Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 4.6: k-parameters and alpha-parameters"
(Die Seite wurde neu angelegt: „ {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Lineare zeitinvariante Systeme/Kupfer–Doppelader }} right| :Für symmetrische Kupfer–Doppel…“) |
|||
| (31 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Linear_and_Time_Invariant_Systems/Properties_of_Balanced_Copper_Pairs |
}} | }} | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:EN_LZI_A_4_6.png|right|frame|Attenuation function per unit length, <br>valid for "copper twin wire" (0.5 mm)]] |
| − | + | For symmetrical copper twisted pairs, the following empirical formula can be found in [PW95], which is valid for the frequency range $0 \le f \le 30 \ \rm MHz$: | |
:$$\alpha_{\rm I} (f) = k_1 + k_2 \cdot (f/f_0)^{k_3} , \hspace{0.15cm} | :$$\alpha_{\rm I} (f) = k_1 + k_2 \cdot (f/f_0)^{k_3} , \hspace{0.15cm} | ||
f_0 = 1\,{\rm MHz} .$$ | f_0 = 1\,{\rm MHz} .$$ | ||
| − | + | In contrast, the attenuation function per unit length of a coaxial cable is usually given in the following form: | |
:$$\alpha_{\rm II}(f) = \alpha_0 + \alpha_1 \cdot f + \alpha_2 \cdot \sqrt {f}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$\alpha_{\rm II}(f) = \alpha_0 + \alpha_1 \cdot f + \alpha_2 \cdot \sqrt {f}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | Especially for the calculation of impulse response and rectangular response it is advantageous also for the copper twisted pairs to choose the second representation form with the cable parameters $\alpha_0$, $\alpha_1$ and $\alpha_2$ instead of the representation with $k_1$, $k_2$ and $k_3$. | |
| − | :* | + | For the conversion, one proceeds as follows: |
| − | + | * From above equations, it is obvious that the coefficient characterizing the DC signal attenuation is $\alpha_0 = k_1$. | |
| − | + | * To determine $\alpha_1$ and $\alpha_2$, it is assumed that the mean square error should be minimum in the range of a given bandwidth $B$: | |
| − | :$${\rm E}[\varepsilon^2(f)] = \ | + | :$${\rm E}\big[\varepsilon^2(f)\big] = \int_{0}^{ |
B} \left [ \alpha_{\rm II} (f) - \alpha_{\rm I} (f)\right ]^2 | B} \left [ \alpha_{\rm II} (f) - \alpha_{\rm I} (f)\right ]^2 | ||
\hspace{0.1cm}{\rm d}f \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow | \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm d}f \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow | ||
\hspace{0.3cm}{\rm Minimum} | \hspace{0.3cm}{\rm Minimum} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm} .$$ | \hspace{0.05cm} .$$ | ||
| − | + | * The difference $\varepsilon^2(f)$ and the mean square error ${\rm E}\big[\varepsilon^2(f)\big]$ are obtained as follows: | |
| − | + | :$$\varepsilon^2(f) = \big [ \alpha_1 \cdot f + \alpha_2 \cdot \sqrt {f} - k_2 \cdot (f/f_0)^{k_3}\big ]^2 | |
| − | :$$\varepsilon^2(f) | + | =\alpha_1^2 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} f^2 + 2 \alpha_1 \alpha_2 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} f^{1.5} + |
| − | = | ||
\alpha_1^2 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} f + k_2^2\hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} \frac{f^{2k_3}}{f_0^{2k_3}} - 2 k_2 \alpha_1 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} | \alpha_1^2 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} f + k_2^2\hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} \frac{f^{2k_3}}{f_0^{2k_3}} - 2 k_2 \alpha_1 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} | ||
