Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 2.15Z: Block Error Probability once more"
From LNTwww
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
[[File:P_ID2574__KC_Z_2_15.png|right|frame|Binominal probabilities]] | [[File:P_ID2574__KC_Z_2_15.png|right|frame|Binominal probabilities]] | ||
| − | Using a Reed–Solomon code with the correctability $t$ and [[Channel_Coding/Error_Probability_and_Areas_of_Application#Block_error_probability_for_RSC_and_BDD|"Bounded Distance Decoding"]] $\rm $ $\rm (BDD)$ is obtained with | + | Using a Reed–Solomon code with the correctability $t$ and [[Channel_Coding/Error_Probability_and_Areas_of_Application#Block_error_probability_for_RSC_and_BDD|"Bounded Distance Decoding"]] $\rm $ $\rm (BDD)$ is obtained for the block error probability with |
* the code word length $n$ and | * the code word length $n$ and | ||
| − | * the symbol falsification probability $\varepsilon_{\rm S}$ | + | * the symbol falsification probability $\varepsilon_{\rm S}$: |
| − | |||
| − | |||
:$${\rm Pr(block\:error)} = | :$${\rm Pr(block\:error)} = | ||
\sum_{f = t + 1}^{n} {n \choose f} \cdot {\varepsilon_{\rm S}}^f \cdot (1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S})^{n-f} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \sum_{f = t + 1}^{n} {n \choose f} \cdot {\varepsilon_{\rm S}}^f \cdot (1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S})^{n-f} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| Line 56: | Line 54: | ||
===Solution=== | ===Solution=== | ||
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1)''' For the $\rm RSC \, (7, \, 3, \, 5)_8$, because $d_{\rm min} = 5 \ \Rightarrow \ t = 2$ gives the block error probability: | + | '''(1)''' For the $\rm RSC \, (7, \, 3, \, 5)_8$, because $d_{\rm min} = 5 \ \Rightarrow \ t = 2$ gives the block error probability: |
| − | :$${\rm Pr( | + | :$${\rm Pr(block\:error)} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} |
\sum_{f = 3}^{7} {7 \choose f} \cdot {\varepsilon_{\rm S}}^f \cdot (1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S})^{7-f} $$ | \sum_{f = 3}^{7} {7 \choose f} \cdot {\varepsilon_{\rm S}}^f \cdot (1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S})^{7-f} $$ | ||
| − | :$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}{\rm Pr( | + | :$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}{\rm Pr(block\:error)} ={7 \choose 3} \cdot 0.1^3 \cdot 0.9^4 + {7 \choose 4} \cdot 0.1^4 \cdot 0.9^3 |
+ {7 \choose 5} \cdot 0.1^5 \cdot 0.9^2+ | + {7 \choose 5} \cdot 0.1^5 \cdot 0.9^2+ | ||
{7 \choose 6} \cdot 0.1^6 \cdot 0.9+ {7 \choose 7} \cdot 0.1^7 | {7 \choose 6} \cdot 0.1^6 \cdot 0.9+ {7 \choose 7} \cdot 0.1^7 | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | *According to this calculation, five terms would have to be considered. However, since | + | *According to this calculation, five terms would have to be considered. However, since |
| − | :$${\rm Pr( | + | :$${\rm Pr(block\:error)} = |
\sum_{f = 0}^{n} {n \choose f} \cdot {\varepsilon_{\rm S}}^f \cdot (1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S})^{n-f} = 1$$ | \sum_{f = 0}^{n} {n \choose f} \cdot {\varepsilon_{\rm S}}^f \cdot (1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S})^{n-f} = 1$$ | ||
| − | is also valid, the following calculation is faster: | + | :is also valid, the following calculation is faster: |
| − | :$${\rm Pr( | + | :$${\rm Pr(block\:error)} =1 - \big [ {7 \choose 0} \cdot 0.9^7 + {7 \choose 1} \cdot 0.1 \cdot 0.9^6 |
+ {7 \choose 2} \cdot 0.1^2 \cdot 0.9^5 \big ] =1 - \big [ 0.4783 + 0.3720 + 0.1240 \big ] \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{= 2.57 \cdot 10^{-2}} | + {7 \choose 2} \cdot 0.1^2 \cdot 0.9^5 \big ] =1 - \big [ 0.4783 + 0.3720 + 0.1240 \big ] \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{= 2.57 \cdot 10^{-2}} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | '''(2)''' Analogous to the subtask '''(1)''' one obtains here: | + | '''(2)''' Analogous to the subtask '''(1)''' one obtains here: |
| − | :$${\rm Pr( | + | :$${\rm Pr(block\:error)} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} 1 - \big [ 0.99^7 + 7 \cdot 0.01 \cdot 0.99^6 |
