Coherent and Non-Coherent On-Off Keying
Open Applet in new Tab Deutsche Version Öffnen
Contents
Applet Description
Considered is the symbol error probability $p_{\rm S}$ of "On–off keying" $\rm (OOK)$ in the presence of white noise, characterized by the standard deviation $\sigma_{\rm AWGN}$, both in the case of coherent demodulation and in the case of non–coherent demodulation. Plotted for both cases are the probability density functions $\rm (PDF)$ of the received signal $r(t)$ for the possible transmitted symbols $s_0$ and $s_1 \equiv 0$.
- In the coherent case, there are two Gaussian functions around $s_0$ and $s_1$.
- In the incoherent case, there is a Rayleigh–PDF for the symbol $s_1 = 0$ and a Rice–PDF for $s_0 \ne 0$, whose form also depends on the input parameter $C_{\rm Rice}$.
The applet returns the composite probabilities ${\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r_0} \cap \boldsymbol{s_1})$ ⇒ (filled blue area in the PDF graph) and ${\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r_1} \cap \boldsymbol{s_0})$ ⇒ (red area) and as a final result:
- $$p_{\rm S} = {\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r} \ne \boldsymbol{s})= {\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r_0} \cap \boldsymbol{s_1}) + {\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r_1} \cap \boldsymbol{s_0}). $$
- All these quantities also depend on the decision threshold $G$ whose optimal value in each case is also determined.
- In addition, the applet shows which error one makes when approximating the generally more complicated Rice PDF by the best possible Gaussian PDF.
Note: The next section "Theoretical Background" is currently still in German language. The translation is planned as soon as possible.
Theoretical Background
On–Off–Keying with coherent demodulation
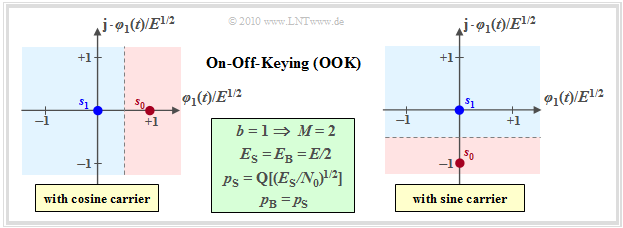
The simplest digital modulation method is "On–off keying" $\rm (OOK)$. This method – also called "Amplitude Shift Keying" $\rm (2–ASK)$ – can be characterized as follows:
- $\rm OOK$ is a binary and one-dimensional modulation method, for example with $s_{1} \equiv 0$ and
- $\boldsymbol{s}_{0} = \{s_0,\ 0\}$ $($for cosinusoidal carrier, left graph$)$ resp.
- $\boldsymbol{s}_{0} = \{0,\ -s_0\}$ $($for sinusoidal carrier, right graph$)$.
- With coherent demodulation, the signal space constellation of the received signal is equal to that of the transmitted signal and again consists of the two points $\boldsymbol{r}_0=\boldsymbol{s}_0$ and $\boldsymbol{r}_1=\boldsymbol{s}_1$.
- In this case, the AWGN noise is one-dimensional with variance $\sigma_{\rm AWGN}^2$ and one obtains corresponding to the "theory part" for the "symbol error probability":
- $$p_{\rm S} = {\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r}\ne \boldsymbol{s})= {\rm Q} \left ( \frac{s_0/2}{\sigma_{\rm AWGN}}\right ) = {\rm Q} \left ( \sqrt{ {E_{\rm S}}/{N_0}}\right ) \hspace{0.05cm}. $$
- Each bit is assigned to a binary symbol $(b = 1, \ M = 2)$; thus, no serial/parallel converter is needed.
- For equally probable symbols, which is assumed for what follows, both the "mean energy per symbol" $(E_{\rm S})$ and the "mean energy per bit" $(E_{\rm B})$ are equal to $E/2$.
- The optimal OOK receiver virtually projects the complex–valued received signal $r(t)$ onto the basis function $\varphi_1(t)$, if one starts from the left sketch (cosine carrier).