\frac{f^{k_3+1}} {f_0^{k_3}}-{2 k_2 \alpha_2} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} \frac{f^{k_3+0.5}}{f_0^{k_3}}$$ | \frac{f^{k_3+1}} {f_0^{k_3}}-{2 k_2 \alpha_2} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} \frac{f^{k_3+0.5}}{f_0^{k_3}}$$ | ||
:$$\Rightarrow | :$$\Rightarrow | ||
| − | \hspace{0.3cm}{\rm E}[\varepsilon^2(f)] = | + | \hspace{0.3cm}{\rm E}\big[\varepsilon^2(f)\big] = \alpha_1^2 |
\hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm}\frac{B^3}{3} + \frac{4}{5} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm}\alpha_1 \alpha_2 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm}B^{2.5} + | \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm}\frac{B^3}{3} + \frac{4}{5} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm}\alpha_1 \alpha_2 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm}B^{2.5} + | ||
\alpha_1^2 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} \frac{B^2}{2} + \frac{k_2^2}{2k_3 +1} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} | \alpha_1^2 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} \frac{B^2}{2} + \frac{k_2^2}{2k_3 +1} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} | ||
| − | \frac{B^{2k_3+1}}{f_0^{2k_3}} | + | \frac{B^{2k_3+1}}{f_0^{2k_3}} - \hspace{0.15cm} |
\frac{2 k_2 \alpha_1}{k_3 + 2} | \frac{2 k_2 \alpha_1}{k_3 + 2} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} | \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} | ||
$$ | $$ | ||
| − | : | + | :This equation contains the cable parameters $\alpha_1$, $\alpha_2$, $k_2$ and $k_3$ to be calculated as well as the bandwidth $B$, within which the approximation should be valid. |
| − | + | * By setting the derivatives of ${\rm E}\big[\varepsilon^2(f)\big]$ to $\alpha_1$ and $\alpha_2$ to zero, two equations are obtained for the best possible coefficients $\alpha_1$ and $\alpha_2$ that minimize the mean square error. These can be represented in the following form: | |
| − | + | :$$\frac{{\rm d}\,{\rm E}\big[\varepsilon^2(f)\big]}{{\rm d}\,{\alpha_1}} = 0 \hspace{0.2cm} | |
| − | :$$\frac{{\rm d}\,{\rm E}[\varepsilon^2(f)]}{{\rm d}\,{\alpha_1}} = 0 \hspace{0.2cm} | ||
\Rightarrow | \Rightarrow | ||
\hspace{0.2cm} \alpha_1 + C_1 \cdot \alpha_2 + C_2 = 0 \hspace{0.05cm} | \hspace{0.2cm} \alpha_1 + C_1 \cdot \alpha_2 + C_2 = 0 \hspace{0.05cm} | ||
| − | , | + | ,$$ |
| − | \frac{{\rm d}\,{\rm E}[\varepsilon^2(f)]}{{\rm d}\,{\alpha_2}} = | + | :$$\frac{{\rm d}\,{\rm E}\big[\varepsilon^2(f)\big]}{{\rm d}\,{\alpha_2}} = |
0 \hspace{0.2cm} | 0 \hspace{0.2cm} | ||
\Rightarrow | \Rightarrow | ||
\hspace{0.2cm} \alpha_1 + D_1 \cdot \alpha_2 + D_2 = 0 \hspace{0.05cm} | \hspace{0.2cm} \alpha_1 + D_1 \cdot \alpha_2 + D_2 = 0 \hspace{0.05cm} | ||
. $$ | . $$ | ||
| + | * From the equation $C_1 \cdot \alpha_2 + C_2 = D_1 \cdot \alpha_2 + D_2$, the coefficient $\alpha_2$ can be calculated and then the coefficient $\alpha_1$ can be calculated from each of the two equations above. | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | The graph shows the attenuation function per unit length for a copper twin wire with $\text{0.5 mm}$ diameter, whose $k$–parameters are: | |
:$$k_1 = 4.4\, {\rm dB}/{\rm km} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm} | :$$k_1 = 4.4\, {\rm dB}/{\rm km} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm} | ||
k_2 = 10.8\, {\rm dB}/{\rm km}\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm}k_3 = 0.60\hspace{0.05cm} | k_2 = 10.8\, {\rm dB}/{\rm km}\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm}k_3 = 0.60\hspace{0.05cm} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | *The red curve shows the function $\alpha(f)$ calculated with this parameters. For $f = 30 \ \rm MHz$ the attenuation function per unit length is $\alpha(f)= 87.5 \ \rm dB/km$. | |
