Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 3.9: Conditional Mutual Information"
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Information_Theory/Different_Entropy_Measures_of_Two-Dimensional_Random_Variables |
}} | }} | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
Three different definitions of mutual information are used in this exercise: | Three different definitions of mutual information are used in this exercise: | ||
| − | *the | + | *the <u>conventional</u> mutual information zwischen $X$ and $W$: |
:$$I(X;W) = H(X) - H(X|\hspace{0.05cm}W) \hspace{0.05cm},$$ | :$$I(X;W) = H(X) - H(X|\hspace{0.05cm}W) \hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
| − | * the | + | * the <u>conditional</u> mutual information between $X$ and $W$ with a <u>given fixed value</u> $Z = z$: |
:$$I(X;W \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z = z) = H(X\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z = z) - H(X|\hspace{0.05cm}W ,\hspace{0.05cm} Z = z) \hspace{0.05cm},$$ | :$$I(X;W \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z = z) = H(X\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z = z) - H(X|\hspace{0.05cm}W ,\hspace{0.05cm} Z = z) \hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
| − | * the | + | * the <u>conditional</u> mutual information between $X$ and $W$ for a <u>given random variable</u> $Z$: |
:$$I(X;W \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z ) = H(X\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z ) - H(X|\hspace{0.05cm}W \hspace{0.05cm} Z ) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$I(X;W \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z ) = H(X\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z ) - H(X|\hspace{0.05cm}W \hspace{0.05cm} Z ) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
Hints: | Hints: | ||
| − | * | + | *The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Information_Theory/Verschiedene_Entropien_zweidimensionaler_Zufallsgrößen|Different entropies of two-dimensional random variables]]. |
*In particular, reference is made to the page [[Information_Theory/Verschiedene_Entropien_zweidimensionaler_Zufallsgrößen#Conditional_mutual_information|Conditional mutual information]]. | *In particular, reference is made to the page [[Information_Theory/Verschiedene_Entropien_zweidimensionaler_Zufallsgrößen#Conditional_mutual_information|Conditional mutual information]]. | ||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
===Solution=== | ===Solution=== | ||
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | [[File:P_ID2814__Inf_A_3_8a.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID2814__Inf_A_3_8a.png|right|frame|Two-dimensional probability mass functions for $Z = 1$]] |
'''(1)''' The upper graph is valid for $Z = 1$ ⇒ $W = X + Y$. | '''(1)''' The upper graph is valid for $Z = 1$ ⇒ $W = X + Y$. | ||
*Under the conditions $P_X(X) = \big [1/2, \ 1/2 \big]$ as well as $P_Y(Y) = \big [1/2, \ 1/2 \big]$ the joint probabilities $P_{ XW|Z=1 }(X, W)$ thus result according to the right graph (grey background). | *Under the conditions $P_X(X) = \big [1/2, \ 1/2 \big]$ as well as $P_Y(Y) = \big [1/2, \ 1/2 \big]$ the joint probabilities $P_{ XW|Z=1 }(X, W)$ thus result according to the right graph (grey background). | ||
| Line 81: | Line 81: | ||
*The first term summarises the two horizontally shaded fields in the graph, the second term the vertically shaded fields. | *The first term summarises the two horizontally shaded fields in the graph, the second term the vertically shaded fields. | ||
| − | *The | + | *The second term do not contribute because of $\log_2 (1) = 0$ . |
| − | [[File:P_ID2815__Inf_A_3_8b.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID2815__Inf_A_3_8b.png|right|frame|Two-dimensional probability mass functions for $Z = 2$]] |
| − | '''(2)''' For $Z = 2$ $W = \{4,\ 6,\ 8\}$ | + | '''(2)''' For $Z = 2$, $W = \{4,\ 6,\ 8\}$ is valid, but nothing changes with respect to the probability functions compared to subtask '''(1)'''. |
*Consequently, the same conditional mutual information is obtained: | *Consequently, the same conditional mutual information is obtained: | ||
| Line 92: | Line 92: | ||
