Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 4.8: Different Error Probabilities"
| (9 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Modulation_Methods/Linear_Digital_Modulation |
}} | }} | ||
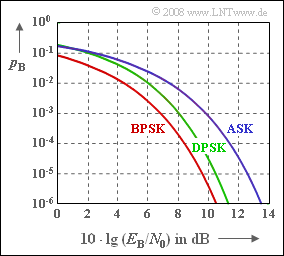
| − | [[File:P_ID1703__Mod_A_4_7.png|right|frame|AWGN | + | [[File:P_ID1703__Mod_A_4_7.png|right|frame|AWGN error probability curves of <br>ASK, BPSK and DPSK]] |
| − | + | Here, the bit error probabilities $p_{\rm B}$ of the digital modulation methods ASK and BPSK are given without further derivation. For example, with the so-called Q function, | |
| − | :$$ {\rm Q} (x) = \frac{\rm 1}{\sqrt{\rm 2\pi}}\cdot \int_{\it x}^{+\infty}\rm e^{\it -u^{\rm 2}/\rm 2}\,d \it u$$ | + | :$$ {\rm Q} (x) = \frac{\rm 1}{\sqrt{\rm 2\pi}}\cdot \int_{\it x}^{+\infty}\rm e^{\it -u^{\rm 2}/\rm 2}\,d \it u,$$ |
| − | + | one obtains for the AWGN channel – characterized by the quotient $E_{\rm B}/N_0$ – and further optimal conditions (for example coherent demodulation) | |
| − | * | + | * for "Amplitude Shift Keying" $\rm (ASK)$: |
:$$ p_{\rm B} = {\rm Q}\left ( \sqrt{{E_{\rm B}}/{N_0 }} \hspace{0.1cm}\right ) \hspace{0.05cm},$$ | :$$ p_{\rm B} = {\rm Q}\left ( \sqrt{{E_{\rm B}}/{N_0 }} \hspace{0.1cm}\right ) \hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
| − | * | + | * for "Binary Phase Shift Keying" $\rm (BPSK)$: |
:$$ p_{\rm B} = {\rm Q}\left ( \sqrt{{2 \cdot E_{\rm B}}/{N_0 }} \hspace{0.1cm}\right ) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$ p_{\rm B} = {\rm Q}\left ( \sqrt{{2 \cdot E_{\rm B}}/{N_0 }} \hspace{0.1cm}\right ) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | * for "Differential Phase Shift Keying" $\rm (DPSK)$ with differential coherent demodulation is: | |
| − | |||
:$$p_{\rm B} ={1}/{2} \cdot {\rm e}^{- E_{\rm B}/{N_0 }}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$p_{\rm B} ={1}/{2} \cdot {\rm e}^{- E_{\rm B}/{N_0 }}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | :However, ASK could also be demodulated non-coherently. In this case the following would apply: | |
:$$ p_{\rm B} = {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm e}^{- E_{\rm B}/(2{N_0 })}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$ p_{\rm B} = {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm e}^{- E_{\rm B}/(2{N_0 })}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | The first three error probabilities are shown in the diagram. For example, for $10 · \lg E_{\rm B}/N_0 = 10 \ \rm dB$ corresponding to the exact functions, one obtains: | |
:$$ p_{\rm B} = 7.83 \cdot 10^{-4}\,\,{\rm (ASK)}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm} p_{\rm B} = 3.87 \cdot 10^{-6}\,\,{\rm (BPSK)}\hspace{0.05cm},$$ | :$$ p_{\rm B} = 7.83 \cdot 10^{-4}\,\,{\rm (ASK)}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm} p_{\rm B} = 3.87 \cdot 10^{-6}\,\,{\rm (BPSK)}\hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
| − | + | For BPSK to reach or fall below the bit error probability $p_{\rm B} = 10^{–5}$ ⇒ $10 · \lg E_{\rm B}/N_0 \ge 9.6 \ \rm dB$. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| Line 27: | Line 23: | ||
| − | + | Notes: | |
| − | * | + | *The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Modulation_Methods/Linear_Digital_Modulation|Linear Digital Modulation]]. |
| − | * | + | *Reference is made in particular to the section [[Modulation_Methods/Linear_Digital_Modulation#Error_probabilities_-_a_brief_overview|Error probabilities - a brief overview]]. |
| − | * | + | *The derivations can be found in the chapter [[Digital_Signal_Transmission/Lineare_digitale_Modulation_–_Kohärente_Demodulation|Linear Digital Modulation - Coherent Demodulation]] of the book "Digital Signal Transmission". |
| − | + | *For numerical evaluations, you can use the following upper bound: | |
| − | * | + | :$$ {\rm Q}_{\rm S} (x) = \frac{\rm 1}{\sqrt{\rm 2\pi} \cdot x}\cdot \rm e^{\it -x^{\rm 2}/\rm 2} \ge {\rm Q} ({\it x})\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ |
