Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 2.1Z: Sum Signal"
m (Oezdemir moved page Aufgabe 2.1Z: Summensignal to Exercise 2.1Z: Summing Signal) |
|||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
}} | }} | ||
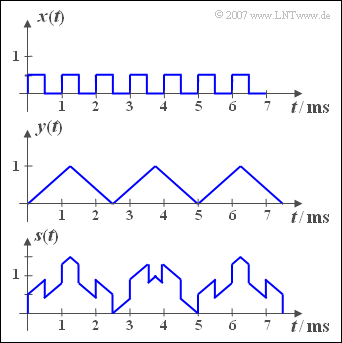
| − | [[File:P_ID319__Sig_Z_2_1.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID319__Sig_Z_2_1.png|right|frame|Rectangular signal, triangular signal, sum signal]] |
| − | + | The adjacent diagram shows the periodic signals ${x(t)}$ and ${y(t)}$, from which the sum ${s(t)}$ – sketched in the lower diagram – and the difference ${d(t)}$ are formed. | |
| − | + | Furthermore, in this task we consider the signal ${w(t)}$, which results from the sum of two periodic signals ${u(t)}$ and $v(t)$ . The base frequencies of these signals are | |
:* $f_u = 998 \,\text{Hz},$ | :* $f_u = 998 \,\text{Hz},$ | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
:* $f_v = 1002 \,\text{Hz}.$ | :* $f_v = 1002 \,\text{Hz}.$ | ||
| − | + | That is all we know about the signals ${u(t)}$ and $v(t)$. | |
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
| − | '' | + | ''Hints:'' |
| − | * | + | *The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Signal_Representation/General_Description|General description of periodic signals]]. |
| − | * | + | *With the interactive applet [[Applets:Period_Duration_of_Periodic_Signals|Period Duration of Periodic Signals]] the resulting period duration of two harmonic oscillations can be determined. |
| − | === | + | ===Questions=== |
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {What is the period duration $T_x$ and the basic frequency $f_x$ of the signal ${x(t)}$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$f_x\ = \ $ { 1 3% } $\text{kHz}$ | $f_x\ = \ $ { 1 3% } $\text{kHz}$ | ||
| − | { | + | {What is the period duration $T_y$ and the basic frequency $f_y$ of the signal ${y(t)}$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$f_y\ = \ $ { 0.4 3% } $\text{kHz}$ | $f_y\ = \ $ { 0.4 3% } $\text{kHz}$ | ||
| − | { | + | {Determine the basic frequency $f_s$ and the period duration $T_s$ of the sum signal ${s(t)}$. <br>Verify your results with the help of the sketched signal. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$T_s\ = \ $ { 5 3% } $\text{ms}$ | $T_s\ = \ $ { 5 3% } $\text{ms}$ | ||
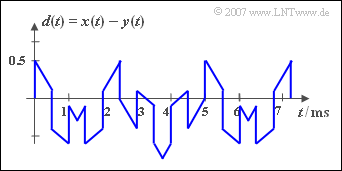
| − | { | + | {What is the period duration $T_d$ of the difference signal ${d(t)}$ ? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$T_d\ = \ $ { 5 3% } $\text{ms}$ | $T_d\ = \ $ { 5 3% } $\text{ms}$ | ||
| − | { | + | {What is the period duration $T_w$ of the signal ${w(t)} = {u(t)} + v(t)$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$T_w\ = \ $ { 500 3% } $\text{ms}$ | $T_w\ = \ $ { 500 3% } $\text{ms}$ | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1)''' | + | '''(1)''' The following applies to the rectangular signal: $T_x = 1 \,\text{ms}$ ⇒ |
| + | :$$f_x \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 1 \, \text{kHz}}.$$ | ||
| + | '''(2)''' The following applies to the triangular signal: $T_y = 2.5 \,\text{ms}$ und | ||
| + | :$$f_y \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0.4\, \text{kHz}}.$$ | ||
| − | + | '''(3)''' The basic frequency $f_s$ of the sum signal $s(t)$ is the greatest common divisor $f_x = 1 \,\text{kHz}$ and $f_y = 0.4 \,\text{kHz}$. | |
| − | + | [[File:P_ID320__Sig_Z_2_1_d_neu.png|right|frame|Difference $d(t) = x(t) - y(t)$]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | *From this follows $f_s = 200 \,\text{Hz}$ and the period duration $T_s\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 5 \,\text{ms}}$. | |
| − | + | * This is also evident from the graphic on the information page. | |
| − | '''(3)''' | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[File:P_ID320__Sig_Z_2_1_d_neu.png|right|frame| | ||
| − | |||
| + | '''(4)''' The period duration $T_d$ does not change compared to the period duration $T_s$, if the signal ${y(t)}$ is not added but subtracted: | ||
| + | :$$T_d = T_s \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 5\, \text{ms}}.$$ | ||
| − | '''(5)''' | + | '''(5)''' The greatest common divisor of $f_u = 998 \,\text{Hz}$ and $f_{v} = 1002 \,\text{Hz}$ is $f_w = 2 \,\text{Hz}$. The inverse of this gives the period duration $T_w \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 500 \,\text{ms}}$. |
| − | |||
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Signal Representation: Exercises|^2.1 Description of Periodic Signals^]] |
Latest revision as of 13:33, 12 April 2021
The adjacent diagram shows the periodic signals ${x(t)}$ and ${y(t)}$, from which the sum ${s(t)}$ – sketched in the lower diagram – and the difference ${d(t)}$ are formed.
Furthermore, in this task we consider the signal ${w(t)}$, which results from the sum of two periodic signals ${u(t)}$ and $v(t)$ . The base frequencies of these signals are
- $f_u = 998 \,\text{Hz},$
- $f_v = 1002 \,\text{Hz}.$
That is all we know about the signals ${u(t)}$ and $v(t)$.
Hints:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter General description of periodic signals.
- With the interactive applet Period Duration of Periodic Signals the resulting period duration of two harmonic oscillations can be determined.
Questions
Solution
- $$f_x \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 1 \, \text{kHz}}.$$
(2) The following applies to the triangular signal: $T_y = 2.5 \,\text{ms}$ und
- $$f_y \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0.4\, \text{kHz}}.$$
(3) The basic frequency $f_s$ of the sum signal $s(t)$ is the greatest common divisor $f_x = 1 \,\text{kHz}$ and $f_y = 0.4 \,\text{kHz}$.
- From this follows $f_s = 200 \,\text{Hz}$ and the period duration $T_s\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 5 \,\text{ms}}$.
- This is also evident from the graphic on the information page.
(4) The period duration $T_d$ does not change compared to the period duration $T_s$, if the signal ${y(t)}$ is not added but subtracted:
- $$T_d = T_s \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 5\, \text{ms}}.$$
(5) The greatest common divisor of $f_u = 998 \,\text{Hz}$ and $f_{v} = 1002 \,\text{Hz}$ is $f_w = 2 \,\text{Hz}$. The inverse of this gives the period duration $T_w \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 500 \,\text{ms}}$.