Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 4.5Z: Tangent Hyperbolic and Inverse"
m (Guenter moved page Aufgabe 4.5Z: Tangens Hyperbolikus und Inverse to Exercise 4.5Z: Tangent Hyperbolic and Inverse) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Channel_Coding/Soft-in_Soft-Out_Decoder}} |
| − | [[File:P_ID3025__KC_Z_4_5_v1.png|right|frame|$y = \tanh {(x)}$ | + | [[File:P_ID3025__KC_Z_4_5_v1.png|right|frame|$y = \tanh {(x)}$ represented on a table]] |
| − | + | In [[Channel_Coding/Soft-in_Soft-Out_Decoder#Calculation_of_extrinsic_LLRs|"Theory Part"]] it was shown, using the example of <i>single parity–check code</i> that the extrinsic $L$ value with respect to the $i$th symbol is defined as follows: | |
| − | :$$L_{\rm E}(i) = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.2cm}\frac{{\rm Pr} \left [w_{\rm H}(\underline{x}^{(-i)})\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm | + | :$$L_{\rm E}(i) = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.2cm}\frac{{\rm Pr} \left [w_{\rm H}(\underline{x}^{(-i)})\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm is \hspace{0.15cm} even} \hspace{0.05cm} | \hspace{0.05cm}\underline{y} \hspace{0.05cm}\right ]}{{\rm Pr} \left [w_{\rm H}(\underline{x}^{(-i)})\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm is \hspace{0.15cm} odd} \hspace{0.05cm} | \hspace{0.05cm}\underline{y} \hspace{0.05cm}\right ]} |
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | This equation is also applicable to many other channel codes. The code word $\underline{x}^{(-i)}$ in this definition includes all symbols except $x_i$ and thus has length $n-1$ only. | |
| − | In | + | In the [[Aufgaben:Exercise_4.4:_Extrinsic_L-values_at_SPC|"Exercise 4.4"]] it was shown that the extrinsic $L$ value can also be written as follows: |
:$$L_{\rm E}(i) = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.2cm} \frac{1 + \pi}{1 - \pi}\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm} | :$$L_{\rm E}(i) = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.2cm} \frac{1 + \pi}{1 - \pi}\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm} | ||
{\rm mit} \hspace{0.3cm} \pi = \prod\limits_{j \ne i}^{n} \hspace{0.15cm}{\rm tanh}(L_j/2) | {\rm mit} \hspace{0.3cm} \pi = \prod\limits_{j \ne i}^{n} \hspace{0.15cm}{\rm tanh}(L_j/2) | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | In | + | In this exercise, we will now look for another calculation possibility. |
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
| − | + | Hints: | |
| − | * | + | *This exercise belongs to the chapter [[Channel_Coding/Soft-in_Soft-Out_Decoder|"Soft–in Soft–out Decoder"]]. |
| − | * | + | *Reference is made in particular to the [[Channel_Coding/Soft-in_Soft-Out_Decoder#Calculation_of_extrinsic_LLRs|"Calculations of extrinsic LLRs"]] page. |
| − | * | + | * Above you can see a table with the numerical values of the function $y = \tanh(x)$ ⇒ <i>hyperbolic tangent</i>. |
| − | * | + | *With the rows highlighted in red you can read the values of the inverse function $x = \tanh^{-1}(y)$ needed for the subtask '''(5)'''. |
| − | === | + | ===Questions=== |
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {It holds $\underline{L}_{\rm APP} = (+1.0, +0.4, -1.0)$. Calculate the extrinsic $L$ values ⇒ $\underline{L}_E = \big (L_{\rm E}(1), \ L_{\rm E}(2), \ L_{\rm E}(3) \big)$ according to the second equation given: |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$L_{\rm E}(1) \ = \ ${ -0.188387--0.177413 } | $L_{\rm E}(1) \ = \ ${ -0.188387--0.177413 } | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
$L_{\rm E}(3) \ = \ ${ 0.1829 3% } | $L_{\rm E}(3) \ = \ ${ 0.1829 3% } | ||