| − | :$$ {\rm Q}_{\rm S} (x) = \frac{\rm 1}{\sqrt{\rm 2\pi} \cdot x}\cdot \rm e^{\it -x^{\rm 2}/\rm 2} \ge {\rm Q} (x)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | === | + | ===Questions=== |
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {Calculate the '''ASK''' bit error probability for $10 · \lg E_{\rm B}/N_0 = 10 \ \rm dB$ using the upper bound ${\rm Q_S}(x)$. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$p_{\rm B} \ = \ $ { 85 3% } $\ \cdot 10^{-5}$ | $p_{\rm B} \ = \ $ { 85 3% } $\ \cdot 10^{-5}$ | ||
| − | { | + | {Calculate the '''BPSK''' bit error probability for $10 · \lg E_{\rm B}/N_0 = 10 \ \rm dB$ using the upper bound ${\rm Q_S}(x)$. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$p_{\rm B} \ = \ $ { 0.405 3% } $\ \cdot 10^{-5}$ | $p_{\rm B} \ = \ $ { 0.405 3% } $\ \cdot 10^{-5}$ | ||
| − | { | + | {Specify the minimum value for $E_{\rm B}/N_0$ (in dB) for '''ASK''' to achieve the bit error probability $p_{\rm B} = 10^{–5}$. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$10 · \lg E_{\rm B}/N_0 \ = \ $ { 12.6 3% } $\ \rm dB$ | $10 · \lg E_{\rm B}/N_0 \ = \ $ { 12.6 3% } $\ \rm dB$ | ||
| − | { | + | {Calculate the '''DPSK''' bit error probability for $10 · \lg E_{\rm B}/N_0 = 10 \ \rm dB$. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$p_{\rm B} \ = \ $ { 2.27 3% } $\ \cdot 10^{-5}$ | $p_{\rm B} \ = \ $ { 2.27 3% } $\ \cdot 10^{-5}$ | ||
| − | { | + | {For '''DPSK''', specify the minimum value for $E_{\rm B}/N_0$ (in dB) to achieve the bit error probability $p_{\rm B} = 10^{–5}$. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$10 · \lg E_{\rm B}/N_0 \ = \ $ { 10.4 3% } $\ \rm dB$ | $10 · \lg E_{\rm B}/N_0 \ = \ $ { 10.4 3% } $\ \rm dB$ | ||
| − | { | + | {On the other hand, what $E_{\rm B}/N_0$ (in dB) is needed for '''incoherent ASK''' to achieve $p_{\rm B} = 10^{–5}$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$10 · \lg E_{\rm B}/N_0 \ = \ $ { 13.4 3% } $\ \rm dB$ | $10 · \lg E_{\rm B}/N_0 \ = \ $ { 13.4 3% } $\ \rm dB$ | ||
| Line 69: | Line 64: | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1)''' | + | '''(1)''' From $10 · \lg E_{\rm B}/N_0 = 10 \ \rm dB$ follows $ E_{\rm B}/N_0 = 10 $ and thus |
:$$p_{\rm B} = {\rm Q}\left ( \sqrt{10} \right ) \approx {\rm Q_{\rm S}}\left ( \sqrt{10} \right )= \frac{\rm 1}{\sqrt{\rm 20\pi} }\cdot \rm e^{-5 }\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 85 \cdot 10^{-5}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$p_{\rm B} = {\rm Q}\left ( \sqrt{10} \right ) \approx {\rm Q_{\rm S}}\left ( \sqrt{10} \right )= \frac{\rm 1}{\sqrt{\rm 20\pi} }\cdot \rm e^{-5 }\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 85 \cdot 10^{-5}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *The actual value according to the specification sheet is $78.3 · 10^{–5}$. |
| − | * | + | *Thus, the given equation ${\rm Q_S}(x)$ is actually an upper bound for ${\rm Q}(x)$. |
| − | * | + | *The relative error of using ${\rm Q_S}(x)$ instead of ${\rm Q}(x)$ in this case is less than $10\%$. |
| − | '''(2)''' | + | '''(2)''' For BPSK, the corresponding equation is: |
:$$ p_{\rm B} = {\rm Q}\left ( \sqrt{20} \right ) \approx {\rm Q_{\rm S}}\left ( \sqrt{20} \right )= \frac{\rm 1}{\sqrt{\rm 40\pi} }\cdot \rm e^{-10 }\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 0.405 \cdot 10^{-5}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$ p_{\rm B} = {\rm Q}\left ( \sqrt{20} \right ) \approx {\rm Q_{\rm S}}\left ( \sqrt{20} \right )= \frac{\rm 1}{\sqrt{\rm 40\pi} }\cdot \rm e^{-10 }\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 0.405 \cdot 10^{-5}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *Now, by using ${\rm Q_S}(x)$, the relative error is only $5 \%$. |
| − | * | + | *In general: The smaller the error probability, the better the approximation ${\rm Q}(x) ≈ {\rm Q_S}(x)$. |
| − | '''(3)''' | + | '''(3)''' For BPSK, according to the specification, a (logarithmized) value of $9.6\ \rm dB$ is required for this. |
