Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 1.1Z: ISDN Connection"
From LNTwww
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Signal_Representation/Principles_of_communication}} |
[[File:EN_Sig_Z_1_1.png|right|frame|A telephone connection scenario]] | [[File:EN_Sig_Z_1_1.png|right|frame|A telephone connection scenario]] | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
{Which of the statements are true regarding source and transmitter? | {Which of the statements are true regarding source and transmitter? | ||
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + The message source is the caller. The source signal ${q(t)}$ is the acoustic wave of her | + | + The message source is the caller. The source signal ${q(t)}$ is the acoustic wave of her speech signal. |
+ The unit labelled "transmitter" contains, among other things, a signal converter and a modulator. | + The unit labelled "transmitter" contains, among other things, a signal converter and a modulator. | ||
- The transmitted signal $s(t)$ is analog. | - The transmitted signal $s(t)$ is analog. | ||
Latest revision as of 16:35, 23 January 2023
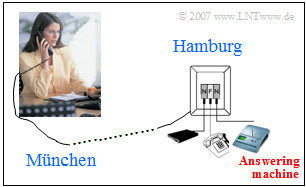
We consider the scenario shown in the picture:
A woman from Munich dials a number in Hamburg with her ISDN phone. However, she cannot reach the person she wants to talk to, so she leaves him a message on tape.
The distortion-free connection is fully described by
- an attenuation coefficient $\alpha$,
- a term $\tau$ and
- the current signal-to-noise ratio (SNR).
Notes: The task shall establish a relation between this real scenario and the functional units of a general communications system mentioned in the theory section .
Questions
Solution
(1) The first two statements are correct:
- The speech signal ${q(t)}$ must first be converted into an electrical signal and then prepared for transmission.
- For ISDN the transmitted signal ${s(t)}$ is digital.
(2) Correct are the solutions 3 and 4:
- The received signal ${r(t)}$ is always analog due to the unavoidable thermal noise.
- The message sink is the answering machine.
- In an ideal transmission system $v(t) = {q(t)}$ should apply.
- However, due to the additive noise term ${n(t)}$, the attenuation $\alpha$ and the delay time $\tau$ the following applies here:
- $$v(t) = \alpha \cdot q ( t - \tau) + n(t).$$
- By our definitions, this is a distortion-free system.