Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 3.7Z: Partial Fraction Decomposition"
m (Text replacement - "Category:Aufgaben zu Lineare zeitinvariante Systeme" to "Category:Exercises for Linear and Time-Invariant Systems") |
|||
| (21 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Linear_and_Time_Invariant_Systems/Inverse_Laplace_Transform |
}} | }} | ||
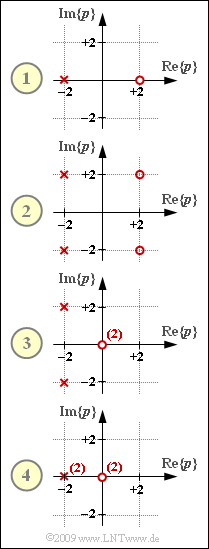
| − | [[File:P_ID1789__LZI_Z_3_7.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID1789__LZI_Z_3_7.png|right|frame|Pole-zero diagrams]] |
| − | In | + | In the graph, four two-port networks are given by their pole–zero diagrams $H_{\rm L}(p)$. |
| − | * | + | * They all have in common that the number $Z$ of zeros is equal to the number $N$ of poles. |
| − | * | + | *The constant factor in each case is $K=1$. |
| − | + | In the special case $Z = N$ the residue theorem cannot be applied directly to compute the impulse response $h(t)$. | |
| − | + | Rather, a "partial fraction decomposition" corresponding to | |
:$$H_{\rm L}(p) =1- H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.05cm}'(p) | :$$H_{\rm L}(p) =1- H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.05cm}'(p) | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}$$ | ||
| − | + | must be made beforehand. Then, | |
:$$h(t) = \delta(t)- h\hspace{0.03cm}'(t) | :$$h(t) = \delta(t)- h\hspace{0.03cm}'(t) | ||
| − | \hspace{0.05cm} | + | \hspace{0.05cm}$$ |
| − | $h\hspace{0.03cm}'(t)$ | + | holds for the impulse response. |
| + | $h\hspace{0.03cm}'(t)$ is the inverse Laplace transform of $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.05cm}'(p)$, where the condition $Z' < N'$ is satisfied. | ||
| − | + | Two of the four configurations given are so-called "all-pass filters". | |
| − | * | + | *This refers to two-port networks for which the Fourier spectrum satisfies the condition $|H(f)| = 1$ ⇒ $a(f) = 0$ . |
| − | *In [[Aufgaben: | + | *In [[Aufgaben:Exercise_3.4Z:_Various_All-Pass_Filters|Exercise 3.4Z]] it is given how the poles and zeros of such an all-pass filter must be positioned. |
| − | + | Furthermore, in this exercise the $p$–transfer function | |
:$$H_{\rm L}^{(5)}(p) =\frac{p/A}{\left (\sqrt{p/A}+\sqrt{A/p} \right )^2} | :$$H_{\rm L}^{(5)}(p) =\frac{p/A}{\left (\sqrt{p/A}+\sqrt{A/p} \right )^2} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}$$ | ||
| − | ⇒ | + | ⇒ "configuration $(5)$" will be examined in more detail, which can be represented by one of the four pole–zero diagrams given in the graph if the parameter $A$ is chosen correctly. |
| Line 33: | Line 34: | ||
| − | + | Please note: | |
| − | * | + | *The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Linear_and_Time_Invariant_Systems/Inverse_Laplace_Transform|Inverse Laplace Transform]]. |
| − | * | + | *In particular, reference is made to the page [[Linear_and_Time_Invariant_Systems/Inverse_Laplace_Transform#Partial_fraction_decomposition|Partial fraction decomposition]]. |
| − | === | + | ===Questions=== |
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {Which of the sketched two-port networks are all-pass filters? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + Configuration $(1)$, |
| − | + | + | + configuration $(2)$, |
| − | - | + | - configuration $(3)$, |
| − | - | + | - configuration $(4)$. |
| − | { | + | {Which two-port network has the transfer function $H_{\rm L}^{(5)}(p)$? |
|type="()"} | |type="()"} | ||
| − | - | + | - Configuration $(1)$, |
| − | - | + | - configuration $(2)$, |
| − | - | + | - configuration $(3)$, |
| − | + | + | + configuration $(4)$. |
| − | { | + | {Compute the function $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.01cm}'(p)$ after a partial fraction decomposition for configuration '''(1)'''. Enter the function value for $p = 0$. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.01cm}'(p = 0) \ = \ $ { 2 3% } | $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.01cm}'(p = 0) \ = \ $ { 2 3% } | ||
