Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 2.4: Distortion Factor and Distortion Power"
| (11 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | [[File:P_ID897__LZI_A_2_4.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID897__LZI_A_2_4.png|right|frame|Given input and output signals]] |
A cosine signal | A cosine signal | ||
:$$x_1(t) = A_x \cdot \cos(\omega_0 t)$$ | :$$x_1(t) = A_x \cdot \cos(\omega_0 t)$$ | ||
| − | with the amplitude $A_x = 1 \ \rm V$ is applied to the input of a | + | with the amplitude $A_x = 1 \ \rm V$ is applied to the input of a communication system to test it. |
| + | |||
| + | Then, the following signal occurs at the system output: | ||
:$$y_1(t) = {0.992 \,\rm V} \cdot \cos(\omega_0 t) - {0.062 \,\rm | :$$y_1(t) = {0.992 \,\rm V} \cdot \cos(\omega_0 t) - {0.062 \,\rm | ||
V} \cdot \cos(2\omega_0 t)+ \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...}$$ | V} \cdot \cos(2\omega_0 t)+ \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...}$$ | ||
| − | In the upper graph the signals $x_1(t)$ and $y_1(t)$ are shown. Harmonics with amplitudes | + | In the upper graph the signals $x_1(t)$ and $y_1(t)$ are shown. Harmonics with amplitudes $\lt 10 \ \rm mV$ are not considered here. |
| Line 20: | Line 22: | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}\text{...}$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...}$$ | ||
| − | It is obvious that the indices "1" and "2" respectively denote the | + | It is obvious that the indices "1" and "2" respectively denote the normalized amplitude of the input signal. |
| − | The system is supposed to be | + | The system is supposed to be analyzed based on the signal–to–distortion–power ratio |
:$$\rho_{\rm V} = { P_{x}}/{P_{\rm V}} \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} 10 \cdot \lg \hspace{0.1cm}\rho_{\rm V} = | :$$\rho_{\rm V} = { P_{x}}/{P_{\rm V}} \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} 10 \cdot \lg \hspace{0.1cm}\rho_{\rm V} = | ||
10 \cdot \lg \hspace{0.1cm}{ P_{x}}/{P_{\rm V}}\hspace{0.3cm} \left( {\rm in \hspace{0.15cm} dB} \right)$$ | 10 \cdot \lg \hspace{0.1cm}{ P_{x}}/{P_{\rm V}}\hspace{0.3cm} \left( {\rm in \hspace{0.15cm} dB} \right)$$ | ||
defined in the section [[Linear_and_Time_Invariant_Systems/Classification_of_the_Distortions#Quantitative_measure_for_the_signal_distortions| Quantitative measure for the signal distortions]] and the distortion factor $K$ : | defined in the section [[Linear_and_Time_Invariant_Systems/Classification_of_the_Distortions#Quantitative_measure_for_the_signal_distortions| Quantitative measure for the signal distortions]] and the distortion factor $K$ : | ||
* $P_x$ denotes the power of the input signal. | * $P_x$ denotes the power of the input signal. | ||
| − | * The distortion power $P_{\rm V}$ | + | * The distortion power (German: "Verrzerrungsleistung" ⇒ "V") $P_{\rm V}$ represents the power (the root mean square) of the difference signal $\varepsilon(t) = y(t) - x(t)$ . |
| − | + | *To determine the powers $P_{x}$ and $P_{\rm V}$ it is necessary to take the average of the squared signals in each case. However, it is easier to calculate the powers in the frequency domain in this task. | |
| − | |||
| − | To determine the powers $P_{x}$ and $P_{\rm V}$ it is necessary to take the average of the squared signals in each case. However, it is easier to calculate the powers in the frequency domain in this task. | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
''Please note:'' | ''Please note:'' | ||