| − | { | + | {Which of the properties does the function $y = \tanh\hspace{-0.05cm}{(x)}$ exhibit? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + $\tanh\hspace{-0.05cm} {(x)} = ({\rm e}^x - {\rm e}^{-x}) \ / \ ({\rm e}^x + {\rm e}^{-x})$ is valid. |
| − | + | + | + $\tanh\hspace{-0.05cm} {(x)} = (1 - {\rm e}^{-2x}) \ / \ (1 + {\rm e}^{-2x})$ is valid. |
| − | + | + | + The function $y = \tanh\hspace{-0.05cm} {(x)}$ is defined for all $x$ values. |
| − | - | + | - $y_{\rm min} = 0$ and $y_{\rm max} → ∞$ is valid. |
| − | + | + | + $y_{\rm min} = -1$ and $y_{\rm max} = +1$ is valid. |
| − | { | + | {What are the properties of the inverse function $x = \tanh^{-1}\hspace{-0.08cm} {(y)}$ ? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - | + | - The function $x = \tanh^{-1}\hspace{-0.05cm} (y)$ is defined for all $y$ values. |
| − | + | + | + $x = \tanh^{-1}\hspace{-0.08cm} {(y)} = 1/2 \cdot \ln {[(1 + y) \ / \ (1 - y)]}$ is valid. |
| − | - | + | - $x_{\rm min} = -1$ and $x_{\rm max} = +1$. |
| − | + | + | + $x_{\rm min} → -∞$ and $x_{\rm max} → +∞$ is valid. |
| − | { | + | {How can $L_{\rm E}(i)$ also be represented? Let $\pi$ be defined as on the specification page. |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - | + | - $L_{\rm E}(i) = \tanh^{-1}\hspace{-0.08cm} {(\pi)}$ is valid. |
| − | + | + | + $L_{\rm E}(i) = 2 \cdot \tanh^{-1}\hspace{-0.08cm} {(\pi)}$ is valid. |
| − | - | + | - $L_{\rm E}(i) = 2 \cdot \tanh^{-1}\hspace{-0.05cm}\big [ {\ln {[(1 + \pi) \ / \ (1 - \pi)]}}\big ]$ is valid. |
| − | { | + | {Calculate the extrinsic $L$ values using the equation given in exercise '''(4)'''. Use the table on the information page for this purpose. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$L_{\rm E}(1) \ = \ ${ -0.18849--0.17751 } | $L_{\rm E}(1) \ = \ ${ -0.18849--0.17751 } | ||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1)''' | + | '''(1)''' According to the specification applies: |
:$$L_{\rm E}(i) = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.2cm} \frac{1 + \pi}{1 - \pi}\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm} | :$$L_{\rm E}(i) = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.2cm} \frac{1 + \pi}{1 - \pi}\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm} | ||
| − | {\rm | + | {\rm with} \hspace{0.3cm} \pi = \prod\limits_{j \ne i}^{3} \hspace{0.15cm}{\rm tanh}(L_j/2) |
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | From the table on the specification page can be read: | |
:$$\tanh {(L_1/2)} = \tanh {(0.5)} = 0.4621,$$ | :$$\tanh {(L_1/2)} = \tanh {(0.5)} = 0.4621,$$ | ||
:$$\tanh {(L_2/2)} = \tanh {(0.2)} = 0.1974.$$ | :$$\tanh {(L_2/2)} = \tanh {(0.2)} = 0.1974.$$ | ||
| − | + | Since the hyperbolic tangent is an odd function, the following applies further | |
:$$\tanh {(L_3/2)} = -\tanh {(0.5)} = -0.4621.$$ | :$$\tanh {(L_3/2)} = -\tanh {(0.5)} = -0.4621.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | * Calculation of $L_{\rm E}(1)$: |
:$$\pi = {\rm tanh}(L_2/2) \cdot {\rm tanh}(L_3/2) = (+0.1974) \cdot (-0.4621) = - 0.0912\hspace{0.3cm} | :$$\pi = {\rm tanh}(L_2/2) \cdot {\rm tanh}(L_3/2) = (+0.1974) \cdot (-0.4621) = - 0.0912\hspace{0.3cm} | ||
\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} L_{\rm E}(1) = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.2cm} \frac{1 -0.0912}{1 +0.0912}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=-0.1829} | \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} L_{\rm E}(1) = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.2cm} \frac{1 -0.0912}{1 +0.0912}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=-0.1829} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | * Calculation of $L_{\rm E}(2)$: |