| − | { | + | {Compute $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.01cm}'(p)$ for configuration $(2)$. Which statements are true here? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.01cm}'(p)$ | + | - $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.01cm}'(p)$ has the same zeros as $H_{\rm L}(p)$. |
| − | + $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.01cm}'(p)$ | + | + $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.01cm}'(p)$ has the same poles as $H_{\rm L}(p)$. |
| − | + | + | + The constant factor of $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.01cm}'(p)$ is $K' = 8$. |
| − | { | + | {Compute $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.01cm}'(p)$ for configuration $(3)$. Which statements are true here? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.01cm}'(p)$ | + | - $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.01cm}'(p)$ has the same zeros as $H_{\rm L}(p)$. |
| − | + $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.01cm}'(p)$ | + | + $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.01cm}'(p)$ has the same poles as $H_{\rm L}(p)$. |
| − | - | + | - The constant factor of $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.01cm}'(p)$ is $K' = 8$. |
| − | { | + | {Compute $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.01cm}'(p)$ for configuration $(4)$. Which statements are true here? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.01cm}'(p)$ | + | - $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.01cm}'(p)$ has the same zeros as $H_{\rm L}(p)$. |
| − | + $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.01cm}'(p)$ | + | + $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.01cm}'(p)$ has the same poles as $H_{\rm L}(p)$. |
| − | - | + | - The constant factor of $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.01cm}'(p)$ is $K' = 8$. |
| Line 88: | Line 89: | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1)''' | + | '''(1)''' The <u> suggested solutions 1 and 2</u> are correct: |
| − | * | + | *According to the criteria given in exercise 3.4Z, there is always an all-pass filter at hand <br>if there is a corresponding zero $p_{\rm o} = + A + {\rm j} \cdot B$ in the right $p$–half-plane for each pole $p_{\rm x} = - A + {\rm j} \cdot B$ in the left half-plane. |
| − | * | + | *Considering $K = 1$ the attenuation function is then $a(f) = 0 \ \rm Np$ ⇒ $|H(f)| = 1$. |
| − | * | + | *The following can be seen from the graph on the information page: The configurations $(1)$ and $(2)$ satisfy exactly these symmetry properties. |
| − | '''(2)''' | + | '''(2)''' The <u> suggested solution 4</u> is correct: |
| − | * | + | *The transfer function $H_{\rm L}^{(5)}(p)$ is also described by configuration $(4)$ as the following calculation shows: |
:$$H_{\rm L}^{(5)}(p) \hspace{0.25cm} = \hspace{0.2cm} \frac{p/A}{(\sqrt{p/A}+\sqrt{A/p})^2} | :$$H_{\rm L}^{(5)}(p) \hspace{0.25cm} = \hspace{0.2cm} \frac{p/A}{(\sqrt{p/A}+\sqrt{A/p})^2} | ||
=\frac{p/A}{{p/A}+2+ {A/p}} | =\frac{p/A}{{p/A}+2+ {A/p}} | ||
| Line 104: | Line 105: | ||
}= H_{\rm L}^{(4)}(p) | }= H_{\rm L}^{(4)}(p) | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *The double zero is at $p_{\rm o} = 0$ and the double pole at $p_{\rm x} = -A = -2$. |
| − | '''(3)''' | + | '''(3)''' The following holds for configuration $(1)$: |
:$$H_{\rm L}(p) =\frac{p-2}{p+2}=\frac{p+2-4}{p+2}= 1 - \frac{4}{p+2}=1- H_{\rm L}\hspace{-0.05cm}'(p) | :$$H_{\rm L}(p) =\frac{p-2}{p+2}=\frac{p+2-4}{p+2}= 1 - \frac{4}{p+2}=1- H_{\rm L}\hspace{-0.05cm}'(p) | ||
\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}H_{\rm L}\hspace{-0.05cm}'(p) = \frac{4}{p+2} | \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}H_{\rm L}\hspace{-0.05cm}'(p) = \frac{4}{p+2} | ||
| Line 117: | Line 118: | ||
| − | '''(4)''' | + | '''(4)''' Similarly, the following is obtained for configuration $(2)$: |