| − | *The task belongs to the chapter [[Linear_and_Time_Invariant_Systems/Nonlinear_Distortion|Nonlinear | + | *The task belongs to the chapter [[Linear_and_Time_Invariant_Systems/Nonlinear_Distortion|Nonlinear Distortions]]. |
*All powers required here refer to the resistance $R = 1 \ \rm \Omega$ and thus have the unit ${\rm V}^2$. | *All powers required here refer to the resistance $R = 1 \ \rm \Omega$ and thus have the unit ${\rm V}^2$. | ||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
+ The lower half-wave is more peaked than the upper half-wave. | + The lower half-wave is more peaked than the upper half-wave. | ||
| − | + The maximum– and | + | + The maximum– and minimum values of $y_2(t)$ are asymmetrically zero. |
- A different frequency would result in a different distortion factor. | - A different frequency would result in a different distortion factor. | ||
| − | { | + | {What is the power $P_x$ of the input signal $x_2(t)$ in ${\rm V}^2$, i.e. in terms of the reference resistance $R = 1 \ \rm \Omega$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$P_x \ = \ $ { 2 1% } $\ {\rm V}^2$ | $P_x \ = \ $ { 2 1% } $\ {\rm V}^2$ | ||
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
+ The distortion factor can be computed using the coefficients $A_1$, $A_2$, $A_3$, ... of the output variable alone. | + The distortion factor can be computed using the coefficients $A_1$, $A_2$, $A_3$, ... of the output variable alone. | ||
- The signal–to–distortion–power ratio $10 \cdot {\rm lg} \ \rho_{\rm V}$ is computable using the coefficients $A_1$, $A_2$, $A_3$, ... alone. | - The signal–to–distortion–power ratio $10 \cdot {\rm lg} \ \rho_{\rm V}$ is computable using the coefficients $A_1$, $A_2$, $A_3$, ... alone. | ||
| − | + For the special case [$A_1 = A_x$ ⇒ no change of the fundamental wave], $\rho_{\rm V}$ and $K$ can be converted directly into each | + | + For the special case [$A_1 = A_x$ ⇒ no change of the fundamental wave], $\rho_{\rm V}$ and $K$ can be converted directly into each other. |
| Line 111: | Line 111: | ||
'''(3)''' <u>The first two proposed solutions</u> are correct: | '''(3)''' <u>The first two proposed solutions</u> are correct: | ||
*Here, the nonlinear distortions cause the lower half-wave to be more peaked than the upper half-wave. | *Here, the nonlinear distortions cause the lower half-wave to be more peaked than the upper half-wave. | ||
| − | *In addition, $y_{\rm max} = 1.75 \ \rm V$ and $y_{\rm min} = -2.25 \ \rm V$ | + | *In addition, $y_{\rm max} = 1.75 \ \rm V$ and $y_{\rm min} = -2.25 \ \rm V$ hold since $y(t)$ does not contain any direct (DC) signals. <br>Hence, there is no symmetry with respect to the zero line anymore. |
*For a nonlinear system, the distortion factor $K$ is independent of the frequency of the cosine input signal but strongly dependent on its amplitude. | *For a nonlinear system, the distortion factor $K$ is independent of the frequency of the cosine input signal but strongly dependent on its amplitude. | ||
| − | '''(4)''' The root mean square (rms) value of a cosine signal is known to be $\sqrt{0.5}$–times the amplitude. The square of this is the "power": | + | '''(4)''' The root mean square (rms) value of a cosine signal is known to be $\sqrt{0.5}$–times the amplitude. The square of this is the "power": |
:$$P_x = \frac{A_x^2}{2} = \frac{(2 \,{\rm V})^2}{2}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 2\,{\rm V^2}}.$$ | :$$P_x = \frac{A_x^2}{2} = \frac{(2 \,{\rm V})^2}{2}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 2\,{\rm V^2}}.$$ | ||
