Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 2.13: Quadrature Amplitude Modulation"
m |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Modulation Methods/Further AM Variants |
}} | }} | ||
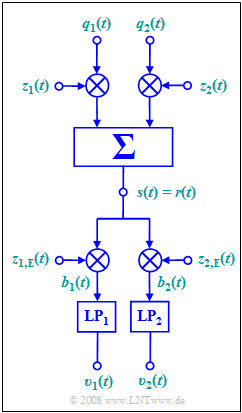
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:EN_Mod_A_2_11.png|right|frame|QAM model under consideration]] |
The "quadrature amplitude modulation" $\rm (QAM)$ explained by the diagram allows the transmission of two source signals $q_1(t)$ and $q_2(t)$ over the same channel | The "quadrature amplitude modulation" $\rm (QAM)$ explained by the diagram allows the transmission of two source signals $q_1(t)$ and $q_2(t)$ over the same channel | ||
*under certain boundary conditions, | *under certain boundary conditions, | ||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
{Which of the following statements apply when $f_1 ≠ f_2$ and $Δϕ_{\rm T} ≠ 0$ (with an arbitrary phase offset)? | {Which of the following statements apply when $f_1 ≠ f_2$ and $Δϕ_{\rm T} ≠ 0$ (with an arbitrary phase offset)? | ||
| − | |type=" | + | |type="()"} |
- $v_1(t) = q_1(t)$ and $v_2(t) = q_2(t)$ both hold. | - $v_1(t) = q_1(t)$ and $v_2(t) = q_2(t)$ both hold. | ||
- Linear distortions occur. | - Linear distortions occur. | ||
Latest revision as of 15:27, 9 April 2022
The "quadrature amplitude modulation" $\rm (QAM)$ explained by the diagram allows the transmission of two source signals $q_1(t)$ and $q_2(t)$ over the same channel
- under certain boundary conditions,
- which are to be determined in this exercise.
In this exercise, with $A_1 = A_2 = 2\ \rm V$:
- $$q_1(t) = A_1 \cdot \cos(2 \pi \cdot f_{\rm 1} \cdot t),$$
- $$q_2(t) = A_2 \cdot \sin(2 \pi \cdot f_{\rm 2} \cdot t)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
For $ω_{\rm T} = 2π · 25\ \rm kHz$, the four carrier signals shown in the diagram are:
- $$z_1(t) = \cos(\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t),$$
- $$ z_2(t) = \sin(\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t),$$
- $$ z_{1,\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm E}}(t) = 2 \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t + \Delta \phi_{\rm T}),$$
- $$ z_{2,\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm E}}(t) = 2 \cdot \sin(\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t + \Delta \phi_{\rm T})\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Both lowpass filters $\rm LP_1$ and $\rm LP_2$ with input signals $b_1(t)$ resp. $b_2(t)$ , remove all frequency components $|f| > f_{\rm T}$.
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter Further AM Variants.
- Particular reference is made to the page Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM).
- It is worth noting that the carrier signals $z_2(t)$ and $z_{2,\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm E}}(t)$ are applied with positive signs here.
- Often – as in the theory section – these carrier signals are given as "minus-sine".
- The following trigonometric transformations are given:
- $$ \cos(\alpha) \cdot \cos(\beta) = 1/2 \cdot \big[ \cos(\alpha - \beta)+ \cos(\alpha + \beta) \big],$$
- $$ \sin(\alpha) \cdot \sin(\beta) = 1/2 \cdot \big[ \cos(\alpha - \beta)- \cos(\alpha + \beta) \big],$$
- $$ \sin(\alpha) \cdot \cos(\beta) = 1/2 \cdot \big[ \sin(\alpha - \beta)+ \sin(\alpha + \beta) \big] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Questions
Solution
- $$s(t) = A_1 \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 1} \cdot t)\cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) + A_2 \cdot \sin(\omega_{\rm 2} \cdot t)\cdot \sin(\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) $$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}s(t) = \frac{A_1}{2}\cdot \cos((\omega_{\rm T} - \omega_{\rm 1})\cdot t) + \frac{A_1}{2}\cdot \cos((\omega_{\rm T} + \omega_{\rm 1})\cdot t) + \frac{A_2}{2}\cdot \cos((\omega_{\rm T} - \omega_{\rm 2})\cdot t) - \frac{A_2}{2}\cdot \cos((\omega_{\rm T} + \omega_{\rm 2})\cdot t)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The second answer is correct.