:$$H_{\rm L}(p) =\frac{(p-2 - {\rm j} \cdot 2)(p-2 + {\rm j} \cdot 2)}{(p+2 - {\rm j} \cdot 2)(p+2 + {\rm j} \cdot 2)}= | :$$H_{\rm L}(p) =\frac{(p-2 - {\rm j} \cdot 2)(p-2 + {\rm j} \cdot 2)}{(p+2 - {\rm j} \cdot 2)(p+2 + {\rm j} \cdot 2)}= | ||
\frac{p^2 -4\cdot p +8 }{p^2 +4\cdot p +8}= | \frac{p^2 -4\cdot p +8 }{p^2 +4\cdot p +8}= | ||
| Line 126: | Line 127: | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | Thus, the <u> suggested solutions 2 and 3</u> are correct in contrast to statement 1: | |
| − | * | + | * While $H_{\rm L}(p)$ has two conjugate complex zeros, |
| − | * | + | * $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.01cm}'(p)$ only has a single zero at $p_{\rm o}\hspace{0.01cm}' = 0$. |
| − | '''(5)''' | + | '''(5)''' The following applies for configuration $(3)$ : |
:$$H_{\rm L}(p) = | :$$H_{\rm L}(p) = | ||
\frac{p^2 }{p^2 +4\cdot p +8}=\frac{p^2 +4\cdot p +8 -4\cdot p -8 }{p^2 +4\cdot p +8} | \frac{p^2 }{p^2 +4\cdot p +8}=\frac{p^2 +4\cdot p +8 -4\cdot p -8 }{p^2 +4\cdot p +8} | ||
| Line 140: | Line 141: | ||
\cdot \frac{p+2}{(p+2 - {\rm j} \cdot 2)(p+2 + {\rm j} \cdot 2)} | \cdot \frac{p+2}{(p+2 - {\rm j} \cdot 2)(p+2 + {\rm j} \cdot 2)} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *The zero of $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.01cm}'(p)$ is now at $p_{\rm o}\hspace{0.01cm}' = -2$. |
| − | * | + | *The constant is $K\hspace{0.01cm}' = 4$ ⇒ only <u> suggested solution 2</u> is correct here. |
| − | '''(6)''' | + | '''(6)''' Finally, the following holds for configuration $(4)$: |
:$$H_{\rm L}(p) = \frac{p^2 }{(p+2)^2}=\frac{p^2 +4\cdot p +4 -4\cdot p -4 }{p^2 +4\cdot p +4} | :$$H_{\rm L}(p) = \frac{p^2 }{(p+2)^2}=\frac{p^2 +4\cdot p +4 -4\cdot p -4 }{p^2 +4\cdot p +4} | ||
= 1- \frac{4\cdot p +4 }{p^2 +4\cdot p +4} | = 1- \frac{4\cdot p +4 }{p^2 +4\cdot p +4} | ||
| Line 151: | Line 152: | ||
\cdot \frac{p+1}{(p+2)^2} | \cdot \frac{p+1}{(p+2)^2} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | <u>Suggested solution 2</u> is correct here. In general, it can be said that: | |
| − | * | + | *The partial fraction decomposition changes the number and position of the zeros. |
| − | * | + | * On the contrary, the poles of $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.01cm}'(p)$ are always identical to those of $H_{\rm L}(p)$. |
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Linear and Time-Invariant Systems: Exercises|^3.3 Inverse Laplace Transform^]] |
Latest revision as of 14:55, 25 January 2022
In the graph, four two-port networks are given by their pole–zero diagrams $H_{\rm L}(p)$.
- They all have in common that the number $Z$ of zeros is equal to the number $N$ of poles.
- The constant factor in each case is $K=1$.
In the special case $Z = N$ the residue theorem cannot be applied directly to compute the impulse response $h(t)$.
Rather, a "partial fraction decomposition" corresponding to
- $$H_{\rm L}(p) =1- H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.05cm}'(p) \hspace{0.05cm}$$
must be made beforehand. Then,
- $$h(t) = \delta(t)- h\hspace{0.03cm}'(t) \hspace{0.05cm}$$
holds for the impulse response. $h\hspace{0.03cm}'(t)$ is the inverse Laplace transform of $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.05cm}'(p)$, where the condition $Z' < N'$ is satisfied.
Two of the four configurations given are so-called "all-pass filters".
- This refers to two-port networks for which the Fourier spectrum satisfies the condition $|H(f)| = 1$ ⇒ $a(f) = 0$ .
- In Exercise 3.4Z it is given how the poles and zeros of such an all-pass filter must be positioned.
Furthermore, in this exercise the $p$–transfer function
- $$H_{\rm L}^{(5)}(p) =\frac{p/A}{\left (\sqrt{p/A}+\sqrt{A/p} \right )^2} \hspace{0.05cm}$$
⇒ "configuration $(5)$" will be examined in more detail, which can be represented by one of the four pole–zero diagrams given in the graph if the parameter $A$ is chosen correctly.