- Because of $N = 1$, the noise can be one-dimensional with the variance $\sigma_n^2 = N_0/2$.
- Using the statements in the section "Error probability for symbols with equal probability", we obtain for the (mean) "symbol error probability":
- \[p_{\rm S} = {\rm Pr}({\cal{E}}) = {\rm Q} \left ( \frac{d/2}{\sigma_n}\right ) = {\rm Q} \left ( \sqrt{\frac{E}{2 N_0}}\right ) = {\rm Q} \left ( \sqrt{{E_{\rm S}}/{N_0}}\right ) \hspace{0.05cm}.\]
- Since each bit is mapped to one symbol, the average bit error probability $p_{\rm B}$ is exactly:
- \[p_{\rm B} = {\rm Q} \left ( \sqrt{{E_{\rm S}}/{N_0}}\right ) = {\rm Q} \left ( \sqrt{{E_{\rm B}}/{N_0}}\right ) \hspace{0.05cm}.\]
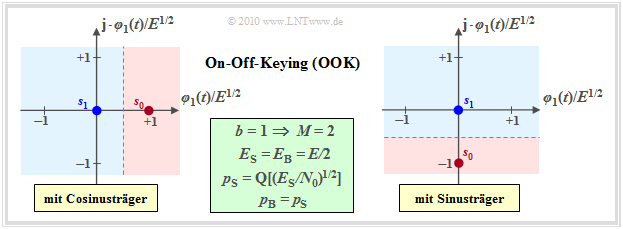
Das einfachste digitale Modulationsverfahren ist On–Off–Keying $\rm (OOK)$. Dieses Verfahren wird teilweise auch als Amplitude Shift Keying $\rm (2–ASK)$ bezeichnet und kann im äquivalenten Tiefpassbereich wie folgt charakterisiert werden:
$\rm OOK$ is a binary and one-dimensional modulation method, for example with $s_{1} \equiv 0$ and
- $\boldsymbol{s}_{0} = \{s_0,\ 0\}$ (for cosine–carrier, left graph) respectively.
- $\boldsymbol{s}_{0} = \{0,\ -s_0\}$ (for sine–carrier, right graph).
In the case of coherent demodulation, the signal space constellation of the received signal is equal to that of the transmitted signal and again consists of the two points $\boldsymbol{r}_0=\boldsymbol{s}_0$ and $\boldsymbol{r}_1=\boldsymbol{s}_1$. In this case, the AWGN–noise is one-dimensional with variance $\sigma_{\rm AWGN}^2$ and one obtains corresponding to the theory part for the symbol error probability' $p_{\rm S} = {\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r}\ne \boldsymbol{s})$:
- $$p_{\rm S} = {\rm Q} \left ( \frac{s_0/2}{\sigma_{\rm AWGN}}\right ) = {\rm Q} \left ( \sqrt{ {E_{\rm S}}/{N_0}}\right ) \hspace{0.05cm}. $$
To this it should be noted:
- Die Funktion ${\rm Q}(x)$ nennt man das "Komplementäre Gaußsche Fehlerintegral". Der Link weist auf das Applet Komplementäre Gaußsche Fehlerfunktionen.
- Obige Gleichung gilt für gleichwahrscheinliche Symbole mit der Entscheiderschwelle $G$ in der Mitte zwischen $\boldsymbol{r}_0$ und $\boldsymbol{r}_1$.
- Der Abstand der beiden Signalpunkte von der Entscheiderschwelle $G$ beträgt somit jeweils $\Delta G = s_0/2$ $($Zähler im Argument der ersten $\rm Q$–Funktion$)$.
- $E_{\rm S}=s_0^2/2 \cdot T$ bezeichnet für diesen Fall die "mittlere Energie pro Symbol" und $N_0=2T \cdot \sigma_{\rm AWGN}^2$ die (einseitige) AWGN–Rauschleistungsdichte.
