Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 4.4Z: Physical Channels in LTE"
From LNTwww
m (Text replacement - "Mobile Kommunikation/Bitübertragungsschicht bei LTE" to "Mobile_Communications/Physical_Layer_for_LTE") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Mobile_Communications/Physical_Layer_for_LTE |
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 15:07, 15 December 2020
The task refers to the two pages
All information required for the task can be found on these pages.
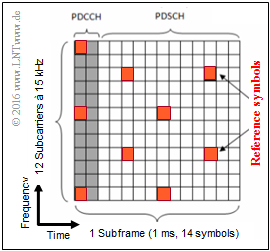
The diagram shows the assignment of the two channels PDCCH and PDSCH in frequency and time:
- One frequency block comprises $180 \ \rm kHz$ and is divided into twelve $15 \ \rm kHz$–subcarriers
- A subframe is one millisecond long and includes $14$ symbols.
- Red marked are so called reference symbols.
Notes:
- The task belongs to the chapter Bitübertragungsschicht bei LTE.
Questionnaire
Sample solution
(1) Correct are the solutions 3 and 4:
The assignment to Downlink or Uplink can be recognized by the second letter. It means:
- PDCCH: Physical Downlink Control Channel,
- PDSCH: Physical Downlink Shared Channel,
- PUCCH: Physical Uplink Control Channel,
- PUSCH: Physical Uplink Shared Channel.
(2) Correct are the solutions 2 and 4:
- A "C" ⇒ Control as third letter indicates a control channel.
- User data are always transferred to the Shared Channels ⇒ "S",
(3) All statements are correct:
- A block in the LTE downlink occupies $180 \ \ \rm kHz$ (twelve subcarriers at $15 \ \ \rm kHz$ each) and has a duration of $1 \ \ \rm ms$.
- The assignment with PDCCH and PDSCH shows that the downlink is being considered.
- The reference symbols are needed to estimate the channel quality and calculate the Channel Quality Indicator (CQI).
- These reference symbols are distributed over different frequencies or symbols (different times) in order to estimate the channel quality as comprehensively as possible.
(4) The statement 1 is true because only two of the $14$ columns are occupied by the control channel PDCCH.
However, this result cannot be generalized. Rather, the division between PDCCH– and PDSCH symbols is dependent on the user's requirements and therefore dynamic.
- For many users with a low data rate, the PDCCH would include three or four symbols, because this requires more intensive tuning than for a few concurrent users with high data rates.
- The information "How many PDCCH symbols" is communicated to the terminal device via the Physical Control Format Indicator Channel (PCFICH).
(5) All statementsabove are correct:
- The data rate of each user depends directly on the number of blocks of width $180 \ \rm kHz$ assigned to him.
- The total LTI frequency width is between $1.4 \ \rm MHz$ and $20 \ \rm MHz$.
- In the frequency band of $1.4 \ \ \rm MHz$ six blocks of $180 \ \ \rm kHz$ are placed.
- The overhead is thus $(1.4 - 6 \cdot 0.18)/1.4 \approx 22.8 \%$.
- At $20 \ \rm MHz$ total frequency width, i.e. $100$ blocks, the overhead is $(20 - 100 \cdot 0.18)/26 = 10 \ \ \%$.
- The more blocks are available in total, the more can be allocated to each individual user if his channel is good and if many other users do not also have high demands at the same time.