Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 1.1: Multiplexing in the GSM System"
| (10 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | [[File:EN_Mod_A_1_1.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:EN_Mod_A_1_1.png|right|frame|Multiplexing in the GSM system]] |
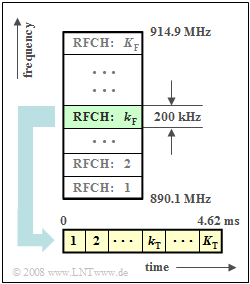
| − | The | + | The "Global System for Mobile Communication" $\rm (GSM)$ standard, which has been established in Europe since 1992, uses both frequency division and time division multiplexing to enable several users to communicate in one cell. |
| − | Some characteristics of the system are given below in somewhat simplified form. A more detailed description can be found in the chapter [[Examples_of_Communication_Systems/Allgemeine_Beschreibung_von_GSM| General Description of GSM]] in the book | + | Some characteristics of the system are given below in a somewhat simplified form. A more detailed description can be found in the chapter [[Examples_of_Communication_Systems/Allgemeine_Beschreibung_von_GSM|General Description of GSM]] in the book "Examples of Communication Systems". |
| − | *The frequency band of the uplink ( | + | *The frequency band of the uplink (connection from the mobile to the base station) is between $\text{890 MHz}$ and $\text{915 MHz}$. |
| − | *This band is used by $K_{\rm F}$ subchannels ( | + | *Taking into account the guard bands $($each $\text{100 kHz)}$ at both ends, a total uplink bandwidth of $\text{24.8 MHz}$ is available. |
| − | * The frequency range for the downlink ( | + | *This band is used by $K_{\rm F}$ subchannels ("Radio Frequency Channels"), which are adjacent in frequency with a respective spacing of $\text{200 kHz}$. The numbering is done with the running variable $k_{\rm F}$, starting with $k_{\rm F} = 1$. |
| − | *Each of these FDMA subchannels is used simultaneously by $K_{\rm T}$ users via TDMA ( | + | * The frequency range for the downlink (connection from the base station to the mobile) is $\text{45 MHz}$ above the uplink and is structured in exactly the same way as the uplink. |
| − | *A time slot of duration $T ≈ 577 \rm µ s$ is available to each user at intervals of $\text{4.62 ms}$ | + | *Each of these FDMA subchannels is used simultaneously by $K_{\rm T}$ users via TDMA ("Time Division Multiple Access"). |
| − | * During this time, the (approximate) $156$ bits describing the | + | *A time slot of duration $T ≈ 577 \ \rm µ s$ is available to each user at intervals of $\text{4.62 ms}$. |
| + | * During this time, the (approximate) $156$ bits describing the speech signal must be transmitted, taking into account data reduction and channel coding. | ||
| Line 21: | Line 22: | ||
| − | + | Hints: | |
| − | *This exercise belongs to the | + | *This exercise belongs to the chapter [[Modulation_Methods/Objectives_of_Modulation_and_Demodulation|Objectives of Modulation and Demodulation]]. |
*Particular reference is made to the pages | *Particular reference is made to the pages | ||
| − | **[[Modulation_Methods/ | + | **[[Modulation_Methods/Objectives_of_Modulation_and_Demodulation#Channel_bundling_.E2.80.93_Frequency_Division_Multiplexing|Channel bundling – Frequency Division Multiplexing]], |
| − | **[[Modulation_Methods/ | + | **[[Modulation_Methods/Objectives_of_Modulation_and_Demodulation#Time_Division_Multiplex_methods|Time Division Multiplex methods]]. |
| Line 31: | Line 32: | ||
===Questions=== | ===Questions=== | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | {How many | + | {How many subchannels result from "Frequency Division Multiplexing"? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$K_{\rm F} \ = \ $ { 124 } | $K_{\rm F} \ = \ $ { 124 } | ||
| − | {What is the | + | {What is the center frequency $f_{\rm M}$ of the "Radio Frequency Channel" in the uplink with number $k_{\rm F} = 100$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$f_{\rm M} \ = \ $ { 910 1% } $\ \rm MHz$ | $f_{\rm M} \ = \ $ { 910 1% } $\ \rm MHz$ | ||
