Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 1.1Z: Binary Entropy Function"
m (Nabil verschob die Seite Zusatzaufgaben:1.1 Binäre Entropiefunktion nach 1.1Z Binäre Entropiefunktion) |
m (Text replacement - "optimisation" to "optimization") |
||
| (26 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Information_Theory/Discrete_Memoryless_Sources |
}} | }} | ||
| − | [[File:P_ID2234__Inf_Z_1_1.png|right|]] | + | [[File:P_ID2234__Inf_Z_1_1.png|right|frame|Binary entropy function <br>in "bits" und "nats"]] |
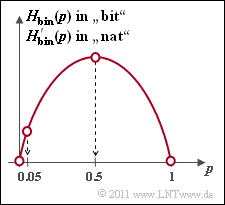
| − | + | We consider a sequence of binary random variables with the symbol set $\{ \rm A, \ B \}$ ⇒ $M = 2$. Let the probabilities of occurrence of the two symbols be $p_{\rm A }= p$ and $p_{\rm B } = 1 - p$. | |
| − | + | The individual sequence elements are statistically independent. The entropy of this message source is equally valid: | |
| − | :$$H_{\rm bin}(p) \hspace{0.1cm} = \hspace{0.1cm} p \cdot {\rm ld}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{\hspace{0.1cm}p\hspace{0.1cm}} + (1-p) \cdot {\rm ld}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{1-p}\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm in \hspace{0.15cm} [bit]}\hspace{0.05cm}, | + | :$$H_{\rm bin}(p) \hspace{0.1cm} = \hspace{0.1cm} p \cdot {\rm ld}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{\hspace{0.1cm}p\hspace{0.1cm}} + (1-p) \cdot {\rm ld}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{1-p}\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm in \hspace{0.15cm} \big [bit \big ]}\hspace{0.05cm},$$ |
| − | + | :$$ H'_{\rm bin}(p) \hspace{0.1cm} = \hspace{0.1cm} p \cdot {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{\hspace{0.1cm}p\hspace{0.1cm}} + (1-p) \cdot {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{1-p}\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm in \hspace{0.15cm} \big [nat\big ]}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | |
| − | + | In these equations, the shorthand terms used are: | |
| − | + | * the "natural" logarithm ⇒ $ {\ln} \hspace{0.09cm} p = \log_{\rm e} \hspace{0.05cm} p$, | |
| + | * the "binary" logarithm ⇒ ${\rm ld} \hspace{0.09cm} p = \log_2 \hspace{0.05cm} p$. | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | The plot shows the binary entropy function as a function of the parameter $p$, assuming $0 ≤ p ≤ 1$ . | |
| − | + | In subtasks '''(5)''' and '''(6)''' the relative error is to be determined if the symbol probability $p$ was determined by simulation $($i.e., as a relative frequency $h)$, resulting in $h = 0.9 \cdot p$ by mistake. The relative error is then given as follows: | |
:$$\varepsilon_{H} = \frac{H_{\rm bin}(h)- H_{\rm bin}(p)}{H_{\rm bin}(p)}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$\varepsilon_{H} = \frac{H_{\rm bin}(h)- H_{\rm bin}(p)}{H_{\rm bin}(p)}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ''Hint:'' | ||
| + | *The task belongs to the chapter [[Information_Theory/Gedächtnislose_Nachrichtenquellen|Discrete Memoryless Sources]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Questions=== | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {How are $H_{\rm bin}(p)$ related to the unit "bit" and $H'_{\rm bin}(p)$ related to the unit "nat"? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + $H_{\rm bin}(p)$ and $H'_{\rm bin}(p)$ differ by a factor. |
| − | - | + | - It holds that $H'_{\rm bin}(p) = H_{\rm bin}(\ln \ p)$. |
| − | - | + | - It holds that $H'_{\rm bin}(p) = 1 + H_{\rm bin}(2 p)$. |
| − | { | + | {Show that the maximum of the binary entropy function is obtained for $p = 0.5$ . What is $H_\text{bin}(p = 0.5)$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $H_\text{bin}(p = 0.5)$ | + | $H_\text{bin}(p = 0.5) \ = \ $ { 1 } $\ \rm bit$ |
| − | { | + | {Calculate the binary entropy value for $p = 0.05$. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $H_\text{bin}(p = 0.05)$ | + | $H_\text{bin}(p = 0.05) \ = \ $ { 0.286 3% } $\ \rm bit$ |
| − | { | + | {Enter the larger of the two $p$–values given by the equation $H_\text{bin}(p)= 0.5 \ \rm bit$ . |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $p$ | + | $p \ = \ $ { 0.89 3% } |
| − | { | + | {Due to insufficient simulation, $p = 0.5$ was determined $10\%$ too low. What is the percentage error with respect to the entropy? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $p = 0.45\ | + | $p = 0.45\ \ {\rm instead of}\ \ p=0.5\hspace{-0.1cm}:\ \ \varepsilon_H \ = \ $ { -0.72--0.68 } $\ \rm \%$ |
| − | { | + | {Due to insufficient simulation, $p = 0.05$ was determined $10\%$ too low. What is the percentage error with respect to the entropy here? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $p = 0.045\ statt\ p=0.05:\ | + | $p = 0.045\ \ {\rm statt}\ \ p=0.05\hspace{-0.1cm}:\ \ \varepsilon_H \ = \ $ { -7.44--7.16 } $\ \rm \%$ |
