Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 4.09: Recursive Systematic Convolutional Codes"
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
===Questions=== | ===Questions=== | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {What is the impulse response $\underline{g}$ ? |
|type="()"} | |type="()"} | ||
| − | + | + | + $\underline{g} = (1, \, 1, \, 1, \, 0, \, 1, \, 1, \, 0, \, 1, \, 1, \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm})$ holds. |
| − | - | + | - $\underline{g} = (1, \, 0, \, 1, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0, \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm})$ holds. |
| − | { | + | {It holds $\underline{u} = (1, \, 1, \, 0, \, 1)$. Which statements hold for the parity sequence $\underline{p}$ ? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - | + | - $\underline{p} = (1, \, 0, \, 1, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0, \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm})$ holds. |
| − | + | + | + $\underline{p} = (1, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0, \, 1, \, 1, \, 0, \, 1, \, 1, \, 0, \, 1, \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm})$ holds. |
| − | - | + | - With limited information sequence $\underline{u}$ is always also $\underline{p}$ limited. |
| − | { | + | {What is the $D$–transfer function $G(D)$? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + $G(D) = 1 + D + D^2 + D^4 + D^5 + D^7 + D^8 + \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm}$ holds. |
| − | + | + | + $G(D) = (1 + D^2)/(1 + D + D^2)$ holds. |
| − | - | + | - $G(D) = (1 + D + D^2)/(1 + D^2)$ holds. |
| − | { | + | {Now let $\underline{u} = (1, \, 1, \, 1)$ hold. Which statements hold for the parity sequence $\underline{p}$? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + $\underline{p} = (1, \, 0, \, 1, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0, \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm})$ holds. |
| − | - | + | - $\underline{p} = (1, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0, \, 1, \, 1, \, 0, \, 1, \, 1, \, 0, \, 1, \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm})$ holds. |
| − | - | + | - With unlimited impulse response $\underline{g}$ is always also $\underline{p}$ unlimited. |
| − | { | + | {What is the free distance $d_{\rm F}$ of this RSC encoder? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$d_{\rm F} \ = \ ${ 5 3% } | $d_{\rm F} \ = \ ${ 5 3% } | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
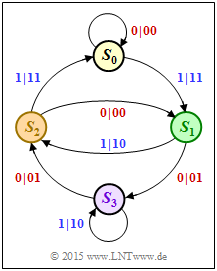
| − | '''(1)''' | + | '''(1)''' Tracing the transitions in the state diagram for the sequence $\underline{u} = (1, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0, \, 0)$ at the input, we get the path |
:$$S_0 → S_1 → S_3 → S_2 → S_1 → S_3 → S_2 → S_1 → S_3 → \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...} \hspace{0.05cm}$$ | :$$S_0 → S_1 → S_3 → S_2 → S_1 → S_3 → S_2 → S_1 → S_3 → \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...} \hspace{0.05cm}$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *For each transition, the first code symbol $x_i^{(1)}$ is equal to the information bit $u_i$ and the code symbol $x_i^{(2)}$ indicates the parity-check bit $p_i$. |
| − | * | + | *This gives the result corresponding to <u>solution proposition 1</u>: |
:$$\underline{p}= (\hspace{0.05cm}1\hspace{0.05cm}, | :$$\underline{p}= (\hspace{0.05cm}1\hspace{0.05cm}, | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}1\hspace{0.05cm}, | \hspace{0.05cm}1\hspace{0.05cm}, | ||
| Line 89: | Line 89: | ||
= \underline{g}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | = \underline{g}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *For any RSC code, the impulse response $\underline{g}$ is infinite in length and becomes periodic at some point, in this example with period $P = 3$ and "$0, \, 1, \, 1$". |
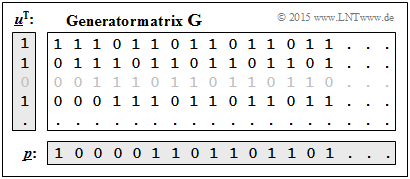
| − | [[File:P_ID3054__KC_A_4_9b_v1.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID3054__KC_A_4_9b_v1.png|right|frame|Clarification of $\underline{p} = (1, \, 1, \, 0, \, 1)^{\rm T} \cdot \mathbf{G}$]] |
| − | '''(2)''' | + | '''(2)''' The graph shows the solution of this exercise according to the equation $\underline{p} = \underline{u}^{\rm T} \cdot \mathbf{G}$. |
| − | * | + | * Here the generator matrix $\mathbf{G}$ is infinitely extended downward and to the right. |