Please note:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter Inverse Laplace Transform.
- In particular, reference is made to the page Partial fraction decomposition.
Questions
Solution
- According to the criteria given in exercise 3.4Z, there is always an all-pass filter at hand
if there is a corresponding zero $p_{\rm o} = + A + {\rm j} \cdot B$ in the right $p$–half-plane for each pole $p_{\rm x} = - A + {\rm j} \cdot B$ in the left half-plane. - Considering $K = 1$ the attenuation function is then $a(f) = 0 \ \rm Np$ ⇒ $|H(f)| = 1$.
- The following can be seen from the graph on the information page: The configurations $(1)$ and $(2)$ satisfy exactly these symmetry properties.
(2) The suggested solution 4 is correct:
- The transfer function $H_{\rm L}^{(5)}(p)$ is also described by configuration $(4)$ as the following calculation shows:
- $$H_{\rm L}^{(5)}(p) \hspace{0.25cm} = \hspace{0.2cm} \frac{p/A}{(\sqrt{p/A}+\sqrt{A/p})^2} =\frac{p/A}{{p/A}+2+ {A/p}} = \hspace{0.2cm}\frac{p^2}{p^2 + 2A \cdot p + A^2} = \frac{p^2}{(p+A)^2 }= H_{\rm L}^{(4)}(p) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The double zero is at $p_{\rm o} = 0$ and the double pole at $p_{\rm x} = -A = -2$.
(3) The following holds for configuration $(1)$:
- $$H_{\rm L}(p) =\frac{p-2}{p+2}=\frac{p+2-4}{p+2}= 1 - \frac{4}{p+2}=1- H_{\rm L}\hspace{-0.05cm}'(p) \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}H_{\rm L}\hspace{-0.05cm}'(p) = \frac{4}{p+2} \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{H_{\rm L}\hspace{-0.05cm}'(p =0) =2} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(4) Similarly, the following is obtained for configuration $(2)$:
- $$H_{\rm L}(p) =\frac{(p-2 - {\rm j} \cdot 2)(p-2 + {\rm j} \cdot 2)}{(p+2 - {\rm j} \cdot 2)(p+2 + {\rm j} \cdot 2)}= \frac{p^2 -4\cdot p +8 }{p^2 +4\cdot p +8}= \hspace{0.2cm}\frac{p^2 +4\cdot p +8 -8\cdot p}{p^2 +4\cdot p +8} =1- \frac{8\cdot p}{p^2 +4\cdot p +8}=1- H_{\rm L}\hspace{-0.05cm}'(p)$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.05cm}'(p) = 8 \cdot \frac{p}{(p+2 - {\rm j} \cdot 2)(p+2 + {\rm j} \cdot 2)} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Thus, the suggested solutions 2 and 3 are correct in contrast to statement 1:
- While $H_{\rm L}(p)$ has two conjugate complex zeros,
- $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.01cm}'(p)$ only has a single zero at $p_{\rm o}\hspace{0.01cm}' = 0$.
(5) The following applies for configuration $(3)$ :
- $$H_{\rm L}(p) = \frac{p^2 }{p^2 +4\cdot p +8}=\frac{p^2 +4\cdot p +8 -4\cdot p -8 }{p^2 +4\cdot p +8} = 1- H_{\rm L}\hspace{-0.05cm}'(p)$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}H_{\rm L}\hspace{-0.05cm}'(p) = 4 \cdot \frac{p+2}{(p+2 - {\rm j} \cdot 2)(p+2 + {\rm j} \cdot 2)} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The zero of $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.01cm}'(p)$ is now at $p_{\rm o}\hspace{0.01cm}' = -2$.
- The constant is $K\hspace{0.01cm}' = 4$ ⇒ only suggested solution 2 is correct here.
(6) Finally, the following holds for configuration $(4)$:
- $$H_{\rm L}(p) = \frac{p^2 }{(p+2)^2}=\frac{p^2 +4\cdot p +4 -4\cdot p -4 }{p^2 +4\cdot p +4} = 1- \frac{4\cdot p +4 }{p^2 +4\cdot p +4} \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.05cm}'(p) = 4 \cdot \frac{p+1}{(p+2)^2} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Suggested solution 2 is correct here. In general, it can be said that:
- The partial fraction decomposition changes the number and position of the zeros.
- On the contrary, the poles of $H_{\rm L}\hspace{0.01cm}'(p)$ are always identical to those of $H_{\rm L}(p)$.