| + | *The blue curve gives the approximation with the $\alpha$–coefficients. This is almost indistinguishable from the red curve within the drawing accuracy. | ||
| − | === | + | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Notes: | ||
| + | *The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Linear_and_Time_Invariant_Systems/Eigenschaften_von_Kupfer–Doppeladern|Properties of Balanced Copper Pairs]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *You can use the (German language) interactive SWF applet [[Applets:Dämpfung_von_Kupferkabeln|"Dämpfung von Kupferkabeln"]] ⇒ "Attenuation of copper cables" . | ||
| + | *[PW95] denotes the following literature reference: Pollakowski, P.; Wellhausen, H.-W.: Eigenschaften symmetrischer Ortsanschlusskabel im Frequenzbereich bis 30 MHz. Deutsche Telekom AG, Forschungs- und Technologiezentrum Darmstadt, 1995. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Questions=== | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {Calculate the parameters $C_1$ and $C_2$ of the equation $\alpha_1 + C_1 \cdot \alpha_2 + C_2 = 0$ resulting from the derivative ${\rm dE\big[\text{...}\big]/d}\alpha_1$. <br>Which results are correct? |
| + | |type="[]"} | ||
| + | + $C_1 = 6/5 \cdot B^{-0.5}$, | ||
| + | - $C_1 = 5/4 \cdot B^{-0.5}$, | ||
| + | - $C_1 = 4/3 \cdot B^{2}$, | ||
| + | - $C_2 = -4/3 \cdot B^{-2$}$, | ||
| + | - $C_2 = -5/2 \cdot k_2/(k_3 +1.5) \cdot B^{k_3 -1} \cdot f_0^{-k_3}$, | ||
| + | + $C_2 = -3 \cdot k_2/(k_3 +2) \cdot B^{k_3 -1} \cdot f_0^{-k_3}$. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {Calculate the parameters $D_1$ and $D_2$ of the equation $ \alpha_1 + D_1 \cdot \alpha_2 + D_2 = 0$ resulting from the derivative ${\rm dE\big[\text{...}\big]/d}\alpha_2$. <br> Which results are correct? | ||
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - | + | - $D_1 = 6/5 \cdot B^{-0.5}$, |
| − | + | + | + $D_1 = 5/4 \cdot B^{-0.5}$, |
| + | - $D_1 = 4/3 \cdot B^{2}$, | ||
| + | - $D_2 = -4/3 \cdot B^{-2}$, | ||
| + | + $D_2 = -5/2 \cdot k_2/(k_3 +1.5) \cdot B^{k_3 -1} \cdot f_0^{-k_3}$, | ||
| + | - $D_2 = -3 \cdot k_2/(k_3 +2) \cdot B^{k_3 -1} \cdot f_0^{-k_3}$. | ||
| − | { | + | {Calculate the coefficients $\alpha_1$ and $\alpha_2$ for the given $k_2$ and $k_3$. <br>Which of the following statements are true? |
| + | |type="[]"} | ||
| + | + For $k_3=1.0$, $\alpha_1 = k_2/f_0$ and $\alpha_2 = 0$. | ||
| + | + For $k_3=0.5$, $\alpha_1 = 0$ and $\alpha_2 = k_2/f_0^{0.5}$. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {Determine the coefficients $\alpha_1$ and $\alpha_2$ numerically for the approximation bandwidth $B = 30 \ \rm MHz$. | ||
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $\alpha$ = { | + | $\alpha_1 \ = \ $ { 0.761 3% } $\ \rm dB/(km\ \cdot \ MHz)$ |
| + | $\alpha_2 \ =\ $ { 11.1 3% } $\ \rm dB/(km\ \cdot \ \sqrt{\rm MHz})$ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {Using the $\alpha$–parameters, calculate the attenuation function per unit length for the frequency $f = 30\ \rm MHz$. | ||
| + | |type="{}"} | ||
| + | $\alpha_{\rm II}(f = 30\ \rm MHz) \ = \ $ { 88.1 3% } $\ \rm dB/km$ | ||
| Line 74: | Line 108: | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''1 | + | '''(1)''' <u>Solutions 1 and 6</u> are correct: |
| − | '''2 | + | *The derivative of the given expected value with respect to $\alpha_1$ gives: |
| − | ''' | + | :$$\frac{{\rm d}\,{\rm E}[\varepsilon^2(f)]}{{\rm d}\,{\alpha_1}} = |