+ 21 \cdot 0.01^2 \cdot 0.99^5 \big ] =1 - \big [ 0.9321 + 0.0659 + 0.0020 \big ] \approx 0 | + 21 \cdot 0.01^2 \cdot 0.99^5 \big ] =1 - \big [ 0.9321 + 0.0659 + 0.0020 \big ] \approx 0 | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | *This means: For the probability $\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 0.01$ the simplified calculation is very error-prone, because a value close to $1$ results for the bracket expression. | + | *This means: For the probability $\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 0.01$ the simplified calculation is very error-prone, because a value close to $1$ results for the bracket expression. |
| + | |||
*The full calculation yields here: | *The full calculation yields here: | ||
| − | :$${\rm Pr( | + | :$${\rm Pr(block\:error)} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} |
{7 \choose 3} \cdot 0.01^3 \cdot 0.99^4 + {7 \choose 4} \cdot 0.01^4 \cdot 0.99^3 + | {7 \choose 3} \cdot 0.01^3 \cdot 0.99^4 + {7 \choose 4} \cdot 0.01^4 \cdot 0.99^3 + | ||
{7 \choose 5} \cdot 0.01^5 \cdot 0.99^2+ {7 \choose 6} \cdot 0.01^6 \cdot 0.99+ | {7 \choose 5} \cdot 0.01^5 \cdot 0.99^2+ {7 \choose 6} \cdot 0.01^6 \cdot 0.99+ | ||
{7 \choose 7} \cdot 0.01^7 $$ | {7 \choose 7} \cdot 0.01^7 $$ | ||
| − | :$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}{\rm Pr( | + | :$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}{\rm Pr(block\:error)}= 10^{-6} \cdot |
\big [ 33.6209 + 0.3396 + 0.0021 + ... \big ] \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{ \approx 3.396 \cdot 10^{-5}} | \big [ 33.6209 + 0.3396 + 0.0021 + ... \big ] \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{ \approx 3.396 \cdot 10^{-5}} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| Line 91: | Line 90: | ||
| − | '''(3)''' From the sample solution to the subtask '''(2)''' the result can be read directly: | + | '''(3)''' From the sample solution to the subtask '''(2)''' the result can be read directly: |
| − | :$${\rm Pr( | + | :$${\rm Pr(block\:error)} \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{ \approx 3.362 \cdot 10^{-5}} |
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | *The relative error is about $-1\%$. | + | *The relative error is about $-1\%$. |
| − | *The minus sign indicates that this is only an approximation and not a bound: | + | |
| − | + | *The minus sign indicates that this is only an approximation and not a bound: The approximate value is slightly smaller than the actual value. | |
| − | '''(4)''' Restricting to the relevant term $(f = 3)$, we get $\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 0.001$: | + | '''(4)''' Restricting to the relevant term $(f = 3)$, we get $\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 0.001$: |
| − | :$${\rm Pr( | + | :$${\rm Pr(block\:error)} \approx |
{7 \choose 3} \cdot [10^{-3}]^3 \cdot 0.999^4 \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{ \approx 3.49 \cdot 10^{-8}} | {7 \choose 3} \cdot [10^{-3}]^3 \cdot 0.999^4 \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{ \approx 3.49 \cdot 10^{-8}} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | *The relative error here is | + | *The relative error here is only about $-0.1\%$. |
| − | '''(5)''' According to the derived approximation, the following holds for the considered code: | + | '''(5)''' According to the derived approximation, the following holds for the considered code: |
| − | :$${\rm Pr( | + | :$${\rm Pr(block\:error)} \approx {7 \choose 3} \cdot {\varepsilon_{\rm S}}^3 = 35 \cdot {\varepsilon_{\rm S}}^3\hspace{0.3cm} |
| − | \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm Pr( | + | \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm Pr(block\:error)} = 10^{-10}: \hspace{0.4cm} {\varepsilon_{\rm S}} = |
\big ( \frac{10^{-10}}{35} \big )^{1/3} = 2.857^{1/3} \cdot 10^{-4} | \big ( \frac{10^{-10}}{35} \big )^{1/3} = 2.857^{1/3} \cdot 10^{-4} | ||
\hspace{0.15cm} \underline{ \approx 1.42 \cdot 10^{-4}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{ \approx 1.42 \cdot 10^{-4}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
Latest revision as of 14:37, 2 November 2022
Using a Reed–Solomon code with the correctability $t$ and "Bounded Distance Decoding" $\rm $ $\rm (BDD)$ is obtained for the block error probability with
- the code word length $n$ and
- the symbol falsification probability $\varepsilon_{\rm S}$:
- $${\rm Pr(block\:error)} = \sum_{f = t + 1}^{n} {n \choose f} \cdot {\varepsilon_{\rm S}}^f \cdot (1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S})^{n-f} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
In this exercise, the block error probability for the $\rm RSC \, (7, \, 3, \, 5)_8$ and various $\varepsilon_{\rm S}$ values shall be calculated and approximated.