| − | |||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | + | '''(1)''' The <u>first suggested solution</u> is correct. The other two specifications do not make sense. | |
| − | + | *The entropy function $H'_{\rm bin}(p)$ is according to the specification: | |
| − | + | :$$H'_{\rm bin}(p) \hspace{0.1cm} = \hspace{0.1cm} p \cdot {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{\hspace{0.1cm}p\hspace{0.1cm}} + (1-p) \cdot {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{1-p} = {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}2 \cdot \left [ p \cdot {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{\hspace{0.1cm}p\hspace{0.1cm}} + (1-p) \cdot {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{1-p}\right ]$$ | |
| − | :$$H'_{\rm bin}(p) \hspace{0.1cm} = \hspace{0.1cm} p \cdot {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{\hspace{0.1cm}p\hspace{0.1cm}} + (1-p) \cdot {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{1-p} = | ||
| − | |||
:$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} H'_{\rm bin}(p) \hspace{0.15cm}{\rm (in \hspace{0.15cm} nat)}= | :$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} H'_{\rm bin}(p) \hspace{0.15cm}{\rm (in \hspace{0.15cm} nat)}= | ||
{\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}2 \cdot H_{\rm bin}(p) \hspace{0.15cm}{\rm (in \hspace{0.15cm} bit)} = 0.693\cdot H_{\rm bin}(p)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}2 \cdot H_{\rm bin}(p) \hspace{0.15cm}{\rm (in \hspace{0.15cm} bit)} = 0.693\cdot H_{\rm bin}(p)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''(2)''' The optimization condition is ${\rm d}H_{\rm bin}(p)/{\rm d}p = 0$ resp. | ||
:$$\frac{{\rm d}H'_{\rm bin}(p)}{{\rm d}p} \stackrel{!}{=} 0 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \frac{\rm d}{{\rm d}p} | :$$\frac{{\rm d}H'_{\rm bin}(p)}{{\rm d}p} \stackrel{!}{=} 0 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \frac{\rm d}{{\rm d}p} | ||
| − | \ | + | \big [ - p \cdot {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}p - (1-p) \cdot {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}({1-p})\big ] \stackrel{!}{=} 0$$ |
:$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | :$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | ||
- {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}p - p \cdot \frac {1}{p}+ {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}(1-p) + (1-p)\cdot \frac {1}{1- p}\stackrel{!}{=} 0$$ | - {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}p - p \cdot \frac {1}{p}+ {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}(1-p) + (1-p)\cdot \frac {1}{1- p}\stackrel{!}{=} 0$$ | ||
:$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac {1-p}{p}= 0 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}\frac {1-p}{p}= 1 | :$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac {1-p}{p}= 0 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}\frac {1-p}{p}= 1 | ||
\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \underline { p = 0.5}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \underline { p = 0.5}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | *The entropy values for $p = 0.5$ are thus: | |
| − | :$$H'_{\rm bin}(p = 0.5) \hspace{0.1cm} = \hspace{0.1cm} -2 \cdot 0.5 \cdot {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}0.5 = {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}2 = 0.693 \, {\rm nat}\hspace{0.05cm}, | + | :$$H'_{\rm bin}(p = 0.5) \hspace{0.1cm} = \hspace{0.1cm} -2 \cdot 0.5 \cdot {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}0.5 = {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}2 = 0.693 \, {\rm nat}\hspace{0.05cm},$$ |
| − | + | :$$ H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.5) \hspace{0.1cm} = \hspace{0.1cm} -2 \cdot 0.5 \cdot {\rm ld}\hspace{0.1cm}0.5 = {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.1cm}2 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 1 \, {\rm bit}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | |
| − | + | ||
| − | :$$H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.05) \hspace{0.1cm} = \hspace{0.1cm} 0.05 \cdot {\rm | + | |
| − | + | '''(3)''' For $p = 5\%$ we get: | |
| + | :$$H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.05) \hspace{0.1cm} = \hspace{0.1cm} 0.05 \cdot {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{0.05}+ 0.95 \cdot {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{0.95}= \frac{1}{0.693} \cdot \big [ 0.05 \cdot {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}20+ 0.95 \cdot {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}1.053\big ] | ||
\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 0.286 \, {\rm bit}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 0.286 \, {\rm bit}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''(4)''' This sub-task cannot be solved in closed form, but by "trial and error". | ||
| + | *A solution gives the result: | ||