| − | ''' | + | \frac{2}{3}\cdot B^3 \cdot \alpha_1 + \frac{4}{5}\cdot B^{2.5} \cdot \alpha_2 |
| − | '''5.''' | + | - \frac{2 k_2 }{k_3 |
| − | '''6.''' | + | + 2} \cdot \frac{B^{k_3+2}}{f_0^{k_3}}= 0 |
| − | ''' | + | \hspace{0.05cm} .$$ |
| + | *By setting it to zero and dividing by $2B^2/3$, we obtain: | ||
| + | :$$\alpha_1 + \frac{6}{5}\cdot B^{-0.5} \cdot \alpha_2 | ||
| + | - \frac{3 k_2 }{k_3 | ||
| + | +2} \cdot \frac{B^{k_3-1}}{f_0^{k_3}}= 0 | ||
| + | \hspace{0.3cm} | ||
| + | \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} C_1 = \frac{6}{5}\cdot B^{-0.5} \hspace{0.05cm} , | ||
| + | \hspace{0.5cm} C_2 = | ||
| + | - \frac{3 k_2 }{k_3 | ||
| + | +2} \cdot \frac{B^{k_3-1}}{f_0^{k_3}} | ||
| + | \hspace{0.05cm} .$$ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(2)''' <u>Solutions 2 and 5</u> are correct: | ||
| + | *Using the same procedure as in subtask '''(1)''', we obtain: | ||
| + | :$$\frac{{\rm d}\,{\rm E}[\varepsilon^2(f)]}{{\rm d}\,{\alpha_2}} = | ||
| + | \frac{4}{5}\cdot B^{2.5} \cdot \alpha_1 + B^{2} \cdot \alpha_2 | ||
| + | - \frac{2 k_2 }{k_3 | ||
| + | + 1.5} \cdot \frac{B^{k_3+1.5}}{f_0^{k_3}}= 0$$ | ||
| + | :$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \alpha_1 + \frac{5}{4}\cdot B^{-0.5} \cdot \alpha_2 | ||
| + | - \frac{2.5 \cdot k_2 }{k_3 | ||
| + | +1.5} \cdot \frac{B^{k_3-1}}{f_0^{k_3}}= 0 | ||
| + | \hspace{0.3cm} | ||
| + | \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}D_1 = \frac{5}{4}\cdot B^{-0.5} \hspace{0.05cm} , | ||
| + | \hspace{0.3cm}D_2 = | ||
| + | - \frac{2.5 \cdot k_2 }{k_3 | ||
| + | +1.5} \cdot \frac{B^{k_3-1}}{f_0^{k_3}} | ||
| + | \hspace{0.05cm} .$$ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(3)''' <u>Both solutions</u> are correct: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *From $C_1 \cdot \alpha_2 + C_2 = D_1 \cdot \alpha_2 + D_2$ we obtain a linear equation for $\alpha_2$. With the result from '''(2)''' we can write: | ||
| + | :$$\alpha_2 = \frac{D_2 - C_2}{C_1 - D_1} = \frac{- \frac{2.5 \cdot k_2 }{k_3 | ||
| + | +1.5} \cdot \frac{B^{k_3-1}}{f_0^{k_3}} + \frac{3 k_2 }{k_3 +2} | ||
| + | \cdot \frac{B^{k_3-1}}{f_0^{k_3}}}{{6}/{5}\cdot B^{-0.5} - | ||
| + | {5}/{4}\cdot B^{-0.5}} = \frac{- {2.5 \cdot k_2 | ||
| + | }\cdot(k_3 +2) + {3 k_2 }\cdot (k_3 +1.5) }{({6}/{5} - | ||
| + | {5}/{4})(k_3 +1.5)(k_3 +2)} \cdot | ||
| + | \frac{B^{k_3-0.5}}{f_0^{k_3}}$$ | ||
| + | :$$ \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}\alpha_2 = 10 \cdot (B/f_0)^{k_3 | ||
| + | -0.5}\cdot \frac{1-k_3}{(k_3 + 1.5)(k_3 + | ||
| + | 2)}\cdot \frac {k_2}{\sqrt{f_0}} | ||
| + | \hspace{0.05cm} .$$ | ||
| + | *For the parameter $\alpha_1$ then holds: | ||
| + | :$$\alpha_1 = - C_1 \cdot \alpha_2 - C_2 = | ||
| + | -\frac{6}{5}\cdot B^{-0.5} \cdot 10 \cdot (B/f_0)^{k_3 | ||
| + | -0.5}\cdot \frac{1-k_3}{(k_3 + 1.5)(k_3 + | ||
| + | 2)}\cdot \frac {k_2}{\sqrt{f_0}} +\frac{3 k_2 }{k_3 +2} | ||
| + | \cdot \frac{B^{k_3-1}}{f_0^{k_3}}$$ | ||
| + | :$$ \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}\alpha_1 = (B/f_0)^{k_3 -1}\cdot | ||
| + | \frac{-12 \cdot (1-k_3) + 3 \cdot (k_3 + 1.5)}{(k_3 + 1.5)(k_3 + | ||
| + | 2)} \cdot \frac {k_2}{f_0} \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}\alpha_1 =15 \cdot (B/f_0)^{k_3 | ||
| + | -1}\cdot \frac{k_3 -0.5}{(k_3 + 1.5)(k_3 + | ||
| + | 2)}\cdot \frac {k_2}{f_0}\hspace{0.05cm} .$$ | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Regardless of the bandwidth, we obtain for $k_3 = 1$: | ||
| + | :$$\alpha_1 = (B/f_0)^{k_3 | ||
