Difference between revisions of "Channel Coding/Reed-Solomon Decoding for the Erasure Channel"
m (Text replacement - "„" to """) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Header | {{Header | ||
| − | |Untermenü=Reed–Solomon–Codes | + | |Untermenü=Reed–Solomon–Codes and Their Decoding |
| − | |Vorherige Seite=Definition | + | |Vorherige Seite=Definition and Properties of Reed-Solomon Codes |
| − | |Nächste Seite= | + | |Nächste Seite=Error Correction According to Reed-Solomon Coding |
}} | }} | ||
| − | == | + | == Block diagram and requirements for RS fault detection == |
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | + | In the [[Channel_Coding/Decoding_of_Linear_Block_Codes#Decoding_at_the_Binary_Erasure_Channel|"Decoding at the Binary Erasure Channel"]] chapter we showed for the binary block codes which calculations the decoder has to perform to decode from an incomplete received word $\underline{y}$ the transmitted code word $\underline{x}$ in the best possible way. In the Reed–Solomon chapter we renamed $\underline{x}$ to $\underline{c}$ . | |
| − | + | This is also based on the [[Channel_Coding/Channel_Models_and_Decision_Structures#Binary_Erasure_Channel_.E2.80.93_BEC| "BEC Channel Model]"] (<i>Binary Erasure Channel</i> ), which marks an uncertain bit as <i>erasure</i> $\rm E$ . In contrast to [[Channel_Coding/Signal_classification#Binary_Symmetric_Channel_.E2.80.93_BSC| BSC]] (<i>Binary Symmetric Channel</i> ) and [[Channel_Coding/Channel_Models_and_Decision_Structures#AWGN_channel_at_Binary_Input| AWGN]] (<i>Additive White Gaussian Noise</i> ) bit errors $(y_i ≠ c_i)$ are excluded here. Each bit of a received word | |
| − | * | + | *thus matches the corresponding bit of the code word $(y_i = c_i)$, or |
| − | * | + | *is already marked as a cancellation $(y_i = \rm E)$.<br> |
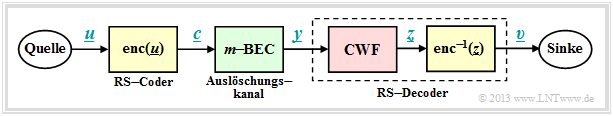
| − | [[File:P ID2544 KC T 2 4 S1 v2.png|center|frame| | + | [[File:P ID2544 KC T 2 4 S1 v2.png|center|frame|Transmission system with Reed-Solomon coding/decoding and erasure channel|class=fit]] |
| − | + | The diagram shows the block diagram, which is slightly different from the model in chapter [[Channel_Coding/Decoding_of_Linear_Block_Codes#Block_diagram_and_requirements|"Decoding linear block codes"]]: | |
| − | * | + | *Since Reed–Solomon codes are linear block codes, information word $\underline{u}$ and code word $\underline{c}$ are also related here via the generator matrix $\boldsymbol{\rm G}$ and the following equation: |
::<math>\underline {c} = {\rm enc}(\underline {u}) = \underline {u} \cdot { \boldsymbol{\rm G}} | ::<math>\underline {c} = {\rm enc}(\underline {u}) = \underline {u} \cdot { \boldsymbol{\rm G}} | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.</math> | \hspace{0.05cm}.</math> | ||
| − | * | + | *For the individual symbols of information block and code word, Reed–Solomon coding applies: |
::<math>u_i \in {\rm GF}(q)\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm}c_i \in {\rm GF}(q)\hspace{0.3cm}{\rm mit}\hspace{0.3cm} q = n+1 = 2^m | ::<math>u_i \in {\rm GF}(q)\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm}c_i \in {\rm GF}(q)\hspace{0.3cm}{\rm mit}\hspace{0.3cm} q = n+1 = 2^m | ||
\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} n = 2^m - 1\hspace{0.05cm}. </math> | \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} n = 2^m - 1\hspace{0.05cm}. </math> | ||
| − | * | + | *Each code symbol $c_i$ is thus represented by $m ≥ 2$ binary symbols (bits). For comparison: For the binary block codes $q=2$, $m=1$ and the code word length $n$ is freely selectable.<br> |
