Exercise 1.1: Music Signals
From LNTwww
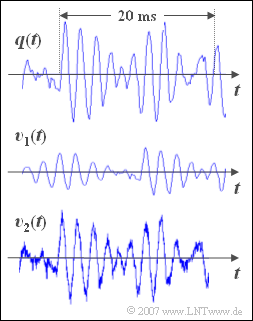
On the right you see a ca. $\text{30 ms}$ long section of a music signal \(q(t)\). It is the piece „For Elise” by Ludwig van Beethoven.
- Underneath are drawn two sink signals \(v_1(t)\) and \(v_2(t)\), which were recorded after the transmission of the music signal \(q(t)\) over two different channels.
- The following controls allow you to listen to the first fourteen seconds of each of the three audio signals \(q(t)\), \(v_1(t)\) and \(v_2(t)\).
Original signal \(q(t)\)
Sink signal \(v_1(t)\)
Sink signal \(v_2(t)\)
Notes:
- The task belongs to the chapter Principles of Communication.
Questions
Solution
(1) Correct is the solution 2:
- In the marked range of $20$ milliseconds approx. $10$ oscillations can be detected.
- From this the result follows approximately for the signal frequency; $f = {10}/(20 \,\text{ms}) = 500 \,\text{Hz}$.
(2) Correct is the solution 1:
- The signal \(v_1(t)\) is undistorted compared to the original signal \(q(t)\). The following applies: $v_1(t)=\alpha \cdot q(t-\tau) .$
- An attenuation \(\alpha\) and a delay \(\tau\) do not cause distortion, but the signal is then only quieter and comes later than the original.
(3) Correct are the solutions 1 and 3:
- One can recognize both in the displayed signal \(v_2(t)\) and in the audio signal additive noise ⇒ solution 3.
- The signal-to-noise ratio is approx. $\text{30 dB}$; but this cannot be seen from this representation.
- Correct is also the solution 1: Without this noise component \(v_2(t)\) identical with \(q(t)\).
(4) The signal \(v_1(t)\) is identical in form to the original signal \(q(t)\) and differs from it only
- by the attenuation factor $\alpha = \underline{\text{0.3}}$ (dies entspricht etwa $\text{–10 dB)}$
- and the delay $\tau = \underline{10\,\text{ms}}$.