Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 3.3: GSM Frame Structure"
| (17 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Examples_of_Communication_Systems/Radio_Interface |
}} | }} | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:EN_Bei_A_3_3_v2.png|right|frame|GSM frame structure]] |
| − | + | In the 2G cellular mobile communication standard $\rm GSM$ the following frame structure is specified: | |
| − | * | + | *A superframe consists of $51$ multiframes and has duration $T_{\rm SF}$. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | *Each multiframe has $26$ TDMA frames and lasts a total of $T_{\rm MF} = 120 \rm ms$. | ||
| − | + | *Each TDMA frame has duration $T_{\rm TF}$ and is a sequence of eight time slots with duration $T_{\rm burst}$. | |
| + | *For example, in such a time slot, a "Normal Burst" with $156.25$ bits is transmitted. | ||
| − | + | *Of these, however, only $114$ are data bits. Further bits are needed for the so called "Guard Period" $\rm (GP)$, signaling, synchronization and channel estimation. | |
| − | + | *Further, when calculating the net data rate, it must be taken into account that the logical channels SACCH and IDLE require a total of $1.9 \rm kbit/s$. | |
| − | === | + | |
| + | It should also be noted that, in addition to the described multiframe structure with $26$ TDMA frames, there are also multiframes with $51$ TDMA frames, but these are used almost exclusively for the transmission of signaling information. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <u>Hints:</u> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *This exercise belongs to the chapter [[Examples_of_Communication_Systems/Radio_Interface|"Radio Interface"]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Reference is made in particular to the sectione [[Examples_of_Communication_Systems/Radio_Interface#GSM_frame_structure|"GSM frame structure"]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Questions=== | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {How long does a superframe $\rm (SF)$ last? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$T_{\rm SF} \ = \ ${ 6.12 3% } $ \ \rm s$ | $T_{\rm SF} \ = \ ${ 6.12 3% } $ \ \rm s$ | ||
| − | { | + | {What is the duration of a TDMA frame $\rm (TF)$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $T_{\rm | + | $T_{\rm TF} \ = \ ${ 4.615 3% } $ \ \rm ms$ |
| − | { | + | {How long does a burst $($one time slot$)$ last? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $ T_{\rm | + | $ T_{\rm burst} \ = \ ${ 576.9 3% } $ \ \rm µ s$ |
| − | { | + | {At what intervals $\Delta T_{\rm burst}$ is a user assigned time slots $($bursts$)$ ? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $\Delta T_{\rm | + | $\Delta T_{\rm burst} \ = \ ${ 4.615 3% } $ \ \rm ms$ |
| − | { | + | {What is the bit duration? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $T_{\rm B} \ = \ ${ 3.692 3% } $ \ \rm | + | $T_{\rm B} \ = \ ${ 3.692 3% } $ \ \rm µ s$ |
| − | { | + | {What is the total bit rate of the GSM? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$R_{\rm B} \ = \ ${ 270.833 3% } $ \ \rm kbit/s $ | $R_{\rm B} \ = \ ${ 270.833 3% } $ \ \rm kbit/s $ | ||
| − | { | + | {What is the gross data rate of a user? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $R_{\rm | + | $R_{\rm gross} \ = \ ${ 33.854 3% } $ \ \rm kbit/s$ |
| − | { | + | {What is the net data rate of one user? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $R_{\rm | + | $R_{\rm net} \ = \ ${ 22.8 3% } $ \ \rm kbtit/s$ |
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1)''' | + | '''(1)''' A superframe consists of $51$ multiframes with respective durations $T_{\rm MF} = 120 \rm ms$. From this follows: |
| − | '''(2)''' | + | :$$T_{\rm SF} = 51 \cdot T_{\rm MF} \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 6.12\,{\rm s}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ |
| − | '''(3)''' | + | |
| − | '''(4)''' | + | |
| − | '''(5)''' | + | '''(2)''' Each multiframe is divided into $26$ TDMA frames $\rm TFs$ according to the specification. Therefore: |
| − | '''(6)''' | + | :$$T_{\rm TF} = \frac{ T_{\rm MF}}{26} = \frac{ 120\,{\rm ms}}{26} \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 4.615\,{\rm ms}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ |
| − | '''(7)''' | + | |
| + | |||
| + | '''(3)''' A TDMA frame consists of $8$ bursts. Therefore | ||
| + | :$$T_{\rm burst} = \frac{ T_{\rm TF}}{8} = \frac{ 4.615\,{\rm ms}}{8} \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 576.9\,{\rm µ s}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(4)''' The spacing of time slots allocated for a user is | ||
| + | :$$\Delta T_{\rm burst} = T_{\rm TF} \underline{= 4.615 \ \rm ms}.$$ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(5)''' Each burst consists - considering the guard period - of $156.25 \ \rm bits$, which must be transmitted within the time duration $T_{\rm burst} = 576.9 \ \rm \mu s$. This results in: | ||
