Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 3.6Z: Concepts of 3G Mobile Communications Systems"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
}} | }} | ||
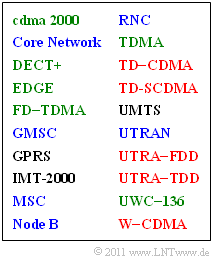
| − | [[File:P_ID2232__Mob_A_3_6.png|right|frame|Terms of the 3G mobile radio systems (except | + | [[File:P_ID2232__Mob_A_3_6.png|right|frame|Terms of the 3G mobile radio systems (except one entry )]] |
On the right there are various terms used in 3G mobile communications systems. | On the right there are various terms used in 3G mobile communications systems. | ||
| − | Third generation systems include, for example, the following standards | + | Third generation systems include, for example, the following standards: |
| − | *[[Mobile_Communications/Characteristics_of_UMTS#The_IMT-2000_standard|IMT–2000]]: This abbreviation stands for $\rm I\hspace{-0.01cm}$nternational $\hspace{0.05cm}\rm M\hspace{-0.01cm}$obile $\hspace{0.05cm}\rm T\hspace{-0.01cm}$elecommunications at the year $2000$; | + | *[[Mobile_Communications/Characteristics_of_UMTS#The_IMT-2000_standard|$\text{IMT–2000}$]]: This abbreviation stands for $\rm I\hspace{-0.01cm}$nternational $\hspace{0.05cm}\rm M\hspace{-0.01cm}$obile $\hspace{0.05cm}\rm T\hspace{-0.01cm}$elecommunications at the year $2000$; |
| − | *[[Mobile_Communications/Die_Charakteristika_von_UMTS#Systemarchitektur_und_Basiseinheiten_bei_UMTS|UMTS]]: | + | *[[Mobile_Communications/Die_Charakteristika_von_UMTS#Systemarchitektur_und_Basiseinheiten_bei_UMTS|$\text{UMTS}$]]: $\rm U\hspace{-0.01cm}$niversal $\rm M\hspace{-0.01cm}$obile $\rm T\hspace{-0.03cm}$elecommunication $\rm S\hspace{-0.01cm}$ystem. |
| − | + | Only one of the twenty listed terms is out of the ordinary. This is a system extension of [[Examples_of_Communication_Systems/General_Description_of_GSM#.23_.C3.9CBERBLICK_To_the_PRINCIPLE_.23|$\rm GSM$]]. | |
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
| − | |||
| − | * | + | |
| − | * | + | ''Notes:'' |
| + | |||
| + | *This task refers to the chapter [[Mobile_Communications/Characteristics_of_UMTS|Characteristics of UMTS]]. | ||
| + | * Reference is also made to the main chapter [[Examples_of_Communication_Systems/General_Description_of_UMTS#.23_.C3.9CBERBLICK_To_the_Fourth_Main_Chapter_.23|UMTS ]] of the book "Examples of Communication Systems". | ||
| + | |||
| Line 30: | Line 33: | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {Which of the following statements are correct? |
|type="()"} | |type="()"} | ||
| − | - | + | - IMT-2000 is a subset of UMTS. |
| − | + UMTS | + | + UMTS is a subset of IMT-2000. |
| − | { | + | {Which statements do the color assignments in the graphic allow? |
|type="()"} | |type="()"} | ||
| − | + | + | + Red entries describe system variants of UMTS. |
| − | - | + | - Green entries describe system variants of UMTS. |
| − | - | + | - Blue entries describe system variants of UMTS. |
| − | { | + | {Continue to look at the color assignment in the graphic. What is valid? |
|type="()"} | |type="()"} | ||
| − | - | + | - Red entries belong to IMT-2000, not to UMTS. |
| − | + | + | + Green entries belong to IMT-2000, not to UMTS. |
| − | { | + | {Which base units secure the transport layer in UMTS? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + The "Core Network" (CN), |
| − | - | + | - the "Gateway Mobile Switching Center" (GMSC), |
| − | - | + | - the "Mobile Switching Center" (MSC), |
| − | + | + | + the "Base Station" (for UMTS: "Node B"), |
| − | - | + | - the "Radio Network Controller" (RNC), |
| − | + | + | + the "UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network" (UTRAN). |
| − | { | + | {Which facilities handle data switching for UMTS? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - | + | - The "Core Network" (CN), |
| − | + | + | + the "Gateway Mobile Switching Center" (GMSC), |
| − | + | + | + the "Mobile Switching Center" (MSC), |
| − | - | + | - the "Base Station" (for UMTS: "Node B"), |
| − | + | + | + the "Radio Network Controller" (RNC), |
| − | + | + the "UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network" (UTRAN). | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
Revision as of 17:58, 24 January 2021
On the right there are various terms used in 3G mobile communications systems.
Third generation systems include, for example, the following standards:
- $\text{IMT–2000}$: This abbreviation stands for $\rm I\hspace{-0.01cm}$nternational $\hspace{0.05cm}\rm M\hspace{-0.01cm}$obile $\hspace{0.05cm}\rm T\hspace{-0.01cm}$elecommunications at the year $2000$;
- $\text{UMTS}$: $\rm U\hspace{-0.01cm}$niversal $\rm M\hspace{-0.01cm}$obile $\rm T\hspace{-0.03cm}$elecommunication $\rm S\hspace{-0.01cm}$ystem.
Only one of the twenty listed terms is out of the ordinary. This is a system extension of $\rm GSM$.
Notes:
- This task refers to the chapter Characteristics of UMTS.
- Reference is also made to the main chapter UMTS of the book "Examples of Communication Systems".
Fragebogen
Musterlösung
(1) Richtig ist die Aussage 2:
- Der IMT–2000–Standard beinhaltet in einer ersten Ebene W–CDMA, TD–CDMA, TDMA und FD–TDMA, wobei nur die beiden zuerst genannten Varianten gleichzeitig dem UMTS–Standard zugerechnet werden.
- Daraus folgt: UMTS ist eine Untermenge von IMT–2000, nicht umgekehrt.
(2) Alle zu UMTS gehörigen Eintragungen sind in der Tabelle rot markiert ⇒ Antwort 1:
Zu W–CDMA zählt man
- UTRA–FDD, die FDD–Komponente des europäischen UMTS–Standards,
- das amerikanische cdma 2000–System, das aber nicht zu UMTS gehört.
Zu TD–CDMA werden hinzugerechnet:
- UTRA–TDD, die TDD–Komponente von UMTS,
- das chinesische TD–SCDMA, mittlerweile in den UMTS–TDD–Standard integriert.
(3) Richtig ist der zweite Lösungsvorschlag:
Die drei Systemvarianten, die zwar zu IMT–2000 gehören, aber nicht zu UMTS, sind:
- TDMA: Hierzu zählen Weiterentwicklungen des GSM–Ablegers EDGE und des amerikanischen Pendants UWC–136,
- FD–TDMA, die Weiterentwicklung des Schnurlos–Telefonie–Standards DECT,
- der amerikanische Standard cdma 2000}.
(4) Richtig sind die Antworten 1, 4 und 6, wie man im Buch „Beispiele von Nachrichtensystemen” , Kapitel UMTS–Netzarchitektur nachlesen kann.
(5) Aus obigem Link geht auch hervor, dass hier die Antworten 2, 3 und 5 zutreffen.
Übrigens:
Der einzige Begriff in der Grafik auf der Angabenseite, der sich nicht auf UMTS bezieht, ist „GPRS” ⇒ General Packet Radio Service ist eine GSM–Erweiterung.