| − | {Which downlink | + | {Which downlink subchannel $($number $k_{\rm F})$ uses the frequency $\text{940 MHz}$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$k_{\rm F} \ = \ $ { 25 } | $k_{\rm F} \ = \ $ { 25 } | ||
| − | {How many | + | {How many subchannels result in GSM through "Time Division Multiplexing"? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$K_{\rm T} \ = \ $ { 8 } | $K_{\rm T} \ = \ $ { 8 } | ||
| − | {How many | + | {How many GSM users can be simultaneously active in one cell? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$K \ = \ $ { 992 1% } | $K \ = \ $ { 992 1% } | ||
| − | {How big is the gross | + | {How big is the gross bit rate for GSM? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $R_{\rm | + | $R_{\rm gross} \ = \ $ { 270 3% } $\ \rm kbit/s$ |
| Line 59: | Line 60: | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1)''' From a total bandwidth of $\text{24.8 MHz}$ and a channel spacing of 200 kHz | + | '''(1)''' From a total bandwidth of $\text{24.8 MHz}$ and a channel spacing of $\text{200 kHz}$ follows: |
:$$K_{\rm F}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 124}.$$ | :$$K_{\rm F}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 124}.$$ | ||
| − | '''(2)''' The | + | '''(2)''' The center frequency of the first channel is $\text{890.2 MHz}$. The "RFCH 100" channel is $\text{ 99 · 200 kHz = 19.8 MHz}$ higher: |
:$$f_{\rm M}= 890.2 \ \rm MHz + 19.8 \ \rm MHz\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 910 \ \rm MHz}.$$ | :$$f_{\rm M}= 890.2 \ \rm MHz + 19.8 \ \rm MHz\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 910 \ \rm MHz}.$$ | ||
| − | '''(3)''' To apply the | + | '''(3)''' To apply the logic from subtask '''(2)''', we transfer the task into the uplink: |
| − | *The same channel with the identifier $k_{\rm F}$, | + | *The same channel with the identifier $k_{\rm F}$, which uses the frequency $\text{940 MHz}$ in the downlink, is located at $\text{895 MHz}$. |
| − | * | + | *Thus: |
:$$k_{\rm F} = 1 + \frac {895 \,\,{\rm MHz } - 890.2 \,\,{\rm MHz } }{0.2 \,\,{\rm MHz }} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 25}.$$ | :$$k_{\rm F} = 1 + \frac {895 \,\,{\rm MHz } - 890.2 \,\,{\rm MHz } }{0.2 \,\,{\rm MHz }} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 25}.$$ | ||
| − | '''(4)''' In | + | '''(4)''' In a TDMA frame of duration $\text{4.62}$ millisekconds, $K_{\rm T}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 8}$ time slots with a respective duration of $T = 577 \ \rm µ s$ can be accommodated. |
| − | :'' | + | :''Note:'' For GSM, $K_{\rm T} = 8$ is actually used. |
| − | '''(5)''' | + | '''(5)''' Using the results of subtasks '''(1)''' und '''(4)''' we obtain: |
:$$K = K_{\rm F} \cdot K_{\rm T} = 124 \cdot 8 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 992}$$ | :$$K = K_{\rm F} \cdot K_{\rm T} = 124 \cdot 8 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 992}$$ | ||
| − | '''(6)''' | + | '''(6)''' Over the course of timespan $T = 577 \ \rm µs$ ⇒ $156$ bits must be transmitted. |
| − | * | + | *Thus, each bit has the time $T_{\rm B} = 3.699 \ \rm µ s$ available. |
| − | * | + | *This results in the (gross) bit rate: |
| − | :$$R_{\rm | + | :$$R_{\rm gross} = \frac {1 }{T_{\rm B}}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 270 \,\,{\rm kbit/s }}.$$ |
| − | * | + | *This gross bit rate includes the training sequence for channel estimation, the redundancy for channel coding in addition to the data representing the speech signal. |
| + | *The net bit rate for the GSM system is only about $\text{13 kbit/s}$ for each of the eight users. | ||
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
Latest revision as of 16:37, 23 January 2023
The "Global System for Mobile Communication" $\rm (GSM)$ standard, which has been established in Europe since 1992, uses both frequency division and time division multiplexing to enable several users to communicate in one cell.