| − | * | + | *For ASK, the logarithmized value must be increased by about $3\ \rm dB$ ⇒ $10 · \lg E_{\rm B}/N_0 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 12.6 \ \rm dB}$. |
| − | '''(4)''' | + | '''(4)''' According to the given DPSK equation, with $ E_{\rm B}/N_0 = 10 $: |
:$$p_{\rm B} = {\rm 1}/{2 }\cdot \rm e^{-10 }\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 2.27 \cdot 10^{-5}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$p_{\rm B} = {\rm 1}/{2 }\cdot \rm e^{-10 }\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 2.27 \cdot 10^{-5}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *As can already be seen from the diagram on the specification page, DPSK with differential coherent demodulation lies between binary phase modulation (BPSK) and binary amplitude modulation (ASK) when coherent demodulation is provided for both. |
| − | '''(5)''' | + | '''(5)''' From the inverse function of the given equation, we obtain: |
:$$ \frac{E_{\rm B}} {N_{\rm 0}}= {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{2 p_{\rm B}}= {\rm ln}(50000)\approx 10.82 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} 10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{E_{\rm B}} {N_{\rm 0}}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 10.4\,\,{\rm dB}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$ \frac{E_{\rm B}} {N_{\rm 0}}= {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{2 p_{\rm B}}= {\rm ln}(50000)\approx 10.82 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} 10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{E_{\rm B}} {N_{\rm 0}}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 10.4\,\,{\rm dB}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | '''(6)''' | + | '''(6)''' The incoherent ASK is again $3\ \rm dB$ worse than the differential coherent DPSK according to the equations given. From this it follows for the sought dB value: |
:$$10 · \lg E_{\rm B}/N_0 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {≈ 13.4 \ \rm dB}.$$ | :$$10 · \lg E_{\rm B}/N_0 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {≈ 13.4 \ \rm dB}.$$ | ||
| Line 109: | Line 104: | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Modulation Methods: Exercises|^4.2 Linear Digital Modulation^]] |
Latest revision as of 15:42, 15 April 2022
Here, the bit error probabilities $p_{\rm B}$ of the digital modulation methods ASK and BPSK are given without further derivation. For example, with the so-called Q function,
- $$ {\rm Q} (x) = \frac{\rm 1}{\sqrt{\rm 2\pi}}\cdot \int_{\it x}^{+\infty}\rm e^{\it -u^{\rm 2}/\rm 2}\,d \it u,$$
one obtains for the AWGN channel – characterized by the quotient $E_{\rm B}/N_0$ – and further optimal conditions (for example coherent demodulation)
- for "Amplitude Shift Keying" $\rm (ASK)$:
- $$ p_{\rm B} = {\rm Q}\left ( \sqrt{{E_{\rm B}}/{N_0 }} \hspace{0.1cm}\right ) \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- for "Binary Phase Shift Keying" $\rm (BPSK)$:
- $$ p_{\rm B} = {\rm Q}\left ( \sqrt{{2 \cdot E_{\rm B}}/{N_0 }} \hspace{0.1cm}\right ) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- for "Differential Phase Shift Keying" $\rm (DPSK)$ with differential coherent demodulation is:
- $$p_{\rm B} ={1}/{2} \cdot {\rm e}^{- E_{\rm B}/{N_0 }}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- However, ASK could also be demodulated non-coherently. In this case the following would apply:
- $$ p_{\rm B} = {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm e}^{- E_{\rm B}/(2{N_0 })}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The first three error probabilities are shown in the diagram. For example, for $10 · \lg E_{\rm B}/N_0 = 10 \ \rm dB$ corresponding to the exact functions, one obtains:
- $$ p_{\rm B} = 7.83 \cdot 10^{-4}\,\,{\rm (ASK)}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm} p_{\rm B} = 3.87 \cdot 10^{-6}\,\,{\rm (BPSK)}\hspace{0.05cm},$$
For BPSK to reach or fall below the bit error probability $p_{\rm B} = 10^{–5}$ ⇒ $10 · \lg E_{\rm B}/N_0 \ge 9.6 \ \rm dB$.
