Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 2.2: Kraft–McMillan Inequality"
| (25 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Information_Theory/General_Description |
}} | }} | ||
| − | [[File:P_ID2416__Inf_A_2_2.png|right| | + | [[File:P_ID2416__Inf_A_2_2.png|right|frame|Four examples of binary codes and three ternary codes]] |
| − | In | + | In the figure some exemplary binary and ternary codes are given. |
| − | + | *With the binary code $\rm B1$ all possible source symbols $q_\mu$ $($with index $\mu = 1$, ... , $8)$ are represented by a encoded sequence $\langle c_\mu \rangle $ of uniform length $L_\mu = 3$ . | |
| + | *This code is unsuitable for data compression for this reason. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | The possibility of data compression arises only when | ||
| + | *the $M$ source symbols are not equally likely, and | ||
| + | *the length $L_\mu$ of the code words are different. | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | For example, the binary code $\rm B2$ has this property: | |
| + | *Here, one code word each has the length $1$, $2$ and $3$, respectively $(N_1 = 1,\ N_2 = 2,\ N_3 = 3)$. | ||
| + | *Two code words have the length $L_\mu = 4$ $(N_4 = N_5 = 4)$. | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | A prerequisite for the decodability of such a code is that the code is '''prefix-free''' . | ||
| + | *That is, no code word may be the prefix (i.e., the beginning) of a longer code word. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *A necessary condition for a code for data compression to be prefix-free was stated by Leon Kraft in 1949, called '''Kraft's inequality''': | ||
:$$\sum_{\mu=1}^{M} \hspace{0.2cm} D^{-L_{\mu}} \le 1 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$\sum_{\mu=1}^{M} \hspace{0.2cm} D^{-L_{\mu}} \le 1 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | Here denote | |
| − | * $M$ | + | * $M$ the number of possible source symbols $q_\mu$ ⇒ "symbol set size", |
| − | * $L_\mu$ | + | * $L_\mu$ the length of the code word $c_\mu$ associated with the source symbol $q_\mu$, |
| − | * $D = 2$ | + | * $D = 2$ denotes a binary code $(\rm 0$ or $\rm 1)$ and $D = 3$ denotes a ternary code $(\rm 0$, $\rm 1$, $\rm 2)$. |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | A code can be prefix-free only if Kraft's inequality is satisfied. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The converse does not hold: If Kraft's inequality is satisfied, it does not mean that this code is actually prefix-free. | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | Hint: | |
| − | * | + | *The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Information_Theory/Allgemeine_Beschreibung|General Description of Source Coding]]. |
| − | + | ||
| − | === | + | ===Question=== |
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {Which of the binary codes satisfy Kraft's inequality? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + B1, | + | + $\rm B1$, |
| − | + B2, | + | + $\rm B2$, |
| − | + | + $\rm B3$, | |
| − | - B4. | + | - $\rm B4$. |
| − | { | + | {Which of the given binary codes are prefix-free? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + B1, | + | + $\rm B1$, |
| − | + B2, | + | + $\rm B2$, |
| − | - B3, | + | - $\rm B3$, |
| − | - B4. | + | - $\rm B4$. |
| − | { | + | {Which of the given ternary codes are prefix-free? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + T1, | + | + $\rm T1$, |
| − | - T2, | + | - $\rm T2$, |
| − | + T3. | + | + $\rm T3$. |
| − | { | + | {What are the characteristics of the ternary code $\rm T1$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $ N_1 \ = $ { 1 } | + | $ N_1 \ = \ $ { 1 } |
| − | $ N_2 \ = $ { 2 } | + | $ N_2 \ = \ $ { 2 } |
| − | $ N_3 \ = $ { 6 } | + | $ N_3 \ = \ $ { 6 } |