:$$\pi = {\rm tanh}(L_1/2) \cdot {\rm tanh}(L_3/2) = (+0.4621) \cdot (-0.4621) = - 0.2135\hspace{0.3cm} | :$$\pi = {\rm tanh}(L_1/2) \cdot {\rm tanh}(L_3/2) = (+0.4621) \cdot (-0.4621) = - 0.2135\hspace{0.3cm} | ||
\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} L_{\rm E}(2) = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.2cm} \frac{1 -0.2135}{1 +0.2135}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=-0.4337} | \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} L_{\rm E}(2) = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.2cm} \frac{1 -0.2135}{1 +0.2135}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=-0.4337} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | * Calculation of $L_{\rm E}(3)$: |
:$$\pi = {\rm tanh}(L_1/2) \cdot {\rm tanh}(L_2/2) = (+0.4621) \cdot (+0.1974) = + 0.0912\hspace{0.3cm} | :$$\pi = {\rm tanh}(L_1/2) \cdot {\rm tanh}(L_2/2) = (+0.4621) \cdot (+0.1974) = + 0.0912\hspace{0.3cm} | ||
\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} L_{\rm E}(3) = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.2cm} \frac{1 +0.0912}{1 -0.0912}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=+0.1829}= - L_{\rm E}(1) | \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} L_{\rm E}(3) = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.2cm} \frac{1 +0.0912}{1 -0.0912}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=+0.1829}= - L_{\rm E}(1) | ||
| Line 98: | Line 98: | ||
| − | '''(2)''' <u> | + | '''(2)''' <u>The correct solutions are 1, 2, 3, and 5</u>: |
| − | * | + | *The function |
| − | :$$y ={\rm tanh}(x) = \frac | + | :$$y ={\rm tanh}(x) = \frac{\rm e}^{x}-{\rm e}^{-x}}{\rm e}^{x}+{\rm e}^{-x}} |
= \frac{1-{\rm e}^{-2x}}{1+{\rm e}^{-2x}}$$ | = \frac{1-{\rm e}^{-2x}}{1+{\rm e}^{-2x}}$$ | ||
| − | + | is computable for all $x$ values and $\tanh(-x) = -\tanh(x)$ holds. | |
| − | * | + | *For large values of $x$, ${\rm e}^{-2x}$ becomes very small, so that in the limiting case $x → ∞$ the limit $y = 1$ is obtained. |
| − | '''(3)''' | + | '''(3)''' Since the hyperbolic tangent only yields values between $±1$, the inverse function $x = \tanh^{-1}(y)$ can also only be evaluated for $|y| ≤ 1$. |
| − | + | By rearranging the given equation | |
:$$x ={\rm tanh}^{-1}(y) = 1/2 \cdot {\rm ln} \hspace{0.2cm} \frac{1+y}{1-y}$$ | :$$x ={\rm tanh}^{-1}(y) = 1/2 \cdot {\rm ln} \hspace{0.2cm} \frac{1+y}{1-y}$$ | ||
| − | + | one obtains: | |
:$${\rm e}^{2x} = \frac{1+y}{1-y} \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | :$${\rm e}^{2x} = \frac{1+y}{1-y} \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | ||
{\rm e}^{-2x} = \frac{1-y}{1+y} \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | {\rm e}^{-2x} = \frac{1-y}{1+y} \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | ||
| Line 120: | Line 120: | ||
{\rm tanh}(x) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | {\rm tanh}(x) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | This means: | |
| − | * | + | * The equation given in the proposed solution 2 is correct. |
| − | * | + | * In the limiting case $y → 1$, $x = \tanh^{-1}(y) → ∞$ holds. |
| − | * | + | * Also the inverse function is odd ⇒ in the limiting case $y → -1$ goes $x → -∞$. |
| − | + | Accordingly, the <u>proposed solutions 2 and 4</u> are correct. | |
| − | '''(4)''' | + | '''(4)''' Starting from the equation. |
:$$L_{\rm E}(i) = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.2cm} \frac{1 + \pi}{1 - \pi}$$ | :$$L_{\rm E}(i) = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.2cm} \frac{1 + \pi}{1 - \pi}$$ | ||
| − | + | one arrives with the result of '''(3)''' at the equivalent equation corresponding to <u>suggested solution 2</u>: | |