Some characteristics of the system are given below in a somewhat simplified form. A more detailed description can be found in the chapter General Description of GSM in the book "Examples of Communication Systems".
- The frequency band of the uplink (connection from the mobile to the base station) is between $\text{890 MHz}$ and $\text{915 MHz}$.
- Taking into account the guard bands $($each $\text{100 kHz)}$ at both ends, a total uplink bandwidth of $\text{24.8 MHz}$ is available.
- This band is used by $K_{\rm F}$ subchannels ("Radio Frequency Channels"), which are adjacent in frequency with a respective spacing of $\text{200 kHz}$. The numbering is done with the running variable $k_{\rm F}$, starting with $k_{\rm F} = 1$.
- The frequency range for the downlink (connection from the base station to the mobile) is $\text{45 MHz}$ above the uplink and is structured in exactly the same way as the uplink.
- Each of these FDMA subchannels is used simultaneously by $K_{\rm T}$ users via TDMA ("Time Division Multiple Access").
- A time slot of duration $T ≈ 577 \ \rm µ s$ is available to each user at intervals of $\text{4.62 ms}$.
- During this time, the (approximate) $156$ bits describing the speech signal must be transmitted, taking into account data reduction and channel coding.
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter Objectives of Modulation and Demodulation.
- Particular reference is made to the pages
Questions
Solution
- $$K_{\rm F}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 124}.$$
(2) The center frequency of the first channel is $\text{890.2 MHz}$. The "RFCH 100" channel is $\text{ 99 · 200 kHz = 19.8 MHz}$ higher:
- $$f_{\rm M}= 890.2 \ \rm MHz + 19.8 \ \rm MHz\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 910 \ \rm MHz}.$$
(3) To apply the logic from subtask (2), we transfer the task into the uplink:
- The same channel with the identifier $k_{\rm F}$, which uses the frequency $\text{940 MHz}$ in the downlink, is located at $\text{895 MHz}$.
- Thus:
- $$k_{\rm F} = 1 + \frac {895 \,\,{\rm MHz } - 890.2 \,\,{\rm MHz } }{0.2 \,\,{\rm MHz }} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 25}.$$
(4) In a TDMA frame of duration $\text{4.62}$ millisekconds, $K_{\rm T}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 8}$ time slots with a respective duration of $T = 577 \ \rm µ s$ can be accommodated.
- Note: For GSM, $K_{\rm T} = 8$ is actually used.
(5) Using the results of subtasks (1) und (4) we obtain:
- $$K = K_{\rm F} \cdot K_{\rm T} = 124 \cdot 8 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 992}$$
(6) Over the course of timespan $T = 577 \ \rm µs$ ⇒ $156$ bits must be transmitted.
- Thus, each bit has the time $T_{\rm B} = 3.699 \ \rm µ s$ available.
- This results in the (gross) bit rate:
- $$R_{\rm gross} = \frac {1 }{T_{\rm B}}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 270 \,\,{\rm kbit/s }}.$$
- This gross bit rate includes the training sequence for channel estimation, the redundancy for channel coding in addition to the data representing the speech signal.
- The net bit rate for the GSM system is only about $\text{13 kbit/s}$ for each of the eight users.