Exercise 4.6Z: ISDN Supply Lines
From LNTwww
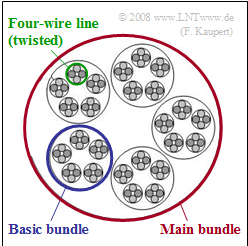
In $\rm ISDN$ ("Integrated Services Digital Networks"), the terminal (near the subscriber) is connected to a local exchange ("OVSt") by a copper pair, with two pairs twisted into a so-called "star quad".
- Several such star quad pairs are twisted to form a basic bundle,
- several basic bundles are combined to form a main bundle (see diagram).
In the network of Deutschen Telekom (formerly: Deutsche Bundespost), mostly copper lines with $\text{0.4 mm}$ core diameter are found, for whose attenuation and phase function given in [PW95] are the following equations:
- $${{a}_{\rm K}(f)}/{\rm dB} = \left [ 5.1 + 14.3 \cdot \left ({f}/{\rm MHz}\right )^{0.59}\right ]\cdot{l}/{\rm km} \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $${b_{\rm K}(f)}/{\rm rad} = \left [ 32.9 \cdot ({f}/{\rm MHz}) + 2.26 \cdot \left ({f}/{\rm MHz}\right )^{0.5}\right ]\cdot {l}/{\rm km} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Here $l$ denotes the line length.
Notes:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter Properties of Balanced Copper Pairs.
- For more information on the attenuation behavior of copper lines, see the page Four-wire and two-wire transmission in the book "Examples of Communication Systems".
- You can use the (German language) interactive HTML5/JS applet "Attenuation of copper cables" to check your results.
- [PW95] denotes the following literature reference: Pollakowski, P.; Wellhausen, H.-W.: Eigenschaften symmetrischer Ortsanschlusskabel im Frequenzbereich bis 30 MHz. Deutsche Telekom AG, Forschungs- und Technologiezentrum Darmstadt, 1995.
Questions
Solution
(1) Two-wire transmission is used in the connection area. The possible connections are therefore equal to the number of pairs in the main cable:
- $$N = 5 \cdot 5 \cdot 2 \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 50}.$$
(2) Solutions 1 and 2 are correct:
- In two-wire transmission, a direction separation method is required, namely the so-called "hybrid coil". This has the task that at receiver $\rm A$ only arrives the transmitted signal of subscriber $\rm B$, but not the own transmitted signal. This is generally quite successful with narrow-band signals – for example speech – but not completely ⇒ solution 1 is correct.
- Solution 2 is also correct. Due to inductive and capacitive couplings, crosstalk can occur from the twin wire located in the same star quad, whereby near-end crosstalk (i.e. the interfering transmitter and the interfered receiver are located together) leads to greater impairments than far-end crosstalk.
- On the other hand, the last solution is not correct. Intersymbol interference ⇒ the mutual interfering influence of neighboring symbols can certainly occur, but it is not related to two-wire transmission. The reason for such intersymbol interference is rather linear distortion, caused by a non-ideal attenuation or phase response.
(3) The DC attenuation by a factor of $4$ can be expressed as follows:
- $$a_{\rm K}(f = 0) = 20 \cdot {\rm lg}\,\,(4) = 12.04\,{\rm dB}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- With the given coefficient $\alpha_0 =5.1 \ \rm dB/km$, this gives the line length $l = 12.04/5.1\; \underline{= 2.36 \ \rm km}$.
(4) Using the given equations and $l = 2.36 \ \rm km$, we obtain:
- $$a_{\rm K}(f = 120\,{\rm kHz}) = (5.1 + 14.3 \cdot 0.12^{\hspace{0.05cm}0.59}) \cdot 2.36\,{\rm dB}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ \approx 21.7\,{\rm dB}}\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$b_{\rm K}(f = 120\,{\rm kHz}) = (32.9 \cdot 0.12 + 2.26 \cdot 0.12^{\hspace{0.05cm}0.5}) \cdot 2.36\,{\rm rad}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ \approx 11.2\,{\rm rad}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$