| − | { | + | {How many trivalent code words $(L_\mu = 3)$ could be added to the $\rm T1$ code without changing the prefix freedom? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $ | + | $\Delta N_3 \ = \ $ { 6 } |
| − | { | + | {The ternary code $\rm T3$ is to be expanded to a total of $N = 9$ code words. How to achieve this without violating the prefix freedom? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - | + | - Addition of four three-valued code words. |
| − | + | + | + Addition of four four-valued code words. |
| − | + | + | + Addition of one trivalent and three tetravalent code words. |
| Line 83: | Line 93: | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | + | '''(1)''' The correct <u>solutions are 1, 2 and 3.</u> The following applies to the binary codes given: | |
| + | * $\rm B1$: $8 \cdot 2^{-3} = 1$ ⇒ condition fulfilled, | ||
| + | * $\rm B2$: $1 \cdot 2^{-1} + 1 \cdot 2^{-2} + 1 \cdot 2^{-3} + 2 \cdot 2^{-4}= 1$ ⇒ condition fulfilled, | ||
| + | * $\rm B3$: $1 \cdot 2^{-1} + 1 \cdot 2^{-2} + 1 \cdot 2^{-3} + 2 \cdot 2^{-4}= 1$ ⇒ condition fulfilled, | ||
| + | * $\rm B4$: $1 \cdot 2^{-1} + 1 \cdot 2^{-2} + 2 \cdot 2^{-3} + 1 \cdot 2^{-4}= 17/16$ ⇒ condition <u>not</u> fulfilled. | ||
| + | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''(2)''' <u>Proposed solutions 1 and 2</u> are correct: | |
| + | *The code $\rm B4$, which does not satisfy Kraft's inequality, is certainly not prefix-free either. | ||
| + | *But if Kraft's inequality is fulfilled, it is still not certain that this code is also prefix-free. | ||
| + | *In code $\rm B3$ the code word "10" is the beginning of the code word "1011". | ||
| + | *In contrast, codes $\rm B1$ and $\rm B2$ are actually prefix-free. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''(3)''' The correct <u>solutions are 1 and 3</u>: | |
| + | *Kraft's inequality is satisfied by all three codes. | ||
| + | *As can be seen from the table, codes $\rm T1$ and $\rm T3$ are indeed prefix-free. | ||
| + | *The code $\rm T2$ , on the other hand, is not prefix-free because "1" is the beginning of the code word "10". | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | ||
| + | '''(4)''' $N_i$ indicates how many code words with $i$ symbols there are in the code. For the code $\rm T1$ it is: | ||
:$$N_1 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 1}\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm}N_2 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 2}\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm}N_3 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 6}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$N_1 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 1}\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm}N_2 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 2}\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm}N_3 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 6}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''(5)''' According to Kraft's inequality, the following must be true | ||
:$$N_1 \cdot 3^{-1} + N_2 \cdot 3^{-2} + N_3 \cdot 3^{-3 } \le 1\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$N_1 \cdot 3^{-1} + N_2 \cdot 3^{-2} + N_3 \cdot 3^{-3 } \le 1\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | For given $N_1 = 1$ and $N_2 = 2$ , this is satisfied as long as holds: | |
:$$N_3 \cdot 3^{-3 } \le 1 - 1/3 - 2/9 = 4/9 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}N_3 \le 12 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm \Delta}\,N_3 | :$$N_3 \cdot 3^{-3 } \le 1 - 1/3 - 2/9 = 4/9 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}N_3 \le 12 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm \Delta}\,N_3 | ||
\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 6}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 6}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | The additional code words are $\rm 210, \,211, \,212, \,220, \,221, \,222$. | |
| + | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''(6)''' For code $\rm T3$ it holds: | |
| − | + | *$S({\rm T3})= 2 \cdot 3^{-1} + 2 \cdot 3^{-2} + 1 \cdot 3^{-3 } = {25}/{27}\hspace{0.05cm}.$ | |
| + | *Because of $S({\rm T3}) \le 1$ the ternary code $\rm T3$ satisfies Kraft's inequality and it is also prefix-free. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Let us now consider the proposed new codes. | |
| − | :$$S({\rm T6})= S({\rm T3}) + 1 \cdot 3^{-3 } + 3 \cdot 3^{-4 } = \frac{75 + 3 + 3}{81}\hspace{0.1cm} = \hspace{0.1cm}1\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm T6 \hspace{0.15cm} | + | * Code $\rm T4$ $(N_1 = 2, \ N_2 = 2, \ N_3 = 5)$: |
| + | :$$S({\rm T4})= S({\rm T3}) + 4 \cdot 3^{-3 } = {29}/{27}\hspace{0.1cm} > \hspace{0.1cm}1\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm T4 \hspace{0.15cm}is\hspace{0.15cm} unsuitable}\hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
| + | * Code $\rm T5$ $(N_1 = 2, \ N_2 = 2, \ N_3 = 1, \ N_4 = 4)$: | ||
| + | :$$S({\rm T5})= S({\rm T3}) + 4 \cdot 3^{-4 } = {79}/{81}\hspace{0.1cm} < \hspace{0.1cm}1\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm T5 \hspace{0.15cm}is\hspace{0.15cm} suitable}\hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
| + | * Code $\rm T6$ $(N_1 = 2, \ N_2 = 2, \ N_3 = 2, \ N_4 = 3)$: | ||
| + | :$$S({\rm T6})= S({\rm T3}) + 1 \cdot 3^{-3 } + 3 \cdot 3^{-4 } = \frac{75 + 3 + 3}{81}\hspace{0.1cm} = \hspace{0.1cm}1\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm T6 \hspace{0.15cm}is\hspace{0.15cm} suitable}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | Thus, <u>the two last proposed solutions</u> are correct. | |
| + | |||
| + | For example, the total $N = 9$ code words of the prefix-free code $\rm T6$ are: | ||
| + | :$$\rm 0, \, 1, \, 20, \,21, \,220, \,221, \,2220, \, 2221 , \,2222.$$ | ||
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Information Theory: Exercises|^2.1 General Description^]] |
Latest revision as of 15:52, 1 November 2022
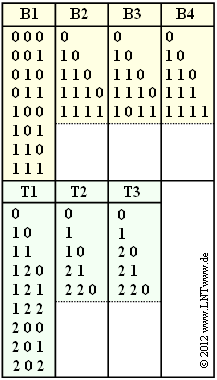
In the figure some exemplary binary and ternary codes are given.
- With the binary code $\rm B1$ all possible source symbols $q_\mu$ $($with index $\mu = 1$, ... , $8)$ are represented by a encoded sequence $\langle c_\mu \rangle $ of uniform length $L_\mu = 3$ .
- This code is unsuitable for data compression for this reason.
The possibility of data compression arises only when
- the $M$ source symbols are not equally likely, and
- the length $L_\mu$ of the code words are different.
For example, the binary code $\rm B2$ has this property:
- Here, one code word each has the length $1$, $2$ and $3$, respectively $(N_1 = 1,\ N_2 = 2,\ N_3 = 3)$.
- Two code words have the length $L_\mu = 4$ $(N_4 = N_5 = 4)$.
A prerequisite for the decodability of such a code is that the code is prefix-free .
- That is, no code word may be the prefix (i.e., the beginning) of a longer code word.
- A necessary condition for a code for data compression to be prefix-free was stated by Leon Kraft in 1949, called Kraft's inequality:
- $$\sum_{\mu=1}^{M} \hspace{0.2cm} D^{-L_{\mu}} \le 1 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Here denote
- $M$ the number of possible source symbols $q_\mu$ ⇒ "symbol set size",
- $L_\mu$ the length of the code word $c_\mu$ associated with the source symbol $q_\mu$,
- $D = 2$ denotes a binary code $(\rm 0$ or $\rm 1)$ and $D = 3$ denotes a ternary code $(\rm 0$, $\rm 1$, $\rm 2)$.
A code can be prefix-free only if Kraft's inequality is satisfied.
The converse does not hold: If Kraft's inequality is satisfied, it does not mean that this code is actually prefix-free.
Hint:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter General Description of Source Coding.