| + | -1}\cdot \frac{15 \cdot (k_3 -0.5)}{(k_3 + 1.5)(k_3 + | ||
| + | 2)}\cdot \frac {k_2}{f_0} = \frac{15 \cdot 0.5}{2.5 \cdot 3}\cdot \frac {k_2}{f_0} | ||
| + | \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = {k_2}/{f_0}}\hspace{0.05cm} | ||
| + | ,$$ | ||
| + | :$$ \alpha_2 = (B/f_0)^{k_3 | ||
| + | -0.5}\cdot \frac{10 \cdot (1-k_3)}{(k_3 + 1.5)(k_3 + | ||
| + | 2)}\cdot \frac {k_2}{\sqrt{f_0}}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0} \hspace{0.05cm} | ||
| + | .$$ | ||
| + | *In contrast, for $k_3 = 0.5$: | ||
| + | :$$\alpha_1 = (B/f_0)^{k_3 | ||
| + | -1}\cdot \frac{15 \cdot (k_3 -0.5)}{(k_3 + 1.5)(k_3 + | ||
| + | 2)}\cdot \frac {k_2}{f_0} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0}\hspace{0.05cm} | ||
| + | ,$$ | ||
| + | :$$ \alpha_2 = (B/f_0)^{k_3 | ||
| + | -0.5}\cdot \frac{10 \cdot (1-k_3)}{(k_3 + 1.5)(k_3 + | ||
| + | 2)}\cdot \frac {k_2}{\sqrt{f_0}}= \frac{10 \cdot 0.5}{2 \cdot 2.5}\cdot \frac {k_2}{\sqrt{f_0}} = \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ {k_2}/{\sqrt{f_0}}} \hspace{0.05cm} | ||
| + | .$$ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(4)''' For the two coefficients, with $k_2 = 10.8 \ \rm dB/km$, $k_3 = 0.6 \ \rm dB/km$ and $B/f_0 = 30$: | ||
| + | :$$\alpha_1 = (B/f_0)^{k_3 | ||
| + | -1}\cdot \frac{15 \cdot (k_3 -0.5)}{(k_3 + 1.5)(k_3 + | ||
| + | 2)}\cdot \frac {k_2}{f_0} = 30^{-0.4}\cdot \frac{15 \cdot 0.1}{2.1 \cdot 2.6}\cdot | ||
| + | \frac {10.8 \, {\rm dB/km} }{1 \, {\rm MHz}} | ||
| + | \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ \approx 0.761\, | ||
| + | {{\rm dB} }/{({\rm km \cdot MHz})}} | ||
| + | \hspace{0.05cm} | ||
| + | ,$$ | ||
| + | :$$ \alpha_2 = (B/f_0)^{k_3 | ||
| + | -0.5}\cdot \frac{10 \cdot (1-k_3)}{(k_3 + 1.5)(k_3 + | ||
| + | 2)}\cdot \frac {k_2}{\sqrt{f_0}}= \frac {k_2}{\sqrt{f_0}} | ||
| + | = 30^{0.1}\cdot \frac{10 \cdot 0.4}{2.1 \cdot 2.6}\cdot \frac | ||
| + | {10.8 \, {\rm dB/km} }{1 \, {\rm MHz^{0.5}}} | ||
| + | \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ \approx 11.1\, | ||
| + | {{\rm dB} }/{({\rm km \cdot \sqrt{MHz}}})}\hspace{0.05cm} | ||
| + | .$$ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(5)''' According to the given equation $\alpha_{\rm II}(f)$ thus also holds: | ||
| + | :$$\alpha_{\rm II}(f = 30 \, {\rm MHz}) = \alpha_0 + \alpha_1 \cdot f + \alpha_2 \cdot \sqrt {f} | ||
| + | = \big [ \hspace{0.05cm} 4.4 + 0.761 \cdot 30 + 11.1 \cdot \sqrt {30}\hspace{0.05cm} | ||
| + | \big ]\frac | ||
| + | {\rm dB}{\rm km } | ||
| + | \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{\approx 88.1\, {\rm dB}/{\rm km }} | ||
| + | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Linear and Time-Invariant Systems: Exercises|^4.3 Balanced Copper Twisted Pair^]] |
Latest revision as of 17:11, 23 November 2021
For symmetrical copper twisted pairs, the following empirical formula can be found in [PW95], which is valid for the frequency range $0 \le f \le 30 \ \rm MHz$:
- $$\alpha_{\rm I} (f) = k_1 + k_2 \cdot (f/f_0)^{k_3} , \hspace{0.15cm} f_0 = 1\,{\rm MHz} .$$
In contrast, the attenuation function per unit length of a coaxial cable is usually given in the following form:
- $$\alpha_{\rm II}(f) = \alpha_0 + \alpha_1 \cdot f + \alpha_2 \cdot \sqrt {f}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Especially for the calculation of impulse response and rectangular response it is advantageous also for the copper twisted pairs to choose the second representation form with the cable parameters $\alpha_0$, $\alpha_1$ and $\alpha_2$ instead of the representation with $k_1$, $k_2$ and $k_3$.