| − | *Actually, the power also depends on the reference resistance $R$ and has the unit " | + | *Actually, the power also depends on the reference resistance $R$ and has the unit "Watt". |
*$P_x = 2 \ \rm W$ is obtained with $R = 1 \ \rm \Omega$ , so exactly the same numerical value as in this simpler calculation. | *$P_x = 2 \ \rm W$ is obtained with $R = 1 \ \rm \Omega$ , so exactly the same numerical value as in this simpler calculation. | ||
| Line 125: | Line 125: | ||
'''(5)''' Denoting | '''(5)''' Denoting | ||
| − | *the amplitude of the | + | *the amplitude of the basic wave of $y_2(t)$ by $A_1$ and |
| − | *the so-called harmonics by $A_2$, $A_3$ and $A_4$ | + | *the so-called harmonics by $A_2$, $A_3$ and $A_4$, |
| − | the distortion power is thus by computing in the frequency domain: | + | the distortion power is thus by computing it in the frequency domain: |
:$$P_{\rm V} = \frac{1}{2} \cdot \big[ (A_1 - A_x)^2 + A_2^2+ | :$$P_{\rm V} = \frac{1}{2} \cdot \big[ (A_1 - A_x)^2 + A_2^2+ | ||
A_3^2+ A_4^2\big] = \frac{1}{2} \cdot \big[ (-2 | A_3^2+ A_4^2\big] = \frac{1}{2} \cdot \big[ (-2 | ||
| Line 135: | Line 135: | ||
\,{\rm V})^2 \big] \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{\approx 0.031 \,{\rm V}^2}.$$ | \,{\rm V})^2 \big] \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{\approx 0.031 \,{\rm V}^2}.$$ | ||
| − | Here, $A_x$ denotes the amplitude of the input signal. The signs of the harmonics do not matter in this calculation. | + | Here, $A_x$ denotes the amplitude of the input signal. The signs of the harmonics do not matter in this calculation. |
| Line 153: | Line 153: | ||
+ \text{...} }{A_x^2}.$$ | + \text{...} }{A_x^2}.$$ | ||
| − | *When calculating the distortion power $P_{\rm V}$ a falsification of the amplitude of the | + | *When calculating the distortion power $P_{\rm V}$ a falsification of the amplitude of the basic wave $($this is now $A_1$ instead of $A_x)$ is also taken into account. Moreover, the distortion power is not in terms of $A_1^2$ but in terms of $A_x^2$ . |
*Generally, the following relationship holds between the signal–to–distortion–power ratio and the distortion factor: | *Generally, the following relationship holds between the signal–to–distortion–power ratio and the distortion factor: | ||
| Line 162: | Line 162: | ||
| − | + | Remarks: | |
| − | *A distortion factor of $1\%$ in this case | + | *A distortion factor of $1\%$ corresponds in this case to the result $10 \cdot \lg \rho_{\rm V} = 40 \,{\rm dB}$. |
| − | *Using the distortion factor $K = 0.125$ from subtask '''(2)''' $10 \cdot \lg \rho_{\rm V} = 18.06 \,{\rm dB}$ would have been obtained immediately with the approximation $A_1 \approx A_x$ . | + | *Using the distortion factor $K = 0.125$ from subtask '''(2)''' ⇒ $10 \cdot \lg \rho_{\rm V} = 18.06 \,{\rm dB}$ would have been obtained immediately with the approximation $A_1 \approx A_x$ . |
*The actual value $(18.10 \ \rm dB)$ calculated in subtask '''(7)''' differs from this only insignificantly. | *The actual value $(18.10 \ \rm dB)$ calculated in subtask '''(7)''' differs from this only insignificantly. | ||
| Line 172: | Line 172: | ||
| − | [[Category:Linear and Time-Invariant Systems: Exercises|^2.2 | + | [[Category:Linear and Time-Invariant Systems: Exercises|^2.2 Nonlinear Distortions^]] |
Latest revision as of 13:56, 1 October 2021
A cosine signal
- $$x_1(t) = A_x \cdot \cos(\omega_0 t)$$
with the amplitude $A_x = 1 \ \rm V$ is applied to the input of a communication system to test it.