| − | * | + | *When coding at symbol level, the BEC model must be extended to $m$ BEC model. With probability $\lambda_m ≈ m \cdot\lambda$ a code symbol $c_i$ is erased $(y_i = \rm E)$ and it holds ${\rm Pr}(y_i = c_i) = 1 - \lambda_m$. For more details on the conversion of the two models, see the [[Aufgaben:Exercise_2.11Z:_Erasure_Channel_for_Symbols|"Exercise 2.11Z"]].<br> |
| − | + | In the following, we deal only with the block <i>code wordfinder</i> (CWF), which extracts from the received vector $\underline{y}$ the vector $\underline{z} ∈ \mathcal{C}_{\rm RS}$ recovering: | |
| − | * | + | *If the number $e$ of extinctions in the vector $\underline{y}$ is sufficiently small, the entire code word can be found with certainty $(\underline{z}=\underline{c})$ .<br> |
| − | * | + | *If too many symbols of the received word $\underline{y}$ are erased, the decoder reports that this word cannot be decoded and may send the sequence again.<br><br> |
| − | + | In the case of the erasure channel ($m$ BEC) unlike the $m$ BSC, which is described in the chapter [[Channel_Coding/Error_Correction_According_to_Reed-Solomon_Coding|"Error correction after Reed-Solomon coding"]] applies, an error decision $(\underline{z} \ne\underline{c})$ is excluded ⇒ Block error probability ${\rm Pr}(\underline{z}\ne\underline{c}) = 0$ ⇒ ${\rm Pr}(\underline{v}\ne\underline{u}) = 0$. | |
| − | * | + | *The reconstructed information word results according to the block diagram (yellow background) to $\underline{v} = {\rm enc}^{-1}(\underline{z})$. |
| − | * | + | *With the generator matrix $\boldsymbol{\rm G}$ can also be written for this: |
::<math>\underline {c} = \underline {u} \cdot { \boldsymbol{\rm G}} | ::<math>\underline {c} = \underline {u} \cdot { \boldsymbol{\rm G}} | ||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}. </math> | \hspace{0.05cm}. </math> | ||
| − | == | + | == Procedure using the RSC as an example (7, 3, 5)<sub>8</sub> == |
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | + | In order to be able to represent the Reed–Solomon decoding at the extinction channel as simply as possible, we start from a concrete task: | |
| − | + | A Reed–Solomon code with parameters $n= 7$, $k= 3$ and $q= 2^3 = 8$ is used. | |
| − | + | Thus, for the information word $\underline{u}$ and the code word $\underline{c}$: | |
::<math>\underline {u} = (u_0, u_1, u_2) \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.15cm} | ::<math>\underline {u} = (u_0, u_1, u_2) \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.15cm} | ||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
\hspace{0.05cm},</math> | \hspace{0.05cm},</math> | ||
| − | + | and the parity-check matrix $\boldsymbol{\rm H}$ is: | |
::<math>{ \boldsymbol{\rm H}} = | ::<math>{ \boldsymbol{\rm H}} = | ||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
\end{pmatrix}\hspace{0.05cm}. </math> | \end{pmatrix}\hspace{0.05cm}. </math> | ||
| − | + | For example, the received vector $\underline {y} = (\alpha, \hspace{0.03cm} 1, \hspace{0.03cm}{\rm E}, \hspace{0.03cm}{\rm E}, \hspace{0.03cm}\alpha^2,{\rm E}, \hspace{0.03cm}\alpha^5)$ is assumed here. Then holds: | |
| − | * | + | *Since the erasure channel produces no errors, four of the code symbols are known to the decoder: |
::<math>c_0 = \alpha^1 \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm} | ::<math>c_0 = \alpha^1 \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm} | ||
| Line 81: | Line 81: | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.</math> | \hspace{0.05cm}.</math> | ||
| − | * | + | *It is obvious that the block "code word finder" – in the block diagram is denoted by '''CWF'''' a vector of the form $\underline {z} = (c_0, \hspace{0.03cm}c_1, \hspace{0.03cm}z_2, \hspace{0.03cm}z_3,\hspace{0.03cm}c_4,\hspace{0.03cm}z_5,\hspace{0.03cm}c_6)$ is to be supplied with $z_2,\hspace{0.03cm}z_3,\hspace{0.03cm}z_5 \in \rm GF(2^3)$.<br> |