- The above equation is reminiscent of the "Biomial Distribution".
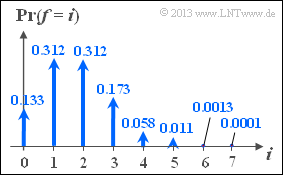
- The graph shows the probabilities of the binomial distribution for parameters $n = 7$ ("code word length") and $\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 0.25$ ("symbol falsification probability").
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter "Error Probability and Application Areas".
- For checking, you can use the interactive HTML5/JavaScript applet "Binomial and Poisson Distribution".
Questions
Solution
(1) For the $\rm RSC \, (7, \, 3, \, 5)_8$, because $d_{\rm min} = 5 \ \Rightarrow \ t = 2$ gives the block error probability:
- $${\rm Pr(block\:error)} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} \sum_{f = 3}^{7} {7 \choose f} \cdot {\varepsilon_{\rm S}}^f \cdot (1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S})^{7-f} $$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}{\rm Pr(block\:error)} ={7 \choose 3} \cdot 0.1^3 \cdot 0.9^4 + {7 \choose 4} \cdot 0.1^4 \cdot 0.9^3 + {7 \choose 5} \cdot 0.1^5 \cdot 0.9^2+ {7 \choose 6} \cdot 0.1^6 \cdot 0.9+ {7 \choose 7} \cdot 0.1^7 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- According to this calculation, five terms would have to be considered. However, since
- $${\rm Pr(block\:error)} = \sum_{f = 0}^{n} {n \choose f} \cdot {\varepsilon_{\rm S}}^f \cdot (1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S})^{n-f} = 1$$
- is also valid, the following calculation is faster:
- $${\rm Pr(block\:error)} =1 - \big [ {7 \choose 0} \cdot 0.9^7 + {7 \choose 1} \cdot 0.1 \cdot 0.9^6 + {7 \choose 2} \cdot 0.1^2 \cdot 0.9^5 \big ] =1 - \big [ 0.4783 + 0.3720 + 0.1240 \big ] \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{= 2.57 \cdot 10^{-2}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) Analogous to the subtask (1) one obtains here:
- $${\rm Pr(block\:error)} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} 1 - \big [ 0.99^7 + 7 \cdot 0.01 \cdot 0.99^6 + 21 \cdot 0.01^2 \cdot 0.99^5 \big ] =1 - \big [ 0.9321 + 0.0659 + 0.0020 \big ] \approx 0 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- This means: For the probability $\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 0.01$ the simplified calculation is very error-prone, because a value close to $1$ results for the bracket expression.
- The full calculation yields here:
- $${\rm Pr(block\:error)} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} {7 \choose 3} \cdot 0.01^3 \cdot 0.99^4 + {7 \choose 4} \cdot 0.01^4 \cdot 0.99^3 + {7 \choose 5} \cdot 0.01^5 \cdot 0.99^2+ {7 \choose 6} \cdot 0.01^6 \cdot 0.99+ {7 \choose 7} \cdot 0.01^7 $$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}{\rm Pr(block\:error)}= 10^{-6} \cdot \big [ 33.6209 + 0.3396 + 0.0021 + ... \big ] \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{ \approx 3.396 \cdot 10^{-5}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(3) From the sample solution to the subtask (2) the result can be read directly:
- $${\rm Pr(block\:error)} \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{ \approx 3.362 \cdot 10^{-5}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The relative error is about $-1\%$.
- The minus sign indicates that this is only an approximation and not a bound: The approximate value is slightly smaller than the actual value.
(4) Restricting to the relevant term $(f = 3)$, we get $\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 0.001$:
- $${\rm Pr(block\:error)} \approx {7 \choose 3} \cdot [10^{-3}]^3 \cdot 0.999^4 \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{ \approx 3.49 \cdot 10^{-8}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The relative error here is only about $-0.1\%$.
(5) According to the derived approximation, the following holds for the considered code:
- $${\rm Pr(block\:error)} \approx {7 \choose 3} \cdot {\varepsilon_{\rm S}}^3 = 35 \cdot {\varepsilon_{\rm S}}^3\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm Pr(block\:error)} = 10^{-10}: \hspace{0.4cm} {\varepsilon_{\rm S}} = \big ( \frac{10^{-10}}{35} \big )^{1/3} = 2.857^{1/3} \cdot 10^{-4} \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{ \approx 1.42 \cdot 10^{-4}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$