\hspace{0.15cm} \underline {=0.5\,{\rm (bit)}} | \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {=0.5\,{\rm (bit)}} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
'''(3)''' The equation is for $Z = \{1,\ 2\}$ with ${\rm Pr}(Z = 1) =p$ and ${\rm Pr}(Z = 2) =1-p$: | '''(3)''' The equation is for $Z = \{1,\ 2\}$ with ${\rm Pr}(Z = 1) =p$ and ${\rm Pr}(Z = 2) =1-p$: | ||
:$$I(X;W \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z) = p \cdot I(X;W \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z = 1) + (1-p) \cdot I(X;W \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z = 2)\hspace{0.15cm} \underline {=0.5\,{\rm (bit)}} | :$$I(X;W \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z) = p \cdot I(X;W \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z = 1) + (1-p) \cdot I(X;W \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z = 2)\hspace{0.15cm} \underline {=0.5\,{\rm (bit)}} | ||
| Line 111: | Line 112: | ||
The result $I(X; W|Z) > I(X; W)$ is true for this example, but also for many other applications: | The result $I(X; W|Z) > I(X; W)$ is true for this example, but also for many other applications: | ||
*If I know $Z$, I know more about the 2D random variable $XW$ than without this knowledge.. | *If I know $Z$, I know more about the 2D random variable $XW$ than without this knowledge.. | ||
| − | *However, one must not | + | *However, one must not generalize this result: |
| − | :Sometimes $I(X; W) > I(X; W|Z)$, actually applies, as in [[Information_Theory/Verschiedene_Entropien_zweidimensionaler_Zufallsgr%C3%B6%C3%9Fen#Conditional_mutual_information| | + | :Sometimes $I(X; W) > I(X; W|Z)$, actually applies, as in [[Information_Theory/Verschiedene_Entropien_zweidimensionaler_Zufallsgr%C3%B6%C3%9Fen#Conditional_mutual_information|Example 4]] in the theory section. |
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
Latest revision as of 09:16, 24 September 2021
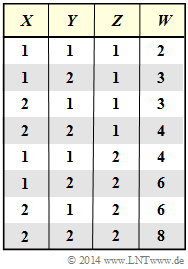
We assume statistically independent random variables $X$, $Y$ and $Z$ with the following properties:
- $$X \in \{1,\ 2 \} \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.35cm} Y \in \{1,\ 2 \} \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.35cm} Z \in \{1,\ 2 \} \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.35cm} P_X(X) = P_Y(Y) = \big [ 1/2, \ 1/2 \big ]\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.35cm}P_Z(Z) = \big [ p, \ 1-p \big ].$$
From $X$, $Y$ and $Z$ we form the new random variable $W = (X+Y) \cdot Z$.
- It is obvious that there are statistical dependencies between $X$ and $W$ ⇒ mutual information $I(X; W) ≠ 0$.
- Furthermore, $I(Y; W) ≠ 0$ as well as $I(Z; W) ≠ 0$ will also apply, but this will not be discussed in detail in this exercise.
Three different definitions of mutual information are used in this exercise:
- the conventional mutual information zwischen $X$ and $W$:
- $$I(X;W) = H(X) - H(X|\hspace{0.05cm}W) \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- the conditional mutual information between $X$ and $W$ with a given fixed value $Z = z$:
- $$I(X;W \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z = z) = H(X\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z = z) - H(X|\hspace{0.05cm}W ,\hspace{0.05cm} Z = z) \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- the conditional mutual information between $X$ and $W$ for a given random variable $Z$:
- $$I(X;W \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z ) = H(X\hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z ) - H(X|\hspace{0.05cm}W \hspace{0.05cm} Z ) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The relationship between the last two definitions is:
- $$I(X;W \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z ) = \sum_{z \hspace{0.1cm}\in \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm supp} (P_{Z})} \hspace{-0.2cm} P_Z(z) \cdot I(X;W \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z = z)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Hints:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter Different entropies of two-dimensional random variables.
- In particular, reference is made to the page Conditional mutual information.
Questions
Solution
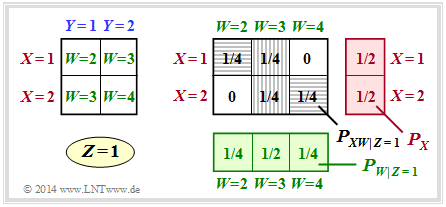
(1) The upper graph is valid for $Z = 1$ ⇒ $W = X + Y$.