For the conversion, one proceeds as follows:
- From above equations, it is obvious that the coefficient characterizing the DC signal attenuation is $\alpha_0 = k_1$.
- To determine $\alpha_1$ and $\alpha_2$, it is assumed that the mean square error should be minimum in the range of a given bandwidth $B$:
- $${\rm E}\big[\varepsilon^2(f)\big] = \int_{0}^{ B} \left [ \alpha_{\rm II} (f) - \alpha_{\rm I} (f)\right ]^2 \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm d}f \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}{\rm Minimum} \hspace{0.05cm} .$$
- The difference $\varepsilon^2(f)$ and the mean square error ${\rm E}\big[\varepsilon^2(f)\big]$ are obtained as follows:
- $$\varepsilon^2(f) = \big [ \alpha_1 \cdot f + \alpha_2 \cdot \sqrt {f} - k_2 \cdot (f/f_0)^{k_3}\big ]^2 =\alpha_1^2 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} f^2 + 2 \alpha_1 \alpha_2 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} f^{1.5} + \alpha_1^2 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} f + k_2^2\hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} \frac{f^{2k_3}}{f_0^{2k_3}} - 2 k_2 \alpha_1 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} \frac{f^{k_3+1}} {f_0^{k_3}}-{2 k_2 \alpha_2} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} \frac{f^{k_3+0.5}}{f_0^{k_3}}$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}{\rm E}\big[\varepsilon^2(f)\big] = \alpha_1^2 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm}\frac{B^3}{3} + \frac{4}{5} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm}\alpha_1 \alpha_2 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm}B^{2.5} + \alpha_1^2 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} \frac{B^2}{2} + \frac{k_2^2}{2k_3 +1} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} \frac{B^{2k_3+1}}{f_0^{2k_3}} - \hspace{0.15cm} \frac{2 k_2 \alpha_1}{k_3 + 2} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} $$
- This equation contains the cable parameters $\alpha_1$, $\alpha_2$, $k_2$ and $k_3$ to be calculated as well as the bandwidth $B$, within which the approximation should be valid.
- By setting the derivatives of ${\rm E}\big[\varepsilon^2(f)\big]$ to $\alpha_1$ and $\alpha_2$ to zero, two equations are obtained for the best possible coefficients $\alpha_1$ and $\alpha_2$ that minimize the mean square error. These can be represented in the following form:
- $$\frac{{\rm d}\,{\rm E}\big[\varepsilon^2(f)\big]}{{\rm d}\,{\alpha_1}} = 0 \hspace{0.2cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.2cm} \alpha_1 + C_1 \cdot \alpha_2 + C_2 = 0 \hspace{0.05cm} ,$$
- $$\frac{{\rm d}\,{\rm E}\big[\varepsilon^2(f)\big]}{{\rm d}\,{\alpha_2}} = 0 \hspace{0.2cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.2cm} \alpha_1 + D_1 \cdot \alpha_2 + D_2 = 0 \hspace{0.05cm} . $$
- From the equation $C_1 \cdot \alpha_2 + C_2 = D_1 \cdot \alpha_2 + D_2$, the coefficient $\alpha_2$ can be calculated and then the coefficient $\alpha_1$ can be calculated from each of the two equations above.
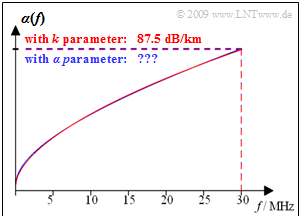
The graph shows the attenuation function per unit length for a copper twin wire with $\text{0.5 mm}$ diameter, whose $k$–parameters are:
- $$k_1 = 4.4\, {\rm dB}/{\rm km} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm} k_2 = 10.8\, {\rm dB}/{\rm km}\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm}k_3 = 0.60\hspace{0.05cm} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The red curve shows the function $\alpha(f)$ calculated with this parameters. For $f = 30 \ \rm MHz$ the attenuation function per unit length is $\alpha(f)= 87.5 \ \rm dB/km$.
