm{dB}}}.$$ | :$$10 \cdot \lg \rho _{d} ( {T_{{\rm{D,}}\,{\rm{opt}}} } ) = 10 \cdot \lg \left( {200} \right) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 23\;{\rm{dB}}}.$$ | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''(3)''' A comparison between the input pulse and the filter frequency response shows that when $\Delta f_{\rm E} = 1/\Delta t_g$ is fitted, it must hold: | ||
:$$\Delta f_{{\rm{E,}}\,{\rm{opt}}} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline { = 1\;{\rm{kHz}}}.$$ | :$$\Delta f_{{\rm{E,}}\,{\rm{opt}}} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline { = 1\;{\rm{kHz}}}.$$ | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''(4)''' <u>Solutions 1 and 3</u> are correct: | ||
| + | *A smaller filter bandwidth is favorable with respect to interference, | ||
| + | *but unfavorable with respect to the useful signal. | ||
| + | *The negative influence (smaller useful signal) outweighs the positive influence (less noise). | ||
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Theory of Stochastic Signals: Exercises|^5.4 Matched Filter^]] |
Latest revision as of 15:56, 21 February 2022
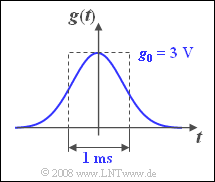
At the input of a reception filter there is
- a Gaussian pulse $g(t)$ with amplitude $g_0$ and equivalent duration $\Delta t_g = 1\hspace{0.08cm} \rm ms$,
- $$g(t) = g_0 \cdot {\rm{e}}^{ - {\rm{\pi }}\left( {t/\Delta t_g } \right)^2 } ,$$
- superimposed by white Gaussian noise with power density $N_0 = 10^{-4}\hspace{0.08cm} \rm V^2 \hspace{-0.1cm}/Hz$.
The pulse energy is $E_g = 0.01\hspace{0.08cm} \rm V^2 s$. Let the reception filter be an acausal Gaussian low-pass filter with frequency response
- $$H_{\rm E} (f) = {\rm{e}}^{ - {\rm{\pi }}\left( {f/\Delta f_{\rm E} } \right)^2 } .$$
The associated impulse response is thus:
- $$h_{\rm E} (t) = \Delta f_{\rm E} \cdot {\rm{e}}^{ - {\rm{\pi }}\left( {\Delta f_{\rm E} \hspace{0.03cm}\cdot \hspace{0.03cm}t} \right)^2 } .$$
The system-theoretical filter bandwidth $\Delta f_{\rm E}$ should be chosen so that the Gaussian low-pass filter is optimally matched to the input impulse $g(t)$. This is then referred to as a: "matched filter".
Notes:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter Matched Filter.
- Use the following definite integral to solve:
- $$\int_0^\infty {{\rm{e}}^{ - a^2 x^2 } {\rm{d}}x = \frac{{\sqrt {\rm{\pi }} }}{2a}} .$$
Questions
Solution
(1) For the energy of an pulse $g(t)$ applies in general, or for this example:
- $$E_g = \int_{ - \infty }^{ + \infty } {g^2(t) \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm{d}}t} = g^2_0 \cdot \int_{ - \infty }^{ + \infty } {{\rm{e}}^{ - 2{\rm{\pi }}\left( {t/\Delta t_g } \right)^2 } \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm{d}}t} .$$
- This equation can be transformed as follows:
- $$E_g = 2 \cdot g_0 ^2 \cdot \int_0^\infty {{\rm{e}}^{ - \left( {\sqrt {2 \rm{\pi }} /\Delta t_g } \right)^2 \cdot \hspace{0.05cm} t^2 }\hspace{0.1cm} {\rm{d}}t} .$$
- With $a = (2\pi)^{1/2}\cdot 1/\Delta t_g$ and the formula given, the following relationship holds:
- $$E_g = 2 \cdot g_0 ^2 \cdot \frac{{\sqrt {\rm{\pi }} }}{2a} = \sqrt 2 \cdot g_0 ^2 \cdot \Delta t_g .$$
- Solving this equation for $g_0$, the final result is:
- $$g_0 = \sqrt {\frac{E_g }{\Delta t_g \cdot \sqrt 2 }} = \sqrt {\frac{{0.01\;{\rm{V}}^{\rm{2}} {\rm{s}}}}{{0.001\;{\rm{s}} \cdot 1.414}}} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline { = 2.659\;{\rm{V}}}.$$
(2) Assuming a matched filter, the S/N ratio at the output is:
- $$\rho _{d} ( {T_{{\rm{D,}}\,{\rm{opt}}} } ) = \frac{2 \cdot E_g }{N_0 } = \frac{{2 \cdot 10^{ - 2} \;{\rm{V}}^{\rm{2}} {\rm{s}}}}{{10^{ - 4} \;{\rm{V}}^{\rm{2}} {\rm{/Hz}}}} = 200.$$
- In logarithmic representation, the following result is obtained:
- $$10 \cdot \lg \rho _{d} ( {T_{{\rm{D,}}\,{\rm{opt}}} } ) = 10 \cdot \lg \left( {200} \right) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 23\;{\rm{dB}}}.$$
(3) A comparison between the input pulse and the filter frequency response shows that when $\Delta f_{\rm E} = 1/\Delta t_g$ is fitted, it must hold:
- $$\Delta f_{{\rm{E,}}\,{\rm{opt}}} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline { = 1\;{\rm{kHz}}}.$$
(4) Solutions 1 and 3 are correct:
- A smaller filter bandwidth is favorable with respect to interference,
- but unfavorable with respect to the useful signal.
- The negative influence (smaller useful signal) outweighs the positive influence (less noise).