Translated with www.DeepL.com/Translator (free version)
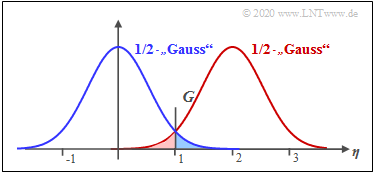
$\text{Beispiel 1:}$ Es gelte $\sigma_{\rm AWGN}= 0.8$ und $s_{0} = 2$, ⇒ $G=1$. Alle diese Werte seien auf den Wert $1\hspace{0.05cm} {\rm V}$ normiert.
Die Grafik zeigt zwei "halbe Gaußfunktionen" um $s_1=0$ (blaue Kurve) und $s_0=2$ (rote Kurve) sowie den Schwellenwert $G$. Die schraffierten Flächen markieren die Symbolfehlerwahrscheinlichkeit.
- Nach der ersten Gleichung gilt mit $\Delta G = s_{0} -G= G-s_1 = 1$:
- $$p_{\rm S} = {\rm Q} ( 1/0.8 )= {\rm Q} ( 1.25 )\approx 10.56 \%.$$
- Ebenso liefert die zweite Gleichung: $E_{\rm S}/{N_0} = 1/4 \cdot s_0^2/\sigma_{\rm AWGN}^2 = 1.5615$:
- $$p_{\rm S} = {\rm Q} (\sqrt{1.5615} )\approx 10.56 \%.$$
Aufgrund der Symmetrie ist der Schwellenwert $G=1$ optimal. In diesem Fall sind die rote und die blaue schraffierte Fläche gleich groß ⇒ die Symbole $\boldsymbol{s}_{0}$ und $\boldsymbol{s}_{1}$ werden in gleicher Weise verfälscht.
Mit $G\ne 1$ ergibt sich eine größere Verfälschungswahrscheinlichkeit. Beispielsweise ergibt sich mit $G=0.6$:
- $$p_{\rm S} = {\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r}\ne \boldsymbol{s}) = {\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r_0} \cap \boldsymbol{s_1}) + {\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r_1} \cap \boldsymbol{s_0})= 1/2 \cdot {\rm Q} ( 0.75)+ 1/2 \cdot {\rm Q} ( 1.75)\approx 13.33\% .$$
Hier ist die Verfälschungswahrscheinlichkeit für das Symbol $\boldsymbol{s}_{1}$ ⇒ blaue gefüllte Fläche ${\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r_0} \cap \boldsymbol{s_1}) \approx 11.33\%$ aufgrund der ungünstig gewählten Entscheiderschwelle sehr viel größer als die des Symbols $\boldsymbol{s}_{0}$ ⇒ rote gefüllte Fläche ${\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r_1} \cap \boldsymbol{s_0}) \approx 2\%$.
On–Off–Keying with noncoherent demodulation
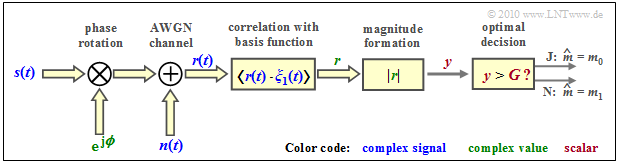
Die folgende Grafik zeigt die Strukur (im äquivalenten Tiefpassbereich) des optimalen OOK–Empfängers für inkohärente Demodulation. Detailbeschreibung
Entsprechend dieser zweiten Grafik gilt:
- Das Eingangssignal $\boldsymbol{r}(t) = \boldsymbol{s}(t) \cdot {\rm e}^{\hspace{0.02cm}{\rm j}\hspace{0.03cm}\phi} + \boldsymbol{n}(t)$ am Empfänger ist aufgrund des aktuellen Phasenwinkels $\phi$ und wegen des komplexen Rauschterms $\boldsymbol{n}(t)$ im allgemeinen komplex.
- Erforderlich ist nun die Korrelation zwischen dem komplexen Empfangssignal $\boldsymbol{r}(t)$ und einer komplexen Basisfunktion $\boldsymbol{\xi}(t)$.