- The blue curve gives the approximation with the $\alpha$–coefficients. This is almost indistinguishable from the red curve within the drawing accuracy.
Notes:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter Properties of Balanced Copper Pairs.
- You can use the (German language) interactive SWF applet "Dämpfung von Kupferkabeln" ⇒ "Attenuation of copper cables" .
- [PW95] denotes the following literature reference: Pollakowski, P.; Wellhausen, H.-W.: Eigenschaften symmetrischer Ortsanschlusskabel im Frequenzbereich bis 30 MHz. Deutsche Telekom AG, Forschungs- und Technologiezentrum Darmstadt, 1995.
Questions
Solution
- The derivative of the given expected value with respect to $\alpha_1$ gives:
- $$\frac{{\rm d}\,{\rm E}[\varepsilon^2(f)]}{{\rm d}\,{\alpha_1}} = \frac{2}{3}\cdot B^3 \cdot \alpha_1 + \frac{4}{5}\cdot B^{2.5} \cdot \alpha_2 - \frac{2 k_2 }{k_3 + 2} \cdot \frac{B^{k_3+2}}{f_0^{k_3}}= 0 \hspace{0.05cm} .$$
- By setting it to zero and dividing by $2B^2/3$, we obtain:
- $$\alpha_1 + \frac{6}{5}\cdot B^{-0.5} \cdot \alpha_2 - \frac{3 k_2 }{k_3 +2} \cdot \frac{B^{k_3-1}}{f_0^{k_3}}= 0 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} C_1 = \frac{6}{5}\cdot B^{-0.5} \hspace{0.05cm} , \hspace{0.5cm} C_2 = - \frac{3 k_2 }{k_3 +2} \cdot \frac{B^{k_3-1}}{f_0^{k_3}} \hspace{0.05cm} .$$
(2) Solutions 2 and 5 are correct:
- Using the same procedure as in subtask (1), we obtain:
- $$\frac{{\rm d}\,{\rm E}[\varepsilon^2(f)]}{{\rm d}\,{\alpha_2}} = \frac{4}{5}\cdot B^{2.5} \cdot \alpha_1 + B^{2} \cdot \alpha_2 - \frac{2 k_2 }{k_3 + 1.5} \cdot \frac{B^{k_3+1.5}}{f_0^{k_3}}= 0$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \alpha_1 + \frac{5}{4}\cdot B^{-0.5} \cdot \alpha_2 - \frac{2.5 \cdot k_2 }{k_3 +1.5} \cdot \frac{B^{k_3-1}}{f_0^{k_3}}= 0 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}D_1 = \frac{5}{4}\cdot B^{-0.5} \hspace{0.05cm} , \hspace{0.3cm}D_2 = - \frac{2.5 \cdot k_2 }{k_3 +1.5} \cdot \frac{B^{k_3-1}}{f_0^{k_3}} \hspace{0.05cm} .$$
(3) Both solutions are correct:
- From $C_1 \cdot \alpha_2 + C_2 = D_1 \cdot \alpha_2 + D_2$ we obtain a linear equation for $\alpha_2$. With the result from (2) we can write:
- $$\alpha_2 = \frac{D_2 - C_2}{C_1 - D_1} = \frac{- \frac{2.5 \cdot k_2 }{k_3 +1.5} \cdot \frac{B^{k_3-1}}{f_0^{k_3}} + \frac{3 k_2 }{k_3 +2} \cdot \frac{B^{k_3-1}}{f_0^{k_3}}}{{6}/{5}\cdot B^{-0.5} - {5}/{4}\cdot B^{-0.5}} = \frac{- {2.5 \cdot k_2 }\cdot(k_3 +2) + {3 k_2 }\cdot (k_3 +1.5) }{({6}/{5} - {5}/{4})(k_3 +1.5)(k_3 +2)} \cdot \frac{B^{k_3-0.5}}{f_0^{k_3}}$$
- $$ \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}\alpha_2 = 10 \cdot (B/f_0)^{k_3 -0.5}\cdot \frac{1-k_3}{(k_3 + 1.5)(k_3 + 2)}\cdot \frac {k_2}{\sqrt{f_0}} \hspace{0.05cm} .$$
- For the parameter $\alpha_1$ then holds:
