Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 3.9: Further Developments of UMTS"
m (Text replacement - "Mobile Kommunikation/Die Charakteristika von UMTS" to "Mobile_Communications/Characteristics_of_UMTS") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Mobile_Communications/Characteristics_of_UMTS |
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 15:04, 15 December 2020
Shortly after the first release of GSM and UMTS, there were already efforts to significantly increase the transmission speed of data transmission. The following standardized system variants were developed:
- HSCSD: High-Speed Circuit-Switched Data,
- GPRS: General Packet Radio Service,
- EDGE: Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution,
- HSUPA: High Speed Uplink Packet Access,
- HSDPA: High Speed Downlink Packet Access.
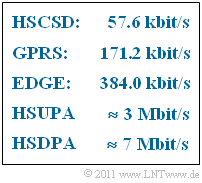
HSUPA and HSDPA are also combined to form High Speed Packet Access ⇒ HSPA. The above chart shows the data transmission rates of these advanced mobile communications standards, whereby we specify so-called "peak data rates" for HSCSD, GPRS and EDGE, which were difficult to achieve under real conditions (at about 2012).
The indicated rates for HSUPA and HSDPA are now quite realistic.
The standard has been modified several times. In 2012, the „peak data rates” for HSUPA have been denoted as $6 \ \rm Mbit/s$ , and equivalently for HSDPA $28.8 \ \rm Mbit/s$ .
- However, it has to be taken into account that under "best conditions", HSCSD/GPRS/EDGE means a single user with a bandwidth $400 \ \rm kHz$ and HSUPA/HSDPA means a single user with a bandwidth $5 \rm MHz$ (i.e. even better conditions).
Notes:
- This task belongs to the chapter Die Charakteristika von UMTS.
- Particular reference is made to the page UMTS–Erweiterungen HSDPA und HSUPA.
Questionnaire
Sample solution
(1) Correct is only the solution 4:
- Only HSDPA and HSUPA are further developments of UMTS.
- HSCSD, GPRS and EDGE, on the other hand, are assigned to the GSM–phase $2+$.
(2) The solutions 3 and 4 are applicable:
- EDGE is actually also counted among the 3G–mobile phone systems, although it was created in the GSM–phase $2+$.
(3) Correct are the solutions 2 and 3:
- With HSCSD, the data rate that can be transmitted in one time slot is increased by $50 \ \%$ from $9.6 \ \rm kbit/s$ (with conventional GSM) to $14.4 \ \rm kbit/s$ by puncturing the convolutional code.
- By bundling four time slots, the maximum transmission rate of $57.6 \ \ \rm kbit/s$ is finally achieved with this circuit-oriented further developed GSM–.
- The best conditions are required for this. In reality, this theoretical value is rather not reached.
(4) Correct are the statements 1 and 3:
- Packet-oriented transmission and some other measures leading to shorter access times result in a data transfer rate of up to $21.4 \ \rm kbit/s$.
- By bundling eight time slots (Multislot Capability) one reaches a maximum of $171.2 \ \ \rm kbit/s$ (this is also a theoretical value).
- As with conventional GSM, only Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying (GMSK) is used as modulation method.
(5) Correct are all proposed solutions:
- EDGE is also package-oriented and provides a total of nine different Modulation and Coding Schemes (MCS) which are selected according to the channel conditions.
- In the higher modes (MCS-5 and higher), the more compact modulation method 8-PSK is used instead of GMSK, in which three bits are transmitted with each input symbol, thus (theoretically) tripling the data rate.
- With MCS-8 (according to the specification $54.5 \ \rm kbit/s$) and seven time slots, one reaches $380.8 \ \rm kbit/s$ and thus the order of magnitude of UMTS.
(6) All solution suggestions are correct:
- At HSPA one uses the Hybrid–ARQ–Verfahren as well as Node–B–Scheduling.
- In addition, modulation, coding and transmission rate are designed adaptiv.
- The optimization factor is not the data rate of individual users, but rather the largest possible cell capacity with regard to all mobile phone users.