- Das Ergebnis ist der (komplexe) Detektorwert $\boldsymbol{r}$, woraus als reelle Entscheidereingangsgröße der Betrag $y = |\boldsymbol{r}(t)|$ gebildet wird.
- Ist $y \gt G$, so wird als Schätzwert $m_0$ für das Symbol $\boldsymbol{s}_{0}$ ausgegeben, andernfalls der Schätzwert $m_1$ für das Symbol $\boldsymbol{s}_{1}$.
- Auch hier ist die mittlere Symbolfehlerwahrscheinlichkeit als Summe zweier Verbundwahrscheinlichkeiten darstellbar:
- $$p_{\rm S} = {\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r}\ne \boldsymbol{s}) = {\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r_0} \cap \boldsymbol{s_1}) + {\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r_1} \cap \boldsymbol{s_0}).$$
Fehlerwahrscheinlichkeitsberechnung unter Berücksichtigung von Rayleigh– und Riceverteilung
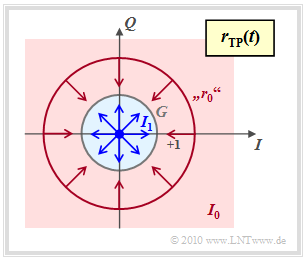
Zur Berechnung der Symbolfehlerwahrscheinlichkeit bei inkohärenter Demodulation gehen wir von folgender Grafik aus. Dargestellt ist das Empfangssignal im äquivalenten Tiefpassbereich in der komplexen Ebene.
- Der Punkt $\boldsymbol{s_1}=0$ führt im Empfangsignal wieder zu $\boldsymbol{r_1}=0$.
- Dagegen kann $\boldsymbol{r}_0 = \boldsymbol{s}_0 \cdot {\rm e}^{\hspace{0.02cm}{\rm j}\hspace{0.03cm}\phi}$ auf jedem Punkt eines Kreises mit Radius $1$ liegen, da die Phase $\phi$ unbekannt ist.
- Der Entscheidungsprozess unter Berücksichtigung des AWGN–Rauschens ist nun zweidimensional zu interpretieren, wie durch die Pfeile in der Grafik angedeutet.
- Die Entscheidungsregion $I_1$ für das Symbol $\boldsymbol{s_1}$ ist der blau gefüllte Kreis mit Radius $G$, wobei der richtige Wert von $G$ noch zu bestimmen ist.
- Liegt der Empfangswert $\boldsymbol{r}$ außerhalb dieses Kreises also im rot hinterlegten Gebiet $I_0$, so fällt die Entscheidung zugunsten von $\boldsymbol{s_0}$.
$\rm Rayleigh–Anteil$
Unter Berücksichtigung des AWGN–Rauschens gilt $\boldsymbol{r_1}=\boldsymbol{s_1} + \boldsymbol{n_1}$. Die Rauschkomponente $\boldsymbol{n_1}$ besitzt eine Rayleighverteilung $($Betrag der beiden mittelwertfreien Gaußkomponenten für $I$ und $Q)$.
Deren bedingte WDF lautet mit der rotationssymmetrischen Rauschkomponente $\eta$ mit $\sigma=\sigma_{\rm AWGN}$ :
- $$f_{y\hspace{0.05cm}\vert \hspace{0.05cm}\boldsymbol{s_1}} (\eta \hspace{0.05cm}\vert \hspace{0.05cm} \boldsymbol{s_1})=\frac{\eta}{\sigma^2}\cdot {\rm e}^{-\eta^2 / ( 2 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}\sigma^2) } = f_{\rm Rayleigh}(\eta) .$$
Damit erhält man für die bedingte Wahrscheinlichkeit
- $${\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r_0}|\boldsymbol{s_1}) = \int_{G}^{\infty}f_{\rm Rayleigh}(\eta) \,{\rm d} \eta \hspace{0.05cm},$$
und mit dem Faktor $1/2$ wegen der gleichwahrscheinlichen Sendesymbole die Verbundwahrscheinlichkeit:
- $${\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r_0} \cap \boldsymbol{s_1}) = 1/2 \cdot {\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r_0}|\boldsymbol{s_1})= 1/2 \cdot \int_{G}^{\infty}f_{\rm Rayleigh}(\eta) \,{\rm d} \eta \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
$\rm Rice–Anteil$
Die Rauschkomponente $\boldsymbol{n_0}$ besitzt eine Riceverteilung $($Betrag der Gaußkomponenten mit Mittelwerten $m_x$ und $m_y)$ ⇒ Konstante $C=\sqrt{m_x^2 + m_y^2}$
$($Anmerkung: Im Applet wird die Konstante $C$ mit $C_{\rm Rice}$ bezeichnet$)$.
