Exercise 4.3Z: Multiple-Access Methods in LTE
In the case of the 4G mobile radio system LTE, there was a change not only in the type of modulation compared with the 3G system UMTS , but also in the access procedure in particular.A suitable access method is characterized by the fact that as many users of a radio cell as possible can be supplied with the highest possible data rate. The total throughput is decisive.
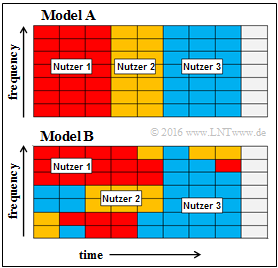
The figure shows two diagrams $\rm A$ and $\rm B$ with exemplary frequency-time assignments. You should decide which access methods should be explained by these two diagrams.
Notes:
- The task belongs to the chapter Anwendung von OFDMA und SC-FDMA in LTE.
- All necessary information can be found on the page Gemeinsamkeiten und Unterschiede zwischen OFDM und OFDMA as well as in the chapter Vielfachzugriffsverfahren in the book „Modulationsverfahren”.
Questionnaire
Sample Solution
(1) Correct are the solutions 3 and 4. LTE uses
- Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) in downlink,
- Single Carrier Frequency Division Multiple Access (SC–FDMA) in uplink.
- Code Division Multiple Access is used in the 3G mobile system UMTS eingesetzt.
- Bei DSL verwendet man Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access.
- Dieses ist aber in diesem Zusammenhang eher als Modulationsverfahren zu verstehen, nicht als Vielfachzugriffsverfahren.
(2) Richtig sind die Antworten 2 und 4:
- Es können mehrere Teilnehmer einen Frequenzblock belegen.
- TDMA ist zusätzlich möglich.
- Der Vorschlag 1 entspricht CDMA, der Vorschlag 3 trifft für OFDM zu.
(3) Entsprechend der Musterlösung zur Aufgabe (2) ist der zweite Vorschlag zutreffend ⇒ Schaubild $\rm B$.
(4) Richtig sind die Lösungsvorschläge 1 und 2 im Gegensatz zum Vorschlag 3:
- Da bei OFDMA die Ressourcenzuteilung sich nicht nur auf den Zeitbereich beschränkt, sondern hier auch der Frequenzbereich optimal einbezogen wird, ist OFDMA flexibler als OFDM. Natürlich werden die Teilnehmer mit den besten Randbedingungen bei der Ressourcenverteilung bevorzugt.
- Angewendet wird also das eher unsolidarische Prinzip „Wem es schon gut geht, dem wird gegeben”. Dieses findet man häufig auch in der Politik vor.
- Unbestritten ist allerdings, dass auf diese Weise der Gesamtdurchsatz der Zelle maximiert wird, was die Optimierungsgrundlage für die Netzbetreiber ist.
- Würde man die gesamte Leistung einem Teilnehmer mit extrem schlechten Bedingungen zur Verfügung stellen, so ginge der Gesamtdurchsatz gegen Null.