| − | * | + | *But since the codeword $\underline {z}$ found by the decoder is also supposed to be a valid Reed–Solomon code word ⇒ $\underline {z} ∈ \mathcal{C}_{\rm RS}$, must hold as well: |
::<math>{ \boldsymbol{\rm H}} \cdot \underline {z}^{\rm T} = \underline {0}^{\rm T} \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | ::<math>{ \boldsymbol{\rm H}} \cdot \underline {z}^{\rm T} = \underline {0}^{\rm T} \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | ||
| Line 108: | Line 108: | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}. </math> | \hspace{0.05cm}. </math> | ||
| − | * | + | *This gives four equations for the unknowns $z_2$, $z_3$ and $z_5$. With unique solution – and only with such – the decoding is successful and one can then say with certainty that indeed $\underline {c} = \underline {z} $ was sent.<br><br> |
| − | == | + | == Solution of the matrix equations using the example of the RSC (7, 3, 5)<sub>8</sub> == |
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | + | Thus, it is necessary to find the admissible codeword $\underline {z}$ that satisfies the determination equation $\boldsymbol{\rm H} \cdot \underline {z}^{\rm T} $ satisfies. For convenience, we split the vector $\underline {z}$ into two partial vectors, viz. | |
| − | * | + | *the vector $\underline {z}_{\rm E} = (z_2, z_3, z_5)$ of the erased symbols (index "$\rm E$" for <i>erasures</i> ),<br> |
| − | * | + | *the vector $\underline {z}_{\rm K} = (c_0, c_1,c_4, c_6)$ of known symbols (index "$\rm K$" for <i>correct</i> ).<br><br> |
| − | + | With the associated partial matrices (each with $n-k = 4$ rows) | |
::<math>{ \boldsymbol{\rm H}}_{\rm E} = | ::<math>{ \boldsymbol{\rm H}}_{\rm E} = | ||
| Line 136: | Line 136: | ||
\end{pmatrix}</math> | \end{pmatrix}</math> | ||
| − | + | the equation of determination is thus: | |
::<math>{ \boldsymbol{\rm H}}_{\rm E} \cdot \underline {z}_{\rm E}^{\rm T} + | ::<math>{ \boldsymbol{\rm H}}_{\rm E} \cdot \underline {z}_{\rm E}^{\rm T} + | ||
| Line 144: | Line 144: | ||
{ \boldsymbol{\rm H}}_{\rm K} \cdot \underline {z}_{\rm K}^{\rm T}\hspace{0.05cm}. </math> | { \boldsymbol{\rm H}}_{\rm K} \cdot \underline {z}_{\rm K}^{\rm T}\hspace{0.05cm}. </math> | ||
| − | * | + | *Since for all elements $z_i ∈ {\rm GF}(2^m)$ the [[Channel_Coding/Some_Basics_of_Algebra#Definition_of_a_Galois_field |"additive inverse"]] ${\rm Inv_A}(z_i)= (- z_i) = z_i$ holds in the same way |
::<math>{ \boldsymbol{\rm H}}_{\rm E} \cdot \underline {z}_{\rm E}^{\rm T} = | ::<math>{ \boldsymbol{\rm H}}_{\rm E} \cdot \underline {z}_{\rm E}^{\rm T} = | ||
| Line 168: | Line 168: | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.</math> | \hspace{0.05cm}.</math> | ||
| − | * | + | *The right-hand side of the equation results for the considered example ⇒ $\underline {z}_{\rm K} = (c_0, c_1,c_4, c_6)$ and is based on the polynomial $p(x) = x^3 + x +1$, which leads to the following powers $($in $\alpha)$ : |
::<math>\alpha^3 =\alpha + 1\hspace{0.05cm}, | ::<math>\alpha^3 =\alpha + 1\hspace{0.05cm}, | ||
| Line 179: | Line 179: | ||
\hspace{0.3cm} \alpha^{10} = \alpha^3 = \alpha + 1\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.1cm} \text{...}</math> | \hspace{0.3cm} \alpha^{10} = \alpha^3 = \alpha + 1\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.1cm} \text{...}</math> | ||
| − | * | + | *Thus, the matrix equation for determining the vector we are looking for $\underline {z}_{\rm E}$: |
::<math>\begin{pmatrix} | ::<math>\begin{pmatrix} | ||
| Line 200: | Line 200: | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}. </math> | \hspace{0.05cm}. </math> | ||
| − | * | + | *Solving this matrix equation (most easily by program), we get |