Notes:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter Linear Digital Modulation.
- Reference is made in particular to the section Error probabilities - a brief overview.
- The derivations can be found in the chapter Linear Digital Modulation - Coherent Demodulation of the book "Digital Signal Transmission".
- For numerical evaluations, you can use the following upper bound:
- $$ {\rm Q}_{\rm S} (x) = \frac{\rm 1}{\sqrt{\rm 2\pi} \cdot x}\cdot \rm e^{\it -x^{\rm 2}/\rm 2} \ge {\rm Q} ({\it x})\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Questions
Solution
- $$p_{\rm B} = {\rm Q}\left ( \sqrt{10} \right ) \approx {\rm Q_{\rm S}}\left ( \sqrt{10} \right )= \frac{\rm 1}{\sqrt{\rm 20\pi} }\cdot \rm e^{-5 }\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 85 \cdot 10^{-5}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The actual value according to the specification sheet is $78.3 · 10^{–5}$.
- Thus, the given equation ${\rm Q_S}(x)$ is actually an upper bound for ${\rm Q}(x)$.
- The relative error of using ${\rm Q_S}(x)$ instead of ${\rm Q}(x)$ in this case is less than $10\%$.
(2) For BPSK, the corresponding equation is:
- $$ p_{\rm B} = {\rm Q}\left ( \sqrt{20} \right ) \approx {\rm Q_{\rm S}}\left ( \sqrt{20} \right )= \frac{\rm 1}{\sqrt{\rm 40\pi} }\cdot \rm e^{-10 }\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 0.405 \cdot 10^{-5}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Now, by using ${\rm Q_S}(x)$, the relative error is only $5 \%$.
- In general: The smaller the error probability, the better the approximation ${\rm Q}(x) ≈ {\rm Q_S}(x)$.
(3) For BPSK, according to the specification, a (logarithmized) value of $9.6\ \rm dB$ is required for this.
- For ASK, the logarithmized value must be increased by about $3\ \rm dB$ ⇒ $10 · \lg E_{\rm B}/N_0 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 12.6 \ \rm dB}$.
(4) According to the given DPSK equation, with $ E_{\rm B}/N_0 = 10 $:
- $$p_{\rm B} = {\rm 1}/{2 }\cdot \rm e^{-10 }\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 2.27 \cdot 10^{-5}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- As can already be seen from the diagram on the specification page, DPSK with differential coherent demodulation lies between binary phase modulation (BPSK) and binary amplitude modulation (ASK) when coherent demodulation is provided for both.
(5) From the inverse function of the given equation, we obtain:
- $$ \frac{E_{\rm B}} {N_{\rm 0}}= {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{2 p_{\rm B}}= {\rm ln}(50000)\approx 10.82 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} 10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{E_{\rm B}} {N_{\rm 0}}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 10.4\,\,{\rm dB}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(6) The incoherent ASK is again $3\ \rm dB$ worse than the differential coherent DPSK according to the equations given. From this it follows for the sought dB value:
- $$10 · \lg E_{\rm B}/N_0 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {≈ 13.4 \ \rm dB}.$$