:$$H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.10) = 0.469 \, {\rm bit}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm}H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.12) = 0.529 \, {\rm bit}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm} | :$$H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.10) = 0.469 \, {\rm bit}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm}H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.12) = 0.529 \, {\rm bit}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm} | ||
| − | H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.11) \approx 0.5 \, {\rm bit} | + | H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.11) \approx 0.5 \, {\rm bit} \hspace{0.3cm} |
| − | + | \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}p_1 \approx 0.11\hspace{0.05cm}. $$ | |
| − | + | *The second solution results from the symmetry of $H_{\rm bin}(p)$ to $p_2 = 1 -p_1 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0.89}$. | |
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(5)''' With $p = 0.45$ one obtains $H_{\rm bin}(p) = 0.993\hspace{0.05cm}\rm bit$. The relative error with respect to entropy is thus | ||
:$$\varepsilon_{H} = \frac{H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.45)- H_{\rm bin}(p= 0.5)}{H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.5)}= \frac{0.993- 1}{1}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= -0.7 \, {\rm \%}} | :$$\varepsilon_{H} = \frac{H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.45)- H_{\rm bin}(p= 0.5)}{H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.5)}= \frac{0.993- 1}{1}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= -0.7 \, {\rm \%}} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | *The minus sign indicates that the entropy value $H_{\rm bin}(p) = 0.993\hspace{0.05cm}\rm bit$ is too small. | |
| + | *If the simulation had yielded the too large value $p = 0.55$ , the entropy and also the relative error would be just as large. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| − | + | '''(6)''' $H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.045) = 0.265\hspace{0.05cm}\rm bit$ is valid. | |
| + | *With the result of subtask '''(3)''' ⇒ $H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.05) = 0.286\hspace{0.05cm}\rm bit$ it follows for the relative error with respect to the entropy: | ||
:$$\varepsilon_{H} = \frac{H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.045)- H_{\rm bin}(p= 0.05)}{H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.05)}= \frac{0.265- 0.286}{0.286}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= -7.3 \, {\rm \%}} | :$$\varepsilon_{H} = \frac{H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.045)- H_{\rm bin}(p= 0.05)}{H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.05)}= \frac{0.265- 0.286}{0.286}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= -7.3 \, {\rm \%}} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | : | + | *The result shows: |
| + | # An incorrect determination of the symbol probabilities by $10\%$ is much more noticeable for $p = 0.05$ due to the steeper $H_{\rm bin}(p)$ course than for $p = 0.5$. | ||
| + | # A too large probability $p = 0.055$ would have led to $H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.055) = 0.307\hspace{0.05cm}\rm bit$ and thus to a distortion of $\varepsilon_H = +7.3\%$. | ||
| + | #In this range, the entropy curve is thus linear (with a good approximation). | ||
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Information Theory: Exercises|^1.1 Memoryless Sources^]] |
Latest revision as of 13:50, 21 September 2021
We consider a sequence of binary random variables with the symbol set $\{ \rm A, \ B \}$ ⇒ $M = 2$. Let the probabilities of occurrence of the two symbols be $p_{\rm A }= p$ and $p_{\rm B } = 1 - p$.
The individual sequence elements are statistically independent. The entropy of this message source is equally valid:
- $$H_{\rm bin}(p) \hspace{0.1cm} = \hspace{0.1cm} p \cdot {\rm ld}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{\hspace{0.1cm}p\hspace{0.1cm}} + (1-p) \cdot {\rm ld}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{1-p}\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm in \hspace{0.15cm} \big [bit \big ]}\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$ H'_{\rm bin}(p) \hspace{0.1cm} = \hspace{0.1cm} p \cdot {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{\hspace{0.1cm}p\hspace{0.1cm}} + (1-p) \cdot {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{1-p}\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm in \hspace{0.15cm} \big [nat\big ]}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
In these equations, the shorthand terms used are:
- the "natural" logarithm ⇒ $ {\ln} \hspace{0.09cm} p = \log_{\rm e} \hspace{0.05cm} p$,
- the "binary" logarithm ⇒ ${\rm ld} \hspace{0.09cm} p = \log_2 \hspace{0.05cm} p$.
The plot shows the binary entropy function as a function of the parameter $p$, assuming $0 ≤ p ≤ 1$ .