::<math>z_2 = \alpha^2\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.25cm}z_3 = \alpha^1\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.25cm}z_5 = \alpha^5 | ::<math>z_2 = \alpha^2\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.25cm}z_3 = \alpha^1\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.25cm}z_5 = \alpha^5 | ||
| Line 206: | Line 206: | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.</math> | \hspace{0.05cm}.</math> | ||
| − | * | + | *The result is correct, as the following control calculations show: |
::<math>\alpha^2 \cdot \alpha^2 + \alpha^3 \cdot \alpha^1 + \alpha^5 \cdot \alpha^5 = | ::<math>\alpha^2 \cdot \alpha^2 + \alpha^3 \cdot \alpha^1 + \alpha^5 \cdot \alpha^5 = | ||
| Line 217: | Line 217: | ||
(\alpha + 1) + (\alpha^2 + 1) + (\alpha^2 + \alpha) = 0\hspace{0.05cm}.</math> | (\alpha + 1) + (\alpha^2 + 1) + (\alpha^2 + \alpha) = 0\hspace{0.05cm}.</math> | ||
| − | * | + | *The corresponding information word is obtained with the [[Channel_Coding/General_Description_of_Linear_Block_Codes#Code_definition_by_the_generator_matrix| "Generator Matrix"]] $\boldsymbol{\rm G}$ to $\underline {v} = \underline {z} \cdot \boldsymbol{\rm G}^{\rm T} = (\alpha^1,\hspace{0.05cm}1,\hspace{0.05cm}\alpha^3)$.<br> |
| − | == | + | == Exercises for the chapter == |
<br> | <br> | ||
[[Aufgaben:2.11_RS–Decodierung_nach_„Erasures”|Aufgabe 2.11: RS–Decodierung nach „Erasures”]] | [[Aufgaben:2.11_RS–Decodierung_nach_„Erasures”|Aufgabe 2.11: RS–Decodierung nach „Erasures”]] | ||
Revision as of 22:36, 3 September 2022
Contents
Block diagram and requirements for RS fault detection
In the "Decoding at the Binary Erasure Channel" chapter we showed for the binary block codes which calculations the decoder has to perform to decode from an incomplete received word $\underline{y}$ the transmitted code word $\underline{x}$ in the best possible way. In the Reed–Solomon chapter we renamed $\underline{x}$ to $\underline{c}$ .
This is also based on the [[Channel_Coding/Channel_Models_and_Decision_Structures#Binary_Erasure_Channel_.E2.80.93_BEC| "BEC Channel Model]"] (Binary Erasure Channel ), which marks an uncertain bit as erasure $\rm E$ . In contrast to BSC (Binary Symmetric Channel ) and AWGN (Additive White Gaussian Noise ) bit errors $(y_i ≠ c_i)$ are excluded here. Each bit of a received word
- thus matches the corresponding bit of the code word $(y_i = c_i)$, or
- is already marked as a cancellation $(y_i = \rm E)$.
The diagram shows the block diagram, which is slightly different from the model in chapter "Decoding linear block codes":
- Since Reed–Solomon codes are linear block codes, information word $\underline{u}$ and code word $\underline{c}$ are also related here via the generator matrix $\boldsymbol{\rm G}$ and the following equation:
- \[\underline {c} = {\rm enc}(\underline {u}) = \underline {u} \cdot { \boldsymbol{\rm G}} \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm mit} \hspace{0.3cm}\underline {u} = (u_0, u_1,\hspace{0.05cm}\text{ ... }\hspace{0.1cm}, u_i, \hspace{0.05cm}\text{ ... }\hspace{0.1cm}, u_{k-1})\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm} \underline {c} = (c_0, c_1, \hspace{0.05cm}\text{ ... }\hspace{0.1cm}, c_i, \hspace{0.05cm}\text{ ... }\hspace{0.1cm}, c_{n-1}) \hspace{0.05cm}.\]
- For the individual symbols of information block and code word, Reed–Solomon coding applies:
- \[u_i \in {\rm GF}(q)\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm}c_i \in {\rm GF}(q)\hspace{0.3cm}{\rm mit}\hspace{0.3cm} q = n+1 = 2^m \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} n = 2^m - 1\hspace{0.05cm}. \]
- Each code symbol $c_i$ is thus represented by $m ≥ 2$ binary symbols (bits). For comparison: For the binary block codes $q=2$, $m=1$ and the code word length $n$ is freely selectable.
