Exercise 2.07Z: Reed-Solomon Code (15, 5, 11) to Base 16
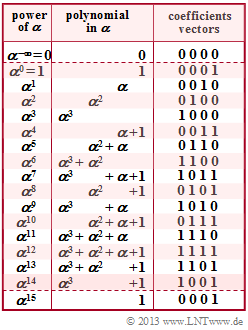
The task at hand is similar to the one in "Exercise 2.7". However, we now refer here to the Galois field $\rm GF(2^4)$, whose elements are given opposite both in powers and polynomial representations and by the coefficient vectors. Further, in $\rm GF(2^4)$:
- $$\alpha^{16} = \alpha^{1}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm} \alpha^{17} = \alpha^{2}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm} \alpha^{18} = \alpha^{3}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm}\text{...} $$
To encode the information block of length $k = 5$,
- $$\underline{u} = (u_0,\ u_1,\ u_2,\ u_3,\ u_4)\hspace{0.05cm},$$
we form the polynomial
- $$u(x) = u_0 + u_1 \cdot x + u_2 \cdot x^2 + u_3 \cdot x^3 + u_4 \cdot x^4 $$
with $u_0, \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...} \hspace{0.1cm} , u_4 ∈ \rm GF(2^4)$.
The $n = 15$ code words are then obtained by substituting into $u(x)$ the elements of $\rm GF(2^4) \ \backslash \ \{0\}$ :
- $$c_0 = u(\alpha^{0})\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm} c_1 = u(\alpha^{1})\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm} c_2 = u(\alpha^{2})\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.15cm} ... \hspace{0.15cm},\hspace{0.20cm} c_{14} = u(\alpha^{14})\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Hints: This exercise belongs to the chapter "Definition and Properties of Reed-Solomon Codes".
Questions
Solution
- $$d_{\rm min} = n - k +1 = 15 - 5 + 1 = 11 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} t = \frac{d_{\rm min}-1}{2}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {=5}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) In general, for the sought polynomial $u(x)$ with $k = 5$:
- $$u(x) = \sum_{i = 0}^{k-1} u_i \cdot x^{i}= u_0 + u_1 \cdot x + u_2 \cdot x^2 + u_3 \cdot x^3 + u_4 \cdot x^4 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- For $u_0 = \alpha^3, \ u_1 = u_2 = 0, \ u_3 = 1$ and $u_4 = \alpha^{10}$ the proposed solution 2 turns out to be correct.
(3) It holds $c_0 = u(\alpha^0) = u(1)$:
- $$c_0 = \alpha^{3} + 1 \cdot 1^3 + \alpha^{10} \cdot 1^{4} = (1000) + (0001) + (0111) = (1110)= \alpha^{11} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The correct solution is therefore the proposed solution 3.
(4) From $c_1 = u(\alpha)$ one obtains the proposed solution 4.
- $$c_1 = u(\alpha^{1}) =\alpha^{3} +1 \cdot \alpha^{3} + \alpha^{10} \cdot \alpha^{4} = \alpha^{14} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(5) For the penultimate symbol $c_{13} = u(\alpha^{13})$ holds:
- $$c_{13} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} u(\alpha^{13}) =\alpha^{3} + 1 \cdot \alpha^{13 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}3} + \alpha^{10} \cdot \alpha^{13 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}4} = \alpha^{3} + \alpha^{39}+ \alpha^{62} =\alpha^{3} + \alpha^{15 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}2} \cdot \alpha^{9}+ \alpha^{15 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}4} \cdot \alpha^{2} = \alpha^{3} + \alpha^{9} + \alpha^{2}$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}c_{13} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} (1000) + (1010) + (0100) = (0110) = \alpha^{5} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The correct solution is therefore the proposed solution 2.
(6) The last code symbol is $c_{14} = u(\alpha^{14})$:
- $$c_{14} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} u(\alpha^{14}) =\alpha^{3} + 1 \cdot \alpha^{14 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}3} + \alpha^{10} \cdot \alpha^{14 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}4} = \alpha^{3} + \alpha^{42}+ \alpha^{66} =\alpha^{3} + \alpha^{15 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}2} \cdot \alpha^{12}+ \alpha^{15 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}4} \cdot \alpha^{6} = \alpha^{3} + \alpha^{12} + \alpha^{6} =$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}c_{14} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm}(1000) + (1111) + (1100) = (1011) = \alpha^{7} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The correct solution is therefore the proposed solution 3.
(7) The code symbol "$0$" occurs just as often as all other symbols "$\alpha^i$" ⇒ proposed solution 3.