- $$f_{y\hspace{0.05cm}\vert \hspace{0.05cm}\boldsymbol{s_0}} (\eta \hspace{0.05cm}\vert \hspace{0.05cm} \boldsymbol{s_0})=\frac{\eta}{\sigma^2}\cdot{\rm e}^{-({C^2+\it \eta^{\rm 2} })/ ({\rm 2 \it \sigma^{\rm 2} })}\cdot {\rm I_0}(\frac{\it \eta\cdot C}{\sigma^{\rm 2} }) = f_{\rm Rice}(\eta) \hspace{1.4cm}{\rm mit} \hspace{1.4cm} {\rm I_0}(\eta) = \sum_{k=0}^{\infty}\frac{(\eta/2)^{2k} }{k! \cdot {\rm \Gamma ({\it k}+1)} }.$$
Damit ergibt sich für die zweite Verbundwahrscheinlichkeit:
- $${\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r_1} \cap \boldsymbol{s_0}) = 1/2 \cdot \int_{0}^{G}f_{\rm Rice}(\eta) \,{\rm d} \eta \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
$\text{Beispiel 2:}$ Die Grafik zeigt das Ergebnis dieser Gleichung für $\sigma_{\rm AWGN} = 0.5$ und $C_{\rm Rice} = 2$. Die Entscheidungsgrenze liegt bei $G \approx 1.25$. Man erkennt aus dieser Darstellung:
- Die Symbolfehlerwahrscheinlichkeit $p_{\rm S}$ ist die Summe der beiden farblich hinterlegten Flächen. Wie im Beispiel 1 für den kohärenten Fall gilt auch hier:
- $$p_{\rm S} = {\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r}\ne \boldsymbol{s}) = {\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r_0} \cap \boldsymbol{s_1}) + {\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r_1} \cap \boldsymbol{s_0}).$$
- Die blau markierte Fläche gibt die Verbundwahrscheinlichkeit ${\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r_0} \cap \boldsymbol{s_1}) \approx 2.2\%$ an. Diese berechnet sich als das Integral über die halbe Rayleigh–WDF im Bereich von $G$ bis $\infty$.
- Die rot markierte Fläche gibt die Verbundwahrscheinlichkeit ${\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r_1} \cap \boldsymbol{s_0}) \approx 2.4\%$ an. Diese berechnet sich als das Integral über die halbe Rice–WDF im Bereich von $0$ bis $G$.
- Somit erhält man $p_{\rm S} \approx 4.6\%$. Anzumerken ist, dass die roten und blauen Flächen nicht gleich sind und dass sich die optimale Entscheidungsgrenze $G_{\rm opt}$ sich aus dem Schnittpunkt der beiden Kurven ergibt.
- Die optimale Entscheidungsgrenze $G_{\rm opt}$ ergibt sich als der Schnittpunkt von blauer und roter Kurve.
Exercises
- Select the number $(1,\ 2$, ... $)$ of the task to be processed. The number "0" corresponds to a "Reset": Setting as at the program start.
- A task description is displayed. Parameter values are adjusted. Solution after pressing "Sample solution".
- Always interpret the graphics and the numerical results. The symbols $s_0$ (adjustable) and ${s}_{1}\equiv 0$ are equal probability.