- When coding at symbol level, the BEC model must be extended to $m$ BEC model. With probability $\lambda_m ≈ m \cdot\lambda$ a code symbol $c_i$ is erased $(y_i = \rm E)$ and it holds ${\rm Pr}(y_i = c_i) = 1 - \lambda_m$. For more details on the conversion of the two models, see the "Exercise 2.11Z".
In the following, we deal only with the block code wordfinder (CWF), which extracts from the received vector $\underline{y}$ the vector $\underline{z} ∈ \mathcal{C}_{\rm RS}$ recovering:
- If the number $e$ of extinctions in the vector $\underline{y}$ is sufficiently small, the entire code word can be found with certainty $(\underline{z}=\underline{c})$ .
- If too many symbols of the received word $\underline{y}$ are erased, the decoder reports that this word cannot be decoded and may send the sequence again.
In the case of the erasure channel ($m$ BEC) unlike the $m$ BSC, which is described in the chapter "Error correction after Reed-Solomon coding" applies, an error decision $(\underline{z} \ne\underline{c})$ is excluded ⇒ Block error probability ${\rm Pr}(\underline{z}\ne\underline{c}) = 0$ ⇒ ${\rm Pr}(\underline{v}\ne\underline{u}) = 0$.
- The reconstructed information word results according to the block diagram (yellow background) to $\underline{v} = {\rm enc}^{-1}(\underline{z})$.
- With the generator matrix $\boldsymbol{\rm G}$ can also be written for this:
- \[\underline {c} = \underline {u} \cdot { \boldsymbol{\rm G}} \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}\underline {z} = \underline {\upsilon} \cdot { \boldsymbol{\rm G}} \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}\underline {\upsilon} = \underline {z} \cdot { \boldsymbol{\rm G}}^{\rm T} \hspace{0.05cm}. \]
Procedure using the RSC as an example (7, 3, 5)8
In order to be able to represent the Reed–Solomon decoding at the extinction channel as simply as possible, we start from a concrete task:
A Reed–Solomon code with parameters $n= 7$, $k= 3$ and $q= 2^3 = 8$ is used.
Thus, for the information word $\underline{u}$ and the code word $\underline{c}$:
- \[\underline {u} = (u_0, u_1, u_2) \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.15cm} \underline {c} = (c_0, c_1, c_2,c_3,c_4,c_5,c_6)\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.15cm} u_i, c_i \in {\rm GF}(2^3) = \{0, 1, \alpha, \alpha^2, \text{...}\hspace{0.05cm} , \alpha^6\} \hspace{0.05cm},\]
and the parity-check matrix $\boldsymbol{\rm H}$ is:
- \[{ \boldsymbol{\rm H}} = \begin{pmatrix} 1 & \alpha^1 & \alpha^2 & \alpha^3 & \alpha^4 & \alpha^5 & \alpha^6\\ 1 & \alpha^2 & \alpha^4 & \alpha^6 & \alpha^1 & \alpha^{3} & \alpha^{5}\\ 1 & \alpha^3 & \alpha^6 & \alpha^2 & \alpha^{5} & \alpha^{1} & \alpha^{4}\\ 1 & \alpha^4 & \alpha^1 & \alpha^{5} & \alpha^{2} & \alpha^{6} & \alpha^{3} \end{pmatrix}\hspace{0.05cm}. \]
For example, the received vector $\underline {y} = (\alpha, \hspace{0.03cm} 1, \hspace{0.03cm}{\rm E}, \hspace{0.03cm}{\rm E}, \hspace{0.03cm}\alpha^2,{\rm E}, \hspace{0.03cm}\alpha^5)$ is assumed here. Then holds:
- Since the erasure channel produces no errors, four of the code symbols are known to the decoder:
- \[c_0 = \alpha^1 \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm} c_1 = 1 \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm} c_4 = \alpha^2 \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm} c_6 = \alpha^5 \hspace{0.05cm}.\]
- It is obvious that the block "code word finder" – in the block diagram is denoted by CWF' a vector of the form $\underline {z} = (c_0, \hspace{0.03cm}c_1, \hspace{0.03cm}z_2, \hspace{0.03cm}z_3,\hspace{0.03cm}c_4,\hspace{0.03cm}z_5,\hspace{0.03cm}c_6)$ is to be supplied with $z_2,\hspace{0.03cm}z_3,\hspace{0.03cm}z_5 \in \rm GF(2^3)$.