| + | :$$T_{\rm B} = \frac{ T_{\rm burst}}{156.25} = \frac{ 576.9\,{\rm µ s}}{156.25} \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 3.69216\,{\rm µ s}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(6)''' For example, the bit rate can be calculated as the reciprocal of the bit duration: | ||
| + | :$$R_{\rm B} = \frac{ 1}{T_{\rm B}} = \frac{ 1}{3.69216\,{\rm µ s}} \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 270.833\,{\rm kbit/s}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(7)''' In each time slot, the data rate $R_{\rm B} \approx 271 \rm kbit/s$. However, since each user is assigned only one of the eight time slots, the gross data rate of a user is | ||
| + | :$$R_{\rm gross} = \frac{ R_{\rm B}}{8} = \frac{ 270.833\,{\rm kbit/s}}{8} \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 33.854\,{\rm kbit/s}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(8)''' For the net data rate, according to the specifications: | ||
| + | :$$R_{\rm net} = \frac{ 114}{156.25} \cdot R_{\rm B} - 1.9\,{\rm kbit/s} \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 22.8\,{\rm kbit/s}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| + | |||
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Examples of Communication Systems: Exercises|^3.2 Radio Interface^]] |
Latest revision as of 17:02, 16 January 2023
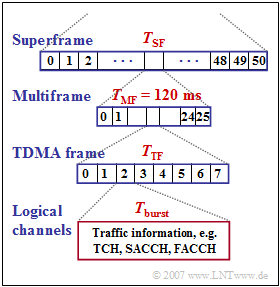
In the 2G cellular mobile communication standard $\rm GSM$ the following frame structure is specified:
- A superframe consists of $51$ multiframes and has duration $T_{\rm SF}$.
- Each multiframe has $26$ TDMA frames and lasts a total of $T_{\rm MF} = 120 \rm ms$.
- Each TDMA frame has duration $T_{\rm TF}$ and is a sequence of eight time slots with duration $T_{\rm burst}$.
- For example, in such a time slot, a "Normal Burst" with $156.25$ bits is transmitted.
- Of these, however, only $114$ are data bits. Further bits are needed for the so called "Guard Period" $\rm (GP)$, signaling, synchronization and channel estimation.
- Further, when calculating the net data rate, it must be taken into account that the logical channels SACCH and IDLE require a total of $1.9 \rm kbit/s$.
It should also be noted that, in addition to the described multiframe structure with $26$ TDMA frames, there are also multiframes with $51$ TDMA frames, but these are used almost exclusively for the transmission of signaling information.
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter "Radio Interface".
- Reference is made in particular to the sectione "GSM frame structure".
Questions
Solution
- $$T_{\rm SF} = 51 \cdot T_{\rm MF} \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 6.12\,{\rm s}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) Each multiframe is divided into $26$ TDMA frames $\rm TFs$ according to the specification. Therefore:
- $$T_{\rm TF} = \frac{ T_{\rm MF}}{26} = \frac{ 120\,{\rm ms}}{26} \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 4.615\,{\rm ms}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(3) A TDMA frame consists of $8$ bursts. Therefore
- $$T_{\rm burst} = \frac{ T_{\rm TF}}{8} = \frac{ 4.615\,{\rm ms}}{8} \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 576.9\,{\rm µ s}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(4) The spacing of time slots allocated for a user is
- $$\Delta T_{\rm burst} = T_{\rm TF} \underline{= 4.615 \ \rm ms}.$$
(5) Each burst consists - considering the guard period - of $156.25 \ \rm bits$, which must be transmitted within the time duration $T_{\rm burst} = 576.9 \ \rm \mu s$. This results in:
- $$T_{\rm B} = \frac{ T_{\rm burst}}{156.25} = \frac{ 576.9\,{\rm µ s}}{156.25} \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 3.69216\,{\rm µ s}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(6) For example, the bit rate can be calculated as the reciprocal of the bit duration:
- $$R_{\rm B} = \frac{ 1}{T_{\rm B}} = \frac{ 1}{3.69216\,{\rm µ s}} \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 270.833\,{\rm kbit/s}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(7) In each time slot, the data rate $R_{\rm B} \approx 271 \rm kbit/s$. However, since each user is assigned only one of the eight time slots, the gross data rate of a user is
- $$R_{\rm gross} = \frac{ R_{\rm B}}{8} = \frac{ 270.833\,{\rm kbit/s}}{8} \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 33.854\,{\rm kbit/s}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(8) For the net data rate, according to the specifications:
- $$R_{\rm net} = \frac{ 114}{156.25} \cdot R_{\rm B} - 1.9\,{\rm kbit/s} \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 22.8\,{\rm kbit/s}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$