Question
Solution
- $\rm B1$: $8 \cdot 2^{-3} = 1$ ⇒ condition fulfilled,
- $\rm B2$: $1 \cdot 2^{-1} + 1 \cdot 2^{-2} + 1 \cdot 2^{-3} + 2 \cdot 2^{-4}= 1$ ⇒ condition fulfilled,
- $\rm B3$: $1 \cdot 2^{-1} + 1 \cdot 2^{-2} + 1 \cdot 2^{-3} + 2 \cdot 2^{-4}= 1$ ⇒ condition fulfilled,
- $\rm B4$: $1 \cdot 2^{-1} + 1 \cdot 2^{-2} + 2 \cdot 2^{-3} + 1 \cdot 2^{-4}= 17/16$ ⇒ condition not fulfilled.
(2) Proposed solutions 1 and 2 are correct:
- The code $\rm B4$, which does not satisfy Kraft's inequality, is certainly not prefix-free either.
- But if Kraft's inequality is fulfilled, it is still not certain that this code is also prefix-free.
- In code $\rm B3$ the code word "10" is the beginning of the code word "1011".
- In contrast, codes $\rm B1$ and $\rm B2$ are actually prefix-free.
(3) The correct solutions are 1 and 3:
- Kraft's inequality is satisfied by all three codes.
- As can be seen from the table, codes $\rm T1$ and $\rm T3$ are indeed prefix-free.
- The code $\rm T2$ , on the other hand, is not prefix-free because "1" is the beginning of the code word "10".
(4) $N_i$ indicates how many code words with $i$ symbols there are in the code. For the code $\rm T1$ it is:
- $$N_1 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 1}\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm}N_2 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 2}\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm}N_3 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 6}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(5) According to Kraft's inequality, the following must be true
- $$N_1 \cdot 3^{-1} + N_2 \cdot 3^{-2} + N_3 \cdot 3^{-3 } \le 1\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
For given $N_1 = 1$ and $N_2 = 2$ , this is satisfied as long as holds:
- $$N_3 \cdot 3^{-3 } \le 1 - 1/3 - 2/9 = 4/9 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}N_3 \le 12 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm \Delta}\,N_3 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 6}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The additional code words are $\rm 210, \,211, \,212, \,220, \,221, \,222$.
(6) For code $\rm T3$ it holds:
- $S({\rm T3})= 2 \cdot 3^{-1} + 2 \cdot 3^{-2} + 1 \cdot 3^{-3 } = {25}/{27}\hspace{0.05cm}.$
- Because of $S({\rm T3}) \le 1$ the ternary code $\rm T3$ satisfies Kraft's inequality and it is also prefix-free.
Let us now consider the proposed new codes.
- Code $\rm T4$ $(N_1 = 2, \ N_2 = 2, \ N_3 = 5)$:
- $$S({\rm T4})= S({\rm T3}) + 4 \cdot 3^{-3 } = {29}/{27}\hspace{0.1cm} > \hspace{0.1cm}1\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm T4 \hspace{0.15cm}is\hspace{0.15cm} unsuitable}\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- Code $\rm T5$ $(N_1 = 2, \ N_2 = 2, \ N_3 = 1, \ N_4 = 4)$:
- $$S({\rm T5})= S({\rm T3}) + 4 \cdot 3^{-4 } = {79}/{81}\hspace{0.1cm} < \hspace{0.1cm}1\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm T5 \hspace{0.15cm}is\hspace{0.15cm} suitable}\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- Code $\rm T6$ $(N_1 = 2, \ N_2 = 2, \ N_3 = 2, \ N_4 = 3)$:
- $$S({\rm T6})= S({\rm T3}) + 1 \cdot 3^{-3 } + 3 \cdot 3^{-4 } = \frac{75 + 3 + 3}{81}\hspace{0.1cm} = \hspace{0.1cm}1\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm T6 \hspace{0.15cm}is\hspace{0.15cm} suitable}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Thus, the two last proposed solutions are correct.
For example, the total $N = 9$ code words of the prefix-free code $\rm T6$ are:
- $$\rm 0, \, 1, \, 20, \,21, \,220, \,221, \,2220, \, 2221 , \,2222.$$