Then, the following signal occurs at the system output:
- $$y_1(t) = {0.992 \,\rm V} \cdot \cos(\omega_0 t) - {0.062 \,\rm V} \cdot \cos(2\omega_0 t)+ \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...}$$
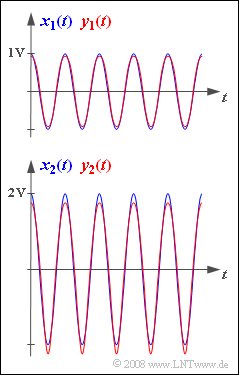
In the upper graph the signals $x_1(t)$ and $y_1(t)$ are shown. Harmonics with amplitudes $\lt 10 \ \rm mV$ are not considered here.
The bottom image shows the input signal $x_2(t)$ with the ampiltude $A_x = 2 \ \rm V$ and the corresponding output signal, again without harmonics smaller than $10 \ \rm mV$:
- $$y_2(t) \hspace{-0.05cm}=\hspace{-0.05cm}{1.938 \,\rm V} \cdot \cos(\omega_0 t)\hspace{-0.05cm} -\hspace{-0.05cm} {0.234 \,\rm V} \cdot \cos(2\omega_0 t) \hspace{-0.05cm}+\hspace{-0.05cm} {0.058 \,\rm V} \cdot \cos(3\omega_0 t)\hspace{-0.05cm} -\hspace{-0.05cm}{0.018 \,\rm V} \cdot \cos(4\omega_0 t) \hspace{-0.05cm}+\hspace{-0.05cm} \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...}$$
It is obvious that the indices "1" and "2" respectively denote the normalized amplitude of the input signal.
The system is supposed to be analyzed based on the signal–to–distortion–power ratio
- $$\rho_{\rm V} = { P_{x}}/{P_{\rm V}} \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} 10 \cdot \lg \hspace{0.1cm}\rho_{\rm V} = 10 \cdot \lg \hspace{0.1cm}{ P_{x}}/{P_{\rm V}}\hspace{0.3cm} \left( {\rm in \hspace{0.15cm} dB} \right)$$
defined in the section Quantitative measure for the signal distortions and the distortion factor $K$ :
- $P_x$ denotes the power of the input signal.
- The distortion power (German: "Verrzerrungsleistung" ⇒ "V") $P_{\rm V}$ represents the power (the root mean square) of the difference signal $\varepsilon(t) = y(t) - x(t)$ .
- To determine the powers $P_{x}$ and $P_{\rm V}$ it is necessary to take the average of the squared signals in each case. However, it is easier to calculate the powers in the frequency domain in this task.
Please note:
- The task belongs to the chapter Nonlinear Distortions.
- All powers required here refer to the resistance $R = 1 \ \rm \Omega$ and thus have the unit ${\rm V}^2$.
Questions
Solution
- $$K \approx K_2 = \frac{0.062 \,\,{\rm V}}{0.992 \,\,{\rm V}} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{\approx 6.25 \%}.$$
(2) For the input amplitude $A_x = 2 \ \rm V$ (bottom sketch) the various distortion factors are:
- $$K_2 = \frac{0.234 \,\,{\rm V}}{1.938 \,\,{\rm V}} \approx 0.121, \hspace{0.5cm} K_3 = \frac{0.058 \,\,{\rm V}}{1.938 \,\,{\rm V}} \approx 0.030, \hspace{0.5cm}K_4 = \frac{0.018 \,\,{\rm V}}{1.938 \,\,{\rm V}} \approx 0.009.$$
- Thus, the overall distortion factor is:
- $$K = \sqrt{K_2^2 + K_3^2 + K_4^2 +\text{ ...} }\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ \approx 12.5 \%}.$$
(3) The first two proposed solutions are correct:
- Here, the nonlinear distortions cause the lower half-wave to be more peaked than the upper half-wave.