:$$L_{\rm E}(i) = 2 \cdot {\rm tanh}^{-1}(\pi)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$L_{\rm E}(i) = 2 \cdot {\rm tanh}^{-1}(\pi)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | '''(5)''' | + | '''(5)''' With the result of the subtask '''(1)''' we get. |
| − | * | + | * for the first extrinsic $L$ value, since $\pi_1 = -0.0912$: |
:$$L_{\rm E}(1) = 2 \cdot {\rm tanh}^{-1}(-0.0912)= -2 \cdot {\rm tanh}^{-1}(0.0912) | :$$L_{\rm E}(1) = 2 \cdot {\rm tanh}^{-1}(-0.0912)= -2 \cdot {\rm tanh}^{-1}(0.0912) | ||
= -2 \cdot 0.0915\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=-0.1830} | = -2 \cdot 0.0915\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=-0.1830} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | * for the second extrinsic $L$ value, since $\pi_2 = -0.2135$: |
:$$L_{\rm E}(2) = -2 \cdot {\rm tanh}^{-1}(0.2135) | :$$L_{\rm E}(2) = -2 \cdot {\rm tanh}^{-1}(0.2135) | ||
= -2 \cdot 0.2168\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=-0.4336} | = -2 \cdot 0.2168\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=-0.4336} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | * for the third extrinsic $L$ value, since $\pi_3 = +0.0912 = -\pi_1$: |
:$$L_{\rm E}(3) = -L_{\rm E}(1) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=+0.1830} | :$$L_{\rm E}(3) = -L_{\rm E}(1) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=+0.1830} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | The result was determined using the red table entries on the information page and, except for rounding errors (multiplication/division by $2$), agrees with the results of subtask '''(1)'''. | |
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
[[Category:Channel Coding: Exercises|^4.1 Soft–in Soft–out Decoder^]] | [[Category:Channel Coding: Exercises|^4.1 Soft–in Soft–out Decoder^]] | ||
Revision as of 00:18, 31 October 2022
In "Theory Part" it was shown, using the example of single parity–check code that the extrinsic $L$ value with respect to the $i$th symbol is defined as follows:
- $$L_{\rm E}(i) = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.2cm}\frac{{\rm Pr} \left [w_{\rm H}(\underline{x}^{(-i)})\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm is \hspace{0.15cm} even} \hspace{0.05cm} | \hspace{0.05cm}\underline{y} \hspace{0.05cm}\right ]}{{\rm Pr} \left [w_{\rm H}(\underline{x}^{(-i)})\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm is \hspace{0.15cm} odd} \hspace{0.05cm} | \hspace{0.05cm}\underline{y} \hspace{0.05cm}\right ]} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
This equation is also applicable to many other channel codes. The code word $\underline{x}^{(-i)}$ in this definition includes all symbols except $x_i$ and thus has length $n-1$ only.
In the "Exercise 4.4" it was shown that the extrinsic $L$ value can also be written as follows:
- $$L_{\rm E}(i) = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.2cm} \frac{1 + \pi}{1 - \pi}\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm mit} \hspace{0.3cm} \pi = \prod\limits_{j \ne i}^{n} \hspace{0.15cm}{\rm tanh}(L_j/2) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
In this exercise, we will now look for another calculation possibility.
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter "Soft–in Soft–out Decoder".
- Reference is made in particular to the "Calculations of extrinsic LLRs" page.
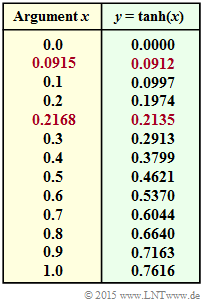
- Above you can see a table with the numerical values of the function $y = \tanh(x)$ ⇒ hyperbolic tangent.
- With the rows highlighted in red you can read the values of the inverse function $x = \tanh^{-1}(y)$ needed for the subtask (5).