- But since the codeword $\underline {z}$ found by the decoder is also supposed to be a valid Reed–Solomon code word ⇒ $\underline {z} ∈ \mathcal{C}_{\rm RS}$, must hold as well:
- \[{ \boldsymbol{\rm H}} \cdot \underline {z}^{\rm T} = \underline {0}^{\rm T} \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \begin{pmatrix} 1 & \alpha^1 & \alpha^2 & \alpha^3 & \alpha^4 & \alpha^5 & \alpha^6\\ 1 & \alpha^2 & \alpha^4 & \alpha^6 & \alpha^1 & \alpha^{3} & \alpha^{5}\\ 1 & \alpha^3 & \alpha^6 & \alpha^2 & \alpha^{5} & \alpha^{1} & \alpha^{4}\\ 1 & \alpha^4 & \alpha^1 & \alpha^{5} & \alpha^{2} & \alpha^{6} & \alpha^{3} \end{pmatrix} \cdot \begin{pmatrix} c_0\\ c_1\\ z_2\\ z_3\\ c_4\\ z_5\\ c_6 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} 0\\ 0\\ 0\\ 0 \end{pmatrix} \hspace{0.05cm}. \]
- This gives four equations for the unknowns $z_2$, $z_3$ and $z_5$. With unique solution – and only with such – the decoding is successful and one can then say with certainty that indeed $\underline {c} = \underline {z} $ was sent.
Solution of the matrix equations using the example of the RSC (7, 3, 5)8
Thus, it is necessary to find the admissible codeword $\underline {z}$ that satisfies the determination equation $\boldsymbol{\rm H} \cdot \underline {z}^{\rm T} $ satisfies. For convenience, we split the vector $\underline {z}$ into two partial vectors, viz.
- the vector $\underline {z}_{\rm E} = (z_2, z_3, z_5)$ of the erased symbols (index "$\rm E$" for erasures ),
- the vector $\underline {z}_{\rm K} = (c_0, c_1,c_4, c_6)$ of known symbols (index "$\rm K$" for correct ).
With the associated partial matrices (each with $n-k = 4$ rows)
- \[{ \boldsymbol{\rm H}}_{\rm E} = \begin{pmatrix} \alpha^2 & \alpha^3 & \alpha^5 \\ \alpha^4 & \alpha^6 & \alpha^{3} \\ \alpha^6 & \alpha^2 & \alpha^{1} \\ \alpha^1 & \alpha^{5} & \alpha^{6} \end{pmatrix} \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.4cm} { \boldsymbol{\rm H}}_{\rm K} \begin{pmatrix} 1 & \alpha^1 & \alpha^4 & \alpha^6\\ 1 & \alpha^2 & \alpha^1 & \alpha^{5}\\ 1 & \alpha^3 & \alpha^{5} & \alpha^{4}\\ 1 & \alpha^4 & \alpha^{2} & \alpha^{3} \end{pmatrix}\]
the equation of determination is thus:
- \[{ \boldsymbol{\rm H}}_{\rm E} \cdot \underline {z}_{\rm E}^{\rm T} + { \boldsymbol{\rm H}}_{\rm K} \cdot \underline {z}_{\rm K}^{\rm T} = \underline {0}^{\rm T} \hspace{0.5cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.5cm} { \boldsymbol{\rm H}}_{\rm E} \cdot \underline {z}_{\rm E}^{\rm T} = - { \boldsymbol{\rm H}}_{\rm K} \cdot \underline {z}_{\rm K}^{\rm T}\hspace{0.05cm}. \]
- Since for all elements $z_i ∈ {\rm GF}(2^m)$ the "additive inverse" ${\rm Inv_A}(z_i)= (- z_i) = z_i$ holds in the same way
- \[{ \boldsymbol{\rm H}}_{\rm E} \cdot \underline {z}_{\rm E}^{\rm T} = { \boldsymbol{\rm H}}_{\rm K} \cdot \underline {z}_{\rm K}^{\rm T} = \begin{pmatrix} 1 & \alpha^1 & \alpha^4 & \alpha^6\\ 1 & \alpha^2 & \alpha^1 & \alpha^{5}\\ 1 & \alpha^3 & \alpha^{5} & \alpha^{4}\\ 1 & \alpha^4 & \alpha^{2} & \alpha^{3} \end{pmatrix} \cdot \begin{pmatrix} \alpha^1\\ 1\\ \alpha^{2}\\ \alpha^{6} \end{pmatrix} = \hspace{0.45cm}... \hspace{0.45cm}= \begin{pmatrix} \alpha^3\\ \alpha^{4}\\ \alpha^{2}\\ 0 \end{pmatrix} \hspace{0.05cm}.\]