| − | * | + | *The correct solution is <u>proposal 2</u>. |
<br clear=all> | <br clear=all> | ||
| − | '''(3)''' | + | '''(3)''' Correct are <u>the proposed solutions 1 and 2</u>: |
| − | * | + | *Between the impulse response $\underline{g}$ and the $D$–transfer function $\mathbf{G}(D)$ there is the relation according to the first proposed solution: |
:$$\underline{g}= (\hspace{-0.05cm}1\hspace{-0.05cm}, | :$$\underline{g}= (\hspace{-0.05cm}1\hspace{-0.05cm}, | ||
\hspace{-0.05cm}1\hspace{-0.05cm}, | \hspace{-0.05cm}1\hspace{-0.05cm}, | ||
| Line 112: | Line 112: | ||
G(D) = 1\hspace{-0.05cm}+\hspace{-0.05cm} D\hspace{-0.05cm} +\hspace{-0.05cm} D^2\hspace{-0.05cm} +\hspace{-0.05cm} D^4 \hspace{-0.05cm}+\hspace{-0.05cm} D^5 \hspace{-0.05cm}+\hspace{-0.05cm} D^7 \hspace{-0.05cm}+\hspace{-0.05cm} D^8 + \hspace{0.05cm} \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | G(D) = 1\hspace{-0.05cm}+\hspace{-0.05cm} D\hspace{-0.05cm} +\hspace{-0.05cm} D^2\hspace{-0.05cm} +\hspace{-0.05cm} D^4 \hspace{-0.05cm}+\hspace{-0.05cm} D^5 \hspace{-0.05cm}+\hspace{-0.05cm} D^7 \hspace{-0.05cm}+\hspace{-0.05cm} D^8 + \hspace{0.05cm} \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *Let us now examine the second proposal: |
:$$G(D) = \frac{1+ D^2}{1+ D + D^2} \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | :$$G(D) = \frac{1+ D^2}{1+ D + D^2} \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | ||
G(D) \cdot [1+ D + D^2] = 1+ D^2 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | G(D) \cdot [1+ D + D^2] = 1+ D^2 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *The following calculation shows that this equation is indeed true: |
:$$(1+ D+ D^2+ D^4 +D^5 + D^7 + D^8 + \hspace{0.05cm} \text{...}) \cdot (1+ D+ D^2 ) =$$ | :$$(1+ D+ D^2+ D^4 +D^5 + D^7 + D^8 + \hspace{0.05cm} \text{...}) \cdot (1+ D+ D^2 ) =$$ | ||
:$$=1+ D+ D^2\hspace{1.05cm} +D^4 + D^5 \hspace{1.05cm} +D^7 + D^8 \hspace{1.05cm} + D^{10}+ \hspace{0.05cm} \text{...}$$ | :$$=1+ D+ D^2\hspace{1.05cm} +D^4 + D^5 \hspace{1.05cm} +D^7 + D^8 \hspace{1.05cm} + D^{10}+ \hspace{0.05cm} \text{...}$$ | ||
| Line 124: | Line 124: | ||
cm}+ D^2} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | cm}+ D^2} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *But since equation (2) is true, the last equation must be false. |
| − | '''(4)''' | + | '''(4)''' Correct is only the <u>proposed solution 1</u>: |
| − | * | + | *From $\underline{u} = (1, \, 1, \, 1)$ follows $U(D) = 1 + D + D^2$. Thus also holds: |
:$$P(D) = U(D) \cdot G(D) = (1+D+D^2) \cdot \frac{1+D^2}{1+D+D^2}= 1+D^2\hspace{0.3cm} | :$$P(D) = U(D) \cdot G(D) = (1+D+D^2) \cdot \frac{1+D^2}{1+D+D^2}= 1+D^2\hspace{0.3cm} | ||
\Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} \underline{p}= (\hspace{0.05cm}1\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} 1\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm}\text{...}\hspace{0.05cm})\hspace{0.05cm}. $$ | \Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} \underline{p}= (\hspace{0.05cm}1\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} 1\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm}\text{...}\hspace{0.05cm})\hspace{0.05cm}. $$ | ||
| − | * | + | * If the variables $u_i$ and $g_i$ were real-valued, the (discrete) convolution $\underline{p} = \underline{u} * \underline{g}$ would always lead to a broadening ⇒ $\underline{p}$ in this case would be broader than $\underline{u}$ and also broader than $\underline{g}$. |
| − | * | + | * On the other hand, for $u_i ∈ {\rm GF}(2)$ and $g_i ∈ {\rm GF}(2)$ it may (but need not) happen that even with unbounded $\underline{u}$ or for unbounded $\underline{g}$ the convolution product $\underline{p} = \underline{u} * \underline{g}$ is bounded. |
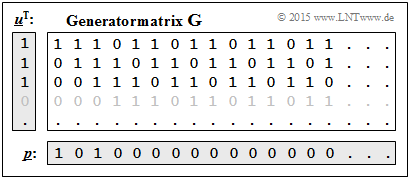
[[File:P_ID3057__KC_A_4_9d_v1.png|right|frame|Verdeutlichung von $\underline{p} = (1, \, 1, \, 1, \, 0, \, ...)^{\rm T} \cdot \mathbf{G}$]] | [[File:P_ID3057__KC_A_4_9d_v1.png|right|frame|Verdeutlichung von $\underline{p} = (1, \, 1, \, 1, \, 0, \, ...)^{\rm T} \cdot \mathbf{G}$]] | ||
| − | * | + | *The result is finally checked according to the equation $\underline{p} = \underline{u}^{\rm T} \cdot \mathbf{G}$ is checked. |
Revision as of 22:08, 29 November 2022
In the "Exercise 4.8" important properties of convolutional codes have already been derived from the state transition diagram, assuming a non-recursive filter structure.