- In addition, $y_{\rm max} = 1.75 \ \rm V$ and $y_{\rm min} = -2.25 \ \rm V$ hold since $y(t)$ does not contain any direct (DC) signals.
Hence, there is no symmetry with respect to the zero line anymore. - For a nonlinear system, the distortion factor $K$ is independent of the frequency of the cosine input signal but strongly dependent on its amplitude.
(4) The root mean square (rms) value of a cosine signal is known to be $\sqrt{0.5}$–times the amplitude. The square of this is the "power":
- $$P_x = \frac{A_x^2}{2} = \frac{(2 \,{\rm V})^2}{2}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 2\,{\rm V^2}}.$$
- Actually, the power also depends on the reference resistance $R$ and has the unit "Watt".
- $P_x = 2 \ \rm W$ is obtained with $R = 1 \ \rm \Omega$ , so exactly the same numerical value as in this simpler calculation.
(5) Denoting
- the amplitude of the basic wave of $y_2(t)$ by $A_1$ and
- the so-called harmonics by $A_2$, $A_3$ and $A_4$,
the distortion power is thus by computing it in the frequency domain:
- $$P_{\rm V} = \frac{1}{2} \cdot \big[ (A_1 - A_x)^2 + A_2^2+ A_3^2+ A_4^2\big] = \frac{1}{2} \cdot \big[ (-2 \,{\rm V} \hspace{-0.05cm}+ \hspace{-0.05cm}1.938 \,{\rm V} )^2 \hspace{-0.05cm}+ \hspace{-0.05cm} (0.234 \,{\rm V})^2 \hspace{-0.05cm}+ \hspace{-0.05cm} (0.058 \,{\rm V})^2 \hspace{-0.05cm}+ \hspace{-0.05cm} (0.018 \,{\rm V})^2 \big] \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{\approx 0.031 \,{\rm V}^2}.$$
Here, $A_x$ denotes the amplitude of the input signal. The signs of the harmonics do not matter in this calculation.
(6) Using the results of subtasks (4) and (5) the following is obtained:
- $$10 \cdot \lg \rho_{V} = 10 \cdot \lg \frac{P_x}{P_{\rm V}}= 10 \cdot \lg \frac{2.000\,{\rm V^2}}{0.031 \,{\rm V}^2} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{\approx 18.10 \,{\rm dB}}.$$
(7) Proposed solutions 1 and 3 are correct:
- The first statement is correct because it holds that
- $$K^2 = \frac{A_2^2 + A_3^2 + A_4^2 + ... }{A_1^2}.$$
- In contrast, the following holds for the reciprocal of the signal–to–distortion–power ratio:
- $${1}/{\rho_{\rm V}} = \frac{(A_1 - A_x)^2+A_2^2 + A_3^2 + A_4^2 + \text{...} }{A_x^2}.$$
- When calculating the distortion power $P_{\rm V}$ a falsification of the amplitude of the basic wave $($this is now $A_1$ instead of $A_x)$ is also taken into account. Moreover, the distortion power is not in terms of $A_1^2$ but in terms of $A_x^2$ .
- Generally, the following relationship holds between the signal–to–distortion–power ratio and the distortion factor:
- $${\rho_{\rm V}} = \frac{A_x^2}{(A_1 - A_x)^2 + K^2 \cdot A_1^2}.$$
- With $A_1 = A_x$ this equation is simplified as follows:
- $${\rho_{\rm V}} = {1}/{ K^2 }.$$
Remarks:
- A distortion factor of $1\%$ corresponds in this case to the result $10 \cdot \lg \rho_{\rm V} = 40 \,{\rm dB}$.
- Using the distortion factor $K = 0.125$ from subtask (2) ⇒ $10 \cdot \lg \rho_{\rm V} = 18.06 \,{\rm dB}$ would have been obtained immediately with the approximation $A_1 \approx A_x$ .
- The actual value $(18.10 \ \rm dB)$ calculated in subtask (7) differs from this only insignificantly.