- Under the conditions $P_X(X) = \big [1/2, \ 1/2 \big]$ as well as $P_Y(Y) = \big [1/2, \ 1/2 \big]$ the joint probabilities $P_{ XW|Z=1 }(X, W)$ thus result according to the right graph (grey background).
- Thus the following applies to the mutual information under the fixed condition $Z = 1$:
- $$I(X;W \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z = 1) \hspace{-0.05cm} = \hspace{-1.1cm}\sum_{(x,w) \hspace{0.1cm}\in \hspace{0.1cm}{\rm supp} (P_{XW}\hspace{0.01cm}|\hspace{0.01cm} Z\hspace{-0.03cm} =\hspace{-0.03cm} 1)} \hspace{-1.1cm} P_{XW\hspace{0.01cm}|\hspace{0.01cm} Z\hspace{-0.03cm} =\hspace{-0.03cm} 1} (x,w) \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{P_{XW\hspace{0.01cm}|\hspace{0.01cm} Z\hspace{-0.03cm} =\hspace{-0.03cm} 1} (x,w) }{P_X(x) \cdot P_{W\hspace{0.01cm}|\hspace{0.01cm} Z\hspace{-0.03cm} =\hspace{-0.03cm} 1} (w) }$$
- $$I(X;W \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z = 1) = 2 \cdot \frac{1}{4} \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1/4}{1/2 \cdot 1/4} + 2 \cdot \frac{1}{4} \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1/4}{1/2 \cdot 1/2} $$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} I(X;W \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z = 1) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {=0.5\,{\rm (bit)}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The first term summarises the two horizontally shaded fields in the graph, the second term the vertically shaded fields.
- The second term do not contribute because of $\log_2 (1) = 0$ .
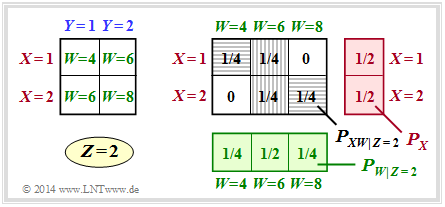
(2) For $Z = 2$, $W = \{4,\ 6,\ 8\}$ is valid, but nothing changes with respect to the probability functions compared to subtask (1).
- Consequently, the same conditional mutual information is obtained:
- $$I(X;W \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z = 2) = I(X;W \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z = 1) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {=0.5\,{\rm (bit)}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(3) The equation is for $Z = \{1,\ 2\}$ with ${\rm Pr}(Z = 1) =p$ and ${\rm Pr}(Z = 2) =1-p$:
- $$I(X;W \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z) = p \cdot I(X;W \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z = 1) + (1-p) \cdot I(X;W \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z = 2)\hspace{0.15cm} \underline {=0.5\,{\rm (bit)}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- It is considered that according to subtasks (1) and (2) the conditional mutual information for given $Z = 1$ and given $Z = 2$ are equal.
- Thus $I(X; W|Z)$, i.e. under the condition of a stochastic random variable $Z = \{1,\ 2\}$ with $P_Z(Z) = \big [p, \ 1 – p\big ]$ is independent of $p$.
- In particular, the result is also valid for $\underline{p = 1/2}$ and $\underline{p = 3/4}$.
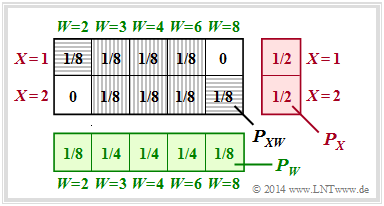
(4) The joint probability $P_{ XW }$ depends on the $Z$–probabilites $p$ and $1 – p$ .
- For $Pr(Z = 1) = Pr(Z = 2) = 1/2$ the scheme sketched on the right results.
- Again, only the two horizontally shaded fields contribute to the mutual information:
- $$ I(X;W) = 2 \cdot \frac{1}{8} \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1/8}{1/2 \cdot 1/8} \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {=0.25\,{\rm (bit)}} \hspace{0.35cm} < \hspace{0.35cm} I(X;W \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} Z) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The result $I(X; W|Z) > I(X; W)$ is true for this example, but also for many other applications:
- If I know $Z$, I know more about the 2D random variable $XW$ than without this knowledge..
- However, one must not generalize this result:
- Sometimes $I(X; W) > I(X; W|Z)$, actually applies, as in Example 4 in the theory section.