- For space reasons, in some of the following questions and sample solutions we also use $\sigma = \sigma_{\rm AWGN}$ and $C = C_{\rm Rice}$.
(1) We consider $\text{coherent}$ demodulation with $\sigma_{\rm AWGN} = 0.5$ and $s_0 = 2$. What is the smallest possible value for the symbol error probability $p_{\rm S}$?
- For coherent demodulation, the PDF of the reception signal is composed of two "half" Gaussian functions around $s_0 = 2$ $($red$)$ and $s_1 = 0$ $($blue$)$.
- Here the minimum $p_{\rm S}$ value results with $G=1$ and $\Delta G = s_{0} -G= G-s_1 = 1$ to $p_{\rm S}= {\rm Q} ( \Delta G/\sigma )={\rm Q} ( 1/0.5 )= {\rm Q} ( 2 )\approx 2.28 \%.$
- With $G=1$ both symbols are falsified equally. The blue area ${\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r_0} \cap \boldsymbol{s_1})$ is equal to the red area ${\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r_1} \cap \boldsymbol{s_0})$. Their sum gives $p_{\rm S}$.
- With $G=0.5$ the red area is almost zero. Nevertheless $p_{\rm S}\approx 8\%$ (sum of both areas) is more than twice as large as with $G_{\rm opt}=1$.
(2) Now let $\sigma = 0.75$. With what $s_0$ value does optimal $G$ give the same symbol error probability as in $(1)$? Then what is the quotient $E_{\rm S}/N_0$?
- In general $p_{\rm S}= {\rm Q}\big ( (s_0/2) / \sigma \big )$. If one increases $\sigma$ from $0. 5$ to $0.75$, then $s_0$ must also be increased ⇒ $s_0 = 3$ ⇒ $p_{\rm S}= {\rm Q} ( 1.5/ 0.75 )= {\rm Q} ( 2 )$.
- Except $p_{\rm S}= {\rm Q}\big ( (s_0/2) / \sigma \big )$ but also holds: $p_{\rm S}= {\rm Q} ( \sqrt{E_{\rm S}/N_0} )$. It follows: $p_{\rm S}= {\rm Q}(2) ={\rm Q} ( \sqrt{E_{\rm S}/N_0})$ ⇒ $\sqrt{E_{\rm S}/N_0}= 2$ ⇒ $E_{\rm S}/N_0= 4$.
- For control: $E_{\rm S}=s_0^2/2 \cdot T, \ N_0=2T \cdot \sigma^2$ ⇒ $E_{\rm S}/N_0 =s_0^2/(4 \cdot \sigma^2)= 3^2/(4 \cdot 0. 75^2)=4$. The same $E_{\rm S}/N_0 =4$ results for the problem $(1)$.
(3) Now consider $\text{non–coherent}$ demodulation with $\sigma_{\rm AWGN} = 0.75$, $C_{\rm Rice} = 2.25$ and $G=2$. What is the symbol error probability $p_{\rm S}$?
- For non–coherent demodulation, the PDF of the reception signal is composed of "half" a Rayleigh function $($blue$)$ and "half" a Rice function $($red$)$.
- ${\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r_0} \cap \boldsymbol{s_1}) \approx 1.43\%$ gives the proportions of the blue curve above $G =2$, and ${\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r_1} \cap \boldsymbol{s_0}) \approx 15. 18\%$ the proportions of the red curve below $G =2$.
- With $G=2$ the sum for the symbol error probability is $p_{\rm S}\approx 16.61\%$ , and with $G_{\rm opt}=1.58$ a slightly better value: $p_{\rm S}\approx 12.25\%$.
(4) Let $X$ be a Rayleigh random variable in general and $Y$ be a Rice random variable, each with above parameters. How large are ${\rm Pr}(X\le 2)$ and ${\rm Pr}(Y\le 2)$ ?
- It holds ${\rm Pr}(Y\le 2) = 2 \cdot {\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r_1} \cap \boldsymbol{s_0}) \approx 30.36\%$, since in the applet the Rice PDF is represented by the factor $1/2$.