Now a rate $1/2$ RSC code is treated in a similar manner. Here "RSC" stands for "Recursive Systematic Convolutional".
The transfer function matrix of an RSC convolutional code can be specified as follows:
- $${\boldsymbol{\rm G}}(D) = \left [ 1\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm} G^{(2)}(D)/G^{(1)}(D) \right ] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Otherwise, exactly the same conditions apply here as in exercise 4.8. We refer again to the following theory pages:
- "Systematic convolutional codes"
- "Representation in the state transition diagram"
- "Definition of the free distance"
- "GF(2) description forms of a digital filter"
- "Application of the D–transform to rate 1/n convolution encoders"
- "Filter structure with fractional–rational transfer function"
In the state transition diagram, the state $S_0$ is always assumed. Two arrows go from each state. The label is "$u_i \hspace{0.05cm}| \hspace{0.05cm} x_i^{(1)}x_i^{(2)}$". For a systematic code, this involves:
- The first code bit is identical to the information bit: $\hspace{0.2cm} x_i^{(1)} = u_i ∈ \{0, \, 1\}$.
- The second code bit is the parity-check bit: $\hspace{0.2cm} x_i^{(2)} = p_i ∈ \{0, \, 1\}$.
Hints:
- The exercise refers to the chapter "Basics of Turbo Codes".
- Similar exercises can be found in chapters 3.1 through 3.3.
- The following vectorial quantities are used in the questions for this exercise:
- the information sequence: $\hspace{0.2cm} \underline{u} = (u_1, \, u_2, \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm} )$,
- the parity-check sequence: $\hspace{0.2cm} \underline{p} = (p_1, \, p_2, \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm})$,
- the impulse response: $\hspace{0.2cm} \underline{g} = (g_1, \, g_2, \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm} ); \hspace{0.2cm}$ this is equal to the parity sequence $\underline{p}$ for $\underline{u} = (1, \, 0, \, 0, \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm} )$.
Questions
Solution
- $$S_0 → S_1 → S_3 → S_2 → S_1 → S_3 → S_2 → S_1 → S_3 → \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...} \hspace{0.05cm}$$
- For each transition, the first code symbol $x_i^{(1)}$ is equal to the information bit $u_i$ and the code symbol $x_i^{(2)}$ indicates the parity-check bit $p_i$.
- This gives the result corresponding to solution proposition 1:
- $$\underline{p}= (\hspace{0.05cm}1\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.05cm}1\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.05cm}1\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.05cm} 0\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.05cm} 1\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.05cm} 1\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.05cm} 0\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.05cm} 1\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.05cm} 1\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm}\text{...} \hspace{0.05cm}) = \underline{g}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- For any RSC code, the impulse response $\underline{g}$ is infinite in length and becomes periodic at some point, in this example with period $P = 3$ and "$0, \, 1, \, 1$".
(2) The graph shows the solution of this exercise according to the equation $\underline{p} = \underline{u}^{\rm T} \cdot \mathbf{G}$.
- Here the generator matrix $\mathbf{G}$ is infinitely extended downward and to the right.
- The correct solution is proposal 2.
