Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 3.5Z: GSM Network Components"
m (Text replacement - "===Sample Solution===" to "===Solution===") |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
}} | }} | ||
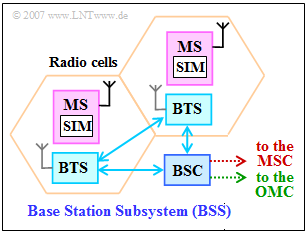
| − | [[File:EN_Mob_A_3_5Z.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:EN_Mob_A_3_5Z.png|right|frame|Base Station Subsystem of GSM]] |
| − | For the mobile phone standard | + | For the mobile phone standard "Global System for Mobile Communications" - abbreviated $\rm GSM$ - the network infrastructure includes the following subsystems: |
| − | * | + | *"Base Station Subsystem" $\rm (BSS)$, |
| − | * | + | *"Switching & Management Subsystem" $\rm (SMSS)$, |
| − | * | + | *"Operation & Maintenance Subsystem" $\rm (OMSS)$. |
| − | |||
| − | The | + | The "Base Station Subsystem" is mainly responsible for the GSM radio network (see diagram), while the "Switching & Management Subsystem" represents the switching network and the "Operation & Maintenance Subsystem" is responsible for operation and maintenance. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | The following terms will continue to be used in the questions on these exercise: | ||
| + | *"Authentication Center" $\rm (AUC)$, | ||
| + | *"Base Station Controller" $\rm (BSC)$, | ||
| + | *"Base Transceiver Station" $\rm (BTS)$, | ||
| + | *"Gateway Mobile Switching Center" $\rm (GMSC)$, | ||
| + | *"Home Location Register" $\rm (HLR)$, | ||
| + | *"Mobile Switching Center" $\rm (MSC)$, | ||
| + | *"Operation and Maintenance Center" $\rm (OMC)$, | ||
| + | *"Visitor Location Register" $\rm (VLR)$. | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | ''Notes:'' This exercise belongs to the chapter [[Mobile_Communications/Characteristics_of_GSM|Characteristics of GSM]]. | |
| Line 40: | Line 39: | ||
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
+ With the BSS, | + With the BSS, | ||
| − | - the SMSS, | + | - with the SMSS, |
| − | - the OMSS. | + | - with the OMSS. |
| − | {Which statements apply to a | + | {Which statements apply to a base transceiver station (BTS)? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
+ It includes the base station's transmitting and receiving devices. | + It includes the base station's transmitting and receiving devices. | ||
- The task of the BTS is to switch calls. | - The task of the BTS is to switch calls. | ||
| − | + In most cases, several BTS are subordinate to a common BSC. | + | + In most cases, several BTS are subordinate to a common base station controller (BSC). |
{How many links can a BTS with multiple antennas support if each antenna covers a sector of $120^\circ$ ? | {How many links can a BTS with multiple antennas support if each antenna covers a sector of $120^\circ$ ? | ||
| Line 55: | Line 54: | ||
{Which of the following components are part of the OMSS? | {Which of the following components are part of the OMSS? | ||
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - The GMSC | + | - The GMSC. |
| − | - The MSC | + | - The MSC. |
| − | + The OMC | + | + The OMC. |
{Which of the following components are databases? | {Which of the following components are databases? | ||
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + The AUC | + | + The AUC. |
| − | - The GMSC | + | - The GMSC. |
| − | + The HLR | + | + The HLR. |
| − | + The VLR | + | + The VLR. |
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
Revision as of 14:11, 23 January 2021
For the mobile phone standard "Global System for Mobile Communications" - abbreviated $\rm GSM$ - the network infrastructure includes the following subsystems:
- "Base Station Subsystem" $\rm (BSS)$,
- "Switching & Management Subsystem" $\rm (SMSS)$,
- "Operation & Maintenance Subsystem" $\rm (OMSS)$.
The "Base Station Subsystem" is mainly responsible for the GSM radio network (see diagram), while the "Switching & Management Subsystem" represents the switching network and the "Operation & Maintenance Subsystem" is responsible for operation and maintenance.
The following terms will continue to be used in the questions on these exercise:
- "Authentication Center" $\rm (AUC)$,
- "Base Station Controller" $\rm (BSC)$,
- "Base Transceiver Station" $\rm (BTS)$,
- "Gateway Mobile Switching Center" $\rm (GMSC)$,
- "Home Location Register" $\rm (HLR)$,
- "Mobile Switching Center" $\rm (MSC)$,
- "Operation and Maintenance Center" $\rm (OMC)$,
- "Visitor Location Register" $\rm (VLR)$.
Notes: This exercise belongs to the chapter Characteristics of GSM.
Fragebogen
Solution
(1) Each mobile station (MS) is in communication with a base transceiver station (BTS). This is part of the Base Station Subsystem (BSS) ⇒ solution 1.
(2) Correct are the statements 1 and 3. In contrast, the base transceiver station is not responsible for switching tasks, but this is rather the task of a mobile switching center (MSC), which is part of the switching and management subsystem (SMSS).
(3) If, as is usually the case with GSM, the individual antennas cover $120^\circ$ sectors, a BTS can provide up to three connection paths ⇒ $N_{\rm max} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 3}$.
(4) Only the Operation and Management Center (OMC) belongs to the OMSS ⇒ Proposal 3 .
- In contrast, MSC and GMSC are components of the mobile switching network (SMSS).
- With regard to OMC, a distinction is made between OMC-B (for BSS monitoring) and OMC-S (for SMSS monitoring).
(5) solutions 1, 3 und 4 are correct:
- The Gateway Mobile Switching Center (GMSC) is a hardware unit that is responsible for switching between the fixed network and the mobile network.
- The other three terms given actually describe databases of the Switching & Management Subsystem (SMSS).
- The Authentication Center (AUC) is responsible for the storage of confidential data and keys.
- The Home Location Register (HLR) is a central register for the entire Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN) for managing unencrypted subscriber data, subscribed services and routing for calls from a mobile operator's own subscribers.
- Contrary, the Visitors' Location Register (VLR) contains information about the current visitors of other operators who are located in the current PLMN.