(2) With $A_1 = A_2 = 2 \ \rm V$ and $f_1 = f_2 = 5\ \rm kHz$, the first and third cosine oscillations constructively overlap and the other two cancel completely.
- Thus, the following simple result is obtained:
- $$ s(t) = 2\,{\rm V} \cdot \cos(2 \pi \cdot 20\,{\rm kHz} \cdot t) \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} s(t = 50\,{\rm µ s}) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 2\,{\rm V}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(3) The first answer is correct:
- For phase-synchronous demodulation $(Δϕ_T = 0)$, the signals before the low-pass filters according to subtask (2) are obtained as:
- $$b_1(t) = 2\,{\rm V} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 20} \cdot t)\cdot 2 \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 25} \cdot t) = 2\,{\rm V} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 5} \cdot t) + 2\,{\rm V} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 45} \cdot t),$$
- $$ b_2(t) = 2\,{\rm V} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 20} \cdot t)\cdot 2 \cdot \sin(\omega_{\rm 25} \cdot t) = 2\,{\rm V} \cdot \sin(\omega_{\rm 5} \cdot t) + 2\,{\rm V} \cdot \sin(\omega_{\rm 45} \cdot t)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Thus, after eliminating the respective $45\ \rm kHz$ components, we get $v_1(t) = q_1(t)$ and $v_2(t) = q_2(t)$.
(4) Analogously to subtask (3) it now holds that:
- $$ b_1(t) = 2\,{\rm V} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 20} \cdot t)\cdot 2 \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 25} \cdot t+ \Delta \phi_{\rm T})= 2\,{\rm V} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 5} \cdot t + \Delta \phi_{\rm T}) + {(45 \,\rm kHz-Anteil )},$$
- $$b_2(t)= 2\,{\rm V} \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm 20} \cdot t)\cdot 2 \cdot \sin(\omega_{\rm 25} \cdot t+ \Delta \phi_{\rm T})= 2\,{\rm V} \cdot \sin(\omega_{\rm 5} \cdot t + \Delta \phi_{\rm T}) + {(45 \,\rm kHz-Anteil )}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The sink signals $v_1(t)$ and $v_2(t)$ in this constellation exhibit delays and thus phase distortions compared with $q_1(t)$ and $q_2(t)$.
- These belong to the class of linear distortions ⇒ Answer 2.
(5) In general, it holds for the received signal:
- $$r(t) = s(t) = q_1(t) \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) + q_2(t) \cdot \sin(\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Multiplication by the receiver-side carrier signals $z_{1,\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm E}}(t)$ and $z_{2,\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm E}}(t)$ and band-limiting leads to the signals
- $$v_1(t) = \cos(\Delta \phi_{\rm T}) \cdot q_1(t) - \sin(\Delta \phi_{\rm T}) \cdot q_2(t),$$
- $$ v_2(t) = \sin(\Delta \phi_{\rm T}) \cdot q_1(t) + \cos(\Delta \phi_{\rm T}) \cdot q_2(t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
From this it can be seen:
- With a phase offset of $Δϕ_{\rm T} = 30^\circ$, the sink signal $v_1(t)$ includes not only the signal $q_1(t)$ attenuated by about $\cos(30^\circ) = 0.866$,
but also the frequency $f_2$ is contained in $q_2(t)$. - This is weighted by the factor $\sin(30^\circ) = 0.5$.
- Thus, nonlinear distortions are present ⇒ Answer 3.