Questions
Solution
- $$L_{\rm E}(i) = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.2cm} \frac{1 + \pi}{1 - \pi}\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm with} \hspace{0.3cm} \pi = \prod\limits_{j \ne i}^{3} \hspace{0.15cm}{\rm tanh}(L_j/2) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
From the table on the specification page can be read:
- $$\tanh {(L_1/2)} = \tanh {(0.5)} = 0.4621,$$
- $$\tanh {(L_2/2)} = \tanh {(0.2)} = 0.1974.$$
Since the hyperbolic tangent is an odd function, the following applies further
- $$\tanh {(L_3/2)} = -\tanh {(0.5)} = -0.4621.$$
- Calculation of $L_{\rm E}(1)$:
- $$\pi = {\rm tanh}(L_2/2) \cdot {\rm tanh}(L_3/2) = (+0.1974) \cdot (-0.4621) = - 0.0912\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} L_{\rm E}(1) = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.2cm} \frac{1 -0.0912}{1 +0.0912}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=-0.1829} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Calculation of $L_{\rm E}(2)$:
- $$\pi = {\rm tanh}(L_1/2) \cdot {\rm tanh}(L_3/2) = (+0.4621) \cdot (-0.4621) = - 0.2135\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} L_{\rm E}(2) = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.2cm} \frac{1 -0.2135}{1 +0.2135}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=-0.4337} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Calculation of $L_{\rm E}(3)$:
- $$\pi = {\rm tanh}(L_1/2) \cdot {\rm tanh}(L_2/2) = (+0.4621) \cdot (+0.1974) = + 0.0912\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} L_{\rm E}(3) = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.2cm} \frac{1 +0.0912}{1 -0.0912}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=+0.1829}= - L_{\rm E}(1) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) The correct solutions are 1, 2, 3, and 5:
- The function
- $$y ={\rm tanh}(x) = \frac{\rm e}^{x}-{\rm e}^{-x}}{\rm e}^{x}+{\rm e}^{-x}} = \frac{1-{\rm e}^{-2x}}{1+{\rm e}^{-2x}}$$
is computable for all $x$ values and $\tanh(-x) = -\tanh(x)$ holds.
- For large values of $x$, ${\rm e}^{-2x}$ becomes very small, so that in the limiting case $x → ∞$ the limit $y = 1$ is obtained.
(3) Since the hyperbolic tangent only yields values between $±1$, the inverse function $x = \tanh^{-1}(y)$ can also only be evaluated for $|y| ≤ 1$.
By rearranging the given equation
- $$x ={\rm tanh}^{-1}(y) = 1/2 \cdot {\rm ln} \hspace{0.2cm} \frac{1+y}{1-y}$$
one obtains:
- $${\rm e}^{2x} = \frac{1+y}{1-y} \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm e}^{-2x} = \frac{1-y}{1+y} \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} (1+y) \cdot {\rm e}^{-2x} = 1-y \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}y = \frac{1-{\rm e}^{-2x}}{1+{\rm e}^{-2x}} = {\rm tanh}(x) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
This means:
- The equation given in the proposed solution 2 is correct.
- In the limiting case $y → 1$, $x = \tanh^{-1}(y) → ∞$ holds.
- Also the inverse function is odd ⇒ in the limiting case $y → -1$ goes $x → -∞$.
Accordingly, the proposed solutions 2 and 4 are correct.
(4) Starting from the equation.
- $$L_{\rm E}(i) = {\rm ln} \hspace{0.2cm} \frac{1 + \pi}{1 - \pi}$$
one arrives with the result of (3) at the equivalent equation corresponding to suggested solution 2:
- $$L_{\rm E}(i) = 2 \cdot {\rm tanh}^{-1}(\pi)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(5) With the result of the subtask (1) we get.
- for the first extrinsic $L$ value, since $\pi_1 = -0.0912$:
- $$L_{\rm E}(1) = 2 \cdot {\rm tanh}^{-1}(-0.0912)= -2 \cdot {\rm tanh}^{-1}(0.0912) = -2 \cdot 0.0915\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=-0.1830} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- for the second extrinsic $L$ value, since $\pi_2 = -0.2135$:
- $$L_{\rm E}(2) = -2 \cdot {\rm tanh}^{-1}(0.2135) = -2 \cdot 0.2168\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=-0.4336} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- for the third extrinsic $L$ value, since $\pi_3 = +0.0912 = -\pi_1$:
- $$L_{\rm E}(3) = -L_{\rm E}(1) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{=+0.1830} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The result was determined using the red table entries on the information page and, except for rounding errors (multiplication/division by $2$), agrees with the results of subtask (1).