- $$\alpha_1 = - C_1 \cdot \alpha_2 - C_2 = -\frac{6}{5}\cdot B^{-0.5} \cdot 10 \cdot (B/f_0)^{k_3 -0.5}\cdot \frac{1-k_3}{(k_3 + 1.5)(k_3 + 2)}\cdot \frac {k_2}{\sqrt{f_0}} +\frac{3 k_2 }{k_3 +2} \cdot \frac{B^{k_3-1}}{f_0^{k_3}}$$
- $$ \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}\alpha_1 = (B/f_0)^{k_3 -1}\cdot \frac{-12 \cdot (1-k_3) + 3 \cdot (k_3 + 1.5)}{(k_3 + 1.5)(k_3 + 2)} \cdot \frac {k_2}{f_0} \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}\alpha_1 =15 \cdot (B/f_0)^{k_3 -1}\cdot \frac{k_3 -0.5}{(k_3 + 1.5)(k_3 + 2)}\cdot \frac {k_2}{f_0}\hspace{0.05cm} .$$
- Regardless of the bandwidth, we obtain for $k_3 = 1$:
- $$\alpha_1 = (B/f_0)^{k_3 -1}\cdot \frac{15 \cdot (k_3 -0.5)}{(k_3 + 1.5)(k_3 + 2)}\cdot \frac {k_2}{f_0} = \frac{15 \cdot 0.5}{2.5 \cdot 3}\cdot \frac {k_2}{f_0} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = {k_2}/{f_0}}\hspace{0.05cm} ,$$
- $$ \alpha_2 = (B/f_0)^{k_3 -0.5}\cdot \frac{10 \cdot (1-k_3)}{(k_3 + 1.5)(k_3 + 2)}\cdot \frac {k_2}{\sqrt{f_0}}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0} \hspace{0.05cm} .$$
- In contrast, for $k_3 = 0.5$:
- $$\alpha_1 = (B/f_0)^{k_3 -1}\cdot \frac{15 \cdot (k_3 -0.5)}{(k_3 + 1.5)(k_3 + 2)}\cdot \frac {k_2}{f_0} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0}\hspace{0.05cm} ,$$
- $$ \alpha_2 = (B/f_0)^{k_3 -0.5}\cdot \frac{10 \cdot (1-k_3)}{(k_3 + 1.5)(k_3 + 2)}\cdot \frac {k_2}{\sqrt{f_0}}= \frac{10 \cdot 0.5}{2 \cdot 2.5}\cdot \frac {k_2}{\sqrt{f_0}} = \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ {k_2}/{\sqrt{f_0}}} \hspace{0.05cm} .$$
(4) For the two coefficients, with $k_2 = 10.8 \ \rm dB/km$, $k_3 = 0.6 \ \rm dB/km$ and $B/f_0 = 30$:
- $$\alpha_1 = (B/f_0)^{k_3 -1}\cdot \frac{15 \cdot (k_3 -0.5)}{(k_3 + 1.5)(k_3 + 2)}\cdot \frac {k_2}{f_0} = 30^{-0.4}\cdot \frac{15 \cdot 0.1}{2.1 \cdot 2.6}\cdot \frac {10.8 \, {\rm dB/km} }{1 \, {\rm MHz}} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ \approx 0.761\, {{\rm dB} }/{({\rm km \cdot MHz})}} \hspace{0.05cm} ,$$
- $$ \alpha_2 = (B/f_0)^{k_3 -0.5}\cdot \frac{10 \cdot (1-k_3)}{(k_3 + 1.5)(k_3 + 2)}\cdot \frac {k_2}{\sqrt{f_0}}= \frac {k_2}{\sqrt{f_0}} = 30^{0.1}\cdot \frac{10 \cdot 0.4}{2.1 \cdot 2.6}\cdot \frac {10.8 \, {\rm dB/km} }{1 \, {\rm MHz^{0.5}}} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ \approx 11.1\, {{\rm dB} }/{({\rm km \cdot \sqrt{MHz}}})}\hspace{0.05cm} .$$
(5) According to the given equation $\alpha_{\rm II}(f)$ thus also holds:
- $$\alpha_{\rm II}(f = 30 \, {\rm MHz}) = \alpha_0 + \alpha_1 \cdot f + \alpha_2 \cdot \sqrt {f} = \big [ \hspace{0.05cm} 4.4 + 0.761 \cdot 30 + 11.1 \cdot \sqrt {30}\hspace{0.05cm} \big ]\frac {\rm dB}{\rm km } \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{\approx 88.1\, {\rm dB}/{\rm km }} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$