- The right-hand side of the equation results for the considered example ⇒ $\underline {z}_{\rm K} = (c_0, c_1,c_4, c_6)$ and is based on the polynomial $p(x) = x^3 + x +1$, which leads to the following powers $($in $\alpha)$ :
- \[\alpha^3 =\alpha + 1\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm} \alpha^4 = \alpha^2 + \alpha\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm} \alpha^5 = \alpha^2 + \alpha + 1\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm} \alpha^6 = \alpha^2 + 1\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm} \alpha^7 \hspace{-0.15cm} = \hspace{-0.15cm} 1\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm} \alpha^8 = \alpha^1 \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm} \alpha^9 = \alpha^2 \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm} \alpha^{10} = \alpha^3 = \alpha + 1\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.1cm} \text{...}\]
- Thus, the matrix equation for determining the vector we are looking for $\underline {z}_{\rm E}$:
- \[\begin{pmatrix} \alpha^2 & \alpha^3 & \alpha^5 \\ \alpha^4 & \alpha^6 & \alpha^{3} \\ \alpha^6 & \alpha^2 & \alpha^{1} \\ \alpha^1 & \alpha^{5} & \alpha^{6} \end{pmatrix} \cdot \begin{pmatrix} z_2\\ z_3\\ z_5 \end{pmatrix} \stackrel{!}{=} \begin{pmatrix} \alpha^3\\ \alpha^{4}\\ \alpha^{2}\\ 0 \end{pmatrix} \hspace{0.05cm}. \]
- Solving this matrix equation (most easily by program), we get
- \[z_2 = \alpha^2\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.25cm}z_3 = \alpha^1\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.25cm}z_5 = \alpha^5 \hspace{0.5cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.5cm}\underline {z} = \left ( \hspace{0.05cm} \alpha^1, \hspace{0.05cm}1, \hspace{0.05cm}\alpha^2, \hspace{0.05cm}\alpha^1, \hspace{0.05cm}\alpha^2, \hspace{0.05cm}\alpha^5, \hspace{0.05cm}\alpha^5 \hspace{0.05cm}\right ) \hspace{0.05cm}.\]
- The result is correct, as the following control calculations show:
- \[\alpha^2 \cdot \alpha^2 + \alpha^3 \cdot \alpha^1 + \alpha^5 \cdot \alpha^5 = \alpha^4 + \alpha^4 + \alpha^{10} = \alpha^{10} = \alpha^3\hspace{0.05cm},\]
- \[\alpha^4 \cdot \alpha^2 + \alpha^6 \cdot \alpha^1 + \alpha^3 \cdot \alpha^5 = (\alpha^2 + 1) + (1) + (\alpha) = \alpha^{2} + \alpha = \alpha^4\hspace{0.05cm},\]
- \[\alpha^6 \cdot \alpha^2 + \alpha^2 \cdot \alpha^1 + \alpha^1 \cdot \alpha^5 = (\alpha) + (\alpha + 1) + (\alpha^2 + 1) = \alpha^{2} \hspace{0.05cm},\]
- \[\alpha^1 \cdot \alpha^2 + \alpha^5 \cdot \alpha^1 + \alpha^6 \cdot \alpha^5 = (\alpha + 1) + (\alpha^2 + 1) + (\alpha^2 + \alpha) = 0\hspace{0.05cm}.\]
- The corresponding information word is obtained with the "Generator Matrix" $\boldsymbol{\rm G}$ to $\underline {v} = \underline {z} \cdot \boldsymbol{\rm G}^{\rm T} = (\alpha^1,\hspace{0.05cm}1,\hspace{0.05cm}\alpha^3)$.
Exercises for the chapter
Aufgabe 2.11: RS–Decodierung nach „Erasures”
Aufgabe 2.11Z: Erasure–Kanal für Symbole