(3) Correct are the proposed solutions 1 and 2:
- Between the impulse response $\underline{g}$ and the $D$–transfer function $\mathbf{G}(D)$ there is the relation according to the first proposed solution:
- $$\underline{g}= (\hspace{-0.05cm}1\hspace{-0.05cm}, \hspace{-0.05cm}1\hspace{-0.05cm}, \hspace{-0.05cm}1\hspace{-0.05cm}, \hspace{-0.05cm}0\hspace{-0.05cm}, \hspace{-0.05cm}1\hspace{-0.05cm}, \hspace{-0.05cm}1\hspace{-0.05cm}, \hspace{-0.05cm}0\hspace{-0.05cm}, \hspace{-0.05cm}1\hspace{-0.05cm}, \hspace{-0.05cm}1\hspace{-0.05cm}, ... ) \quad \circ\!\!-\!\!\!-^{\hspace{-0.25cm}D}\!\!\!-\!\!\bullet\quad G(D) = 1\hspace{-0.05cm}+\hspace{-0.05cm} D\hspace{-0.05cm} +\hspace{-0.05cm} D^2\hspace{-0.05cm} +\hspace{-0.05cm} D^4 \hspace{-0.05cm}+\hspace{-0.05cm} D^5 \hspace{-0.05cm}+\hspace{-0.05cm} D^7 \hspace{-0.05cm}+\hspace{-0.05cm} D^8 + \hspace{0.05cm} \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Let us now examine the second proposal:
- $$G(D) = \frac{1+ D^2}{1+ D + D^2} \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} G(D) \cdot [1+ D + D^2] = 1+ D^2 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The following calculation shows that this equation is indeed true:
- $$(1+ D+ D^2+ D^4 +D^5 + D^7 + D^8 + \hspace{0.05cm} \text{...}) \cdot (1+ D+ D^2 ) =$$
- $$=1+ D+ D^2\hspace{1.05cm} +D^4 + D^5 \hspace{1.05cm} +D^7 + D^8 \hspace{1.05cm} + D^{10}+ \hspace{0.05cm} \text{...}$$
- $$+ \hspace{0.8cm}D+ D^2+D^3 \hspace{1.05cm}+ D^5 + D^6 \hspace{1.05cm} +D^8 + D^9 \hspace{1.25cm} +\hspace{0.05cm} \text{...} $$
- $$+ \hspace{1.63cm} D^2+D^3+ D^4 \hspace{1.05cm}+ D^6 +D^7 \hspace{1.05cm}+ D^9 + D^{10} \hspace{0.12cm}+ \hspace{0.05cm} \text{...}$$
- $$=\underline{1\hspace{0.72 cm}+ D^2} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- But since equation (2) is true, the last equation must be false.
(4) Correct is only the proposed solution 1:
- From $\underline{u} = (1, \, 1, \, 1)$ follows $U(D) = 1 + D + D^2$. Thus also holds:
- $$P(D) = U(D) \cdot G(D) = (1+D+D^2) \cdot \frac{1+D^2}{1+D+D^2}= 1+D^2\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} \underline{p}= (\hspace{0.05cm}1\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} 1\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} 0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm}\text{...}\hspace{0.05cm})\hspace{0.05cm}. $$
- If the variables $u_i$ and $g_i$ were real-valued, the (discrete) convolution $\underline{p} = \underline{u} * \underline{g}$ would always lead to a broadening ⇒ $\underline{p}$ in this case would be broader than $\underline{u}$ and also broader than $\underline{g}$.
- On the other hand, for $u_i ∈ {\rm GF}(2)$ and $g_i ∈ {\rm GF}(2)$ it may (but need not) happen that even with unbounded $\underline{u}$ or for unbounded $\underline{g}$ the convolution product $\underline{p} = \underline{u} * \underline{g}$ is bounded.
- The result is finally checked according to the equation $\underline{p} = \underline{u}^{\rm T} \cdot \mathbf{G}$ is checked.
(5) Nach ähnlicher Vorgehensweise wie in der Aufgabe A4.8, (4) erkennt man:
- Die freie Distanz wird auch hier durch den Pfad $S_0 → S_0 → S_1 → S_2 → S_0 → S_0 → \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...}\hspace{0.05cm}$ bestimmt.
- Die zugehörige Codesequenz $\underline{x}$ ist nun aber " $00 \ 11 \ 10 \ 11 \ 00 \ ... $".
- Damit ergibt sich die freie Distanz zu $d_{\rm F} \ \underline{= 5}$.
- Beim nichtrekursiven Code (Aufgabe 4.8) war dagegen die freie Distanz $d_{\rm F} = 3$.