In subtasks (5) and (6) the relative error is to be determined if the symbol probability $p$ was determined by simulation $($i.e., as a relative frequency $h)$, resulting in $h = 0.9 \cdot p$ by mistake. The relative error is then given as follows:
- $$\varepsilon_{H} = \frac{H_{\rm bin}(h)- H_{\rm bin}(p)}{H_{\rm bin}(p)}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Hint:
- The task belongs to the chapter Discrete Memoryless Sources.
Questions
Solution
- The entropy function $H'_{\rm bin}(p)$ is according to the specification:
- $$H'_{\rm bin}(p) \hspace{0.1cm} = \hspace{0.1cm} p \cdot {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{\hspace{0.1cm}p\hspace{0.1cm}} + (1-p) \cdot {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{1-p} = {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}2 \cdot \left [ p \cdot {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{\hspace{0.1cm}p\hspace{0.1cm}} + (1-p) \cdot {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{1-p}\right ]$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} H'_{\rm bin}(p) \hspace{0.15cm}{\rm (in \hspace{0.15cm} nat)}= {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}2 \cdot H_{\rm bin}(p) \hspace{0.15cm}{\rm (in \hspace{0.15cm} bit)} = 0.693\cdot H_{\rm bin}(p)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) The optimization condition is ${\rm d}H_{\rm bin}(p)/{\rm d}p = 0$ resp.
- $$\frac{{\rm d}H'_{\rm bin}(p)}{{\rm d}p} \stackrel{!}{=} 0 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \frac{\rm d}{{\rm d}p} \big [ - p \cdot {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}p - (1-p) \cdot {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}({1-p})\big ] \stackrel{!}{=} 0$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} - {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}p - p \cdot \frac {1}{p}+ {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}(1-p) + (1-p)\cdot \frac {1}{1- p}\stackrel{!}{=} 0$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac {1-p}{p}= 0 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}\frac {1-p}{p}= 1 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \underline { p = 0.5}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The entropy values for $p = 0.5$ are thus:
- $$H'_{\rm bin}(p = 0.5) \hspace{0.1cm} = \hspace{0.1cm} -2 \cdot 0.5 \cdot {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}0.5 = {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}2 = 0.693 \, {\rm nat}\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$ H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.5) \hspace{0.1cm} = \hspace{0.1cm} -2 \cdot 0.5 \cdot {\rm ld}\hspace{0.1cm}0.5 = {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.1cm}2 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 1 \, {\rm bit}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(3) For $p = 5\%$ we get:
- $$H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.05) \hspace{0.1cm} = \hspace{0.1cm} 0.05 \cdot {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{0.05}+ 0.95 \cdot {\rm log_2}\hspace{0.1cm}\frac{1}{0.95}= \frac{1}{0.693} \cdot \big [ 0.05 \cdot {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}20+ 0.95 \cdot {\rm ln}\hspace{0.1cm}1.053\big ] \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 0.286 \, {\rm bit}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(4) This sub-task cannot be solved in closed form, but by "trial and error".
- A solution gives the result:
- $$H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.10) = 0.469 \, {\rm bit}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm}H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.12) = 0.529 \, {\rm bit}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm} H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.11) \approx 0.5 \, {\rm bit} \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}p_1 \approx 0.11\hspace{0.05cm}. $$
- The second solution results from the symmetry of $H_{\rm bin}(p)$ to $p_2 = 1 -p_1 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 0.89}$.
(5) With $p = 0.45$ one obtains $H_{\rm bin}(p) = 0.993\hspace{0.05cm}\rm bit$. The relative error with respect to entropy is thus
- $$\varepsilon_{H} = \frac{H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.45)- H_{\rm bin}(p= 0.5)}{H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.5)}= \frac{0.993- 1}{1}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= -0.7 \, {\rm \%}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The minus sign indicates that the entropy value $H_{\rm bin}(p) = 0.993\hspace{0.05cm}\rm bit$ is too small.
- If the simulation had yielded the too large value $p = 0.55$ , the entropy and also the relative error would be just as large.
(6) $H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.045) = 0.265\hspace{0.05cm}\rm bit$ is valid.
- With the result of subtask (3) ⇒ $H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.05) = 0.286\hspace{0.05cm}\rm bit$ it follows for the relative error with respect to the entropy:
- $$\varepsilon_{H} = \frac{H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.045)- H_{\rm bin}(p= 0.05)}{H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.05)}= \frac{0.265- 0.286}{0.286}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= -7.3 \, {\rm \%}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The result shows:
- An incorrect determination of the symbol probabilities by $10\%$ is much more noticeable for $p = 0.05$ due to the steeper $H_{\rm bin}(p)$ course than for $p = 0.5$.
- A too large probability $p = 0.055$ would have led to $H_{\rm bin}(p = 0.055) = 0.307\hspace{0.05cm}\rm bit$ and thus to a distortion of $\varepsilon_H = +7.3\%$.
- In this range, the entropy curve is thus linear (with a good approximation).