- In the same way ${\rm Pr}(X> 2) = 2 \cdot {\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r_0} \cap \boldsymbol{s_1}) \approx 2.86\%$ ⇒ ${\rm Pr}(X \le 2)= 1-0.0286 = 97.14\%$.
(5) We consider the values $\sigma_{\rm AWGN} = 0.75$, $C_{\rm Rice} = 2.25$ and $G=G_{\rm opt}=1. 58$. How does $p_{\rm S}$ change when "Rice" is replaced by "Gauss" as best as possible?
- After the exact calculation, using the optimal threshold $G_{\rm opt}=1.58$: ${\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r_0} \cap \boldsymbol{s_1}) \approx 5. 44\%$, ${\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r_1} \cap \boldsymbol{s_0}) \approx 6.81\%$ ⇒ $p_{\rm S}\approx 12.25\%$.
- With the Gaussian approximation, for the same $G$ the first term is not changed. The second term increases to ${\rm Pr}(\boldsymbol{r_1} \cap \boldsymbol{s_0}) \approx 9.29\%$ ⇒ $p_{\rm S}\approx 14.73\%$.
- The new optimization of the threshold $G$ considering the Gaussian approximation leads to $G_{\rm opt}=1.53$ and $p_{\rm S}\approx 14.67\%$.
- The parameters of the Gaussian distribution are set as follows: mean $m_{\rm Gaussian}= C_{\rm Rice}=2.25$, standard deviation $\sigma_{\rm Gaussian}= \sigma_{\rm AWGN}=0.75$.
(6) How do the results change from $(5)$ with $\sigma_{\rm AWGN} = 0. 5$, $C_{\rm Rice} = 1.5$ and with $\sigma_{\rm AWGN} = 1$, $C_{\rm Rice} = 3$ respectively, each with $G=G_{\rm opt}$?
- With the optimal decision threshold $G_{\rm opt}$, the probabilities are the same, both for the exact Rice distribution and with the Gaussian approximation.
- For all three parameter sets, $E_{\rm S}/N_0= 2.25$. This suggests: The results with non–coherent demodulation depend on this characteristic value alone.
(7) Let the setting continue to be $\text{non–coherent/approximation}$ with $C_{\rm Rice} = 3$, $G=G_{\rm opt}$. Vary the AWGN standard deviation in the range $0.5 \le \sigma \le 1$.
Interpret the relative error ⇒ $\rm (False - Correct)/Correct$ as a function of the quotient $E_{\rm S}/N_0$.
- With $\sigma =0.5$ ⇒ $E_{\rm S}/N_0 = 9$ one obtains $p_{\rm S}^{\ \rm (exact)}\approx 0. 32\%$ and $p_{\rm S}^{\ \rm (approximate)}\approx 0.38\%$. The absolute error is $0.06\%$ and the relative error $18.75\%$.
- With $\sigma =1$ ⇒ $E_{\rm S}/N_0 = 2.25$ one obtains $p_{\rm S}^{\ \rm (exact)}\approx 12. 25\%$ and $p_{\rm S}^{\ \rm (approximate)}\approx 14.67\%$. The absolute error is $2.42\%$ and the relative error $19.75\%$.
- ⇒ The Gaussian approximation becomes better with larger $E_{\rm S}/N_0$. This statement can be seen more clearly from the absolute than from the relative error.
(8) Now repeat the last experiment with $\text{coherent}$ demodulation and $s_0 = 3$, $G=G_{\rm opt}$. What conclusion does the comparison with $(7)$ allow?
- The comparison of $(7)$ and $(8)$ shows: For each $E_{\rm S}/N_0$ there is a greater (worse) symbol error probability with non–coherent demodulation.
- For $E_{\rm S}/N_0= 9$: $p_{\rm S}^{\ \rm (coherent)}\approx 0.13\%$ and $p_{\rm S}^{\ \rm (non–coherent)}\approx 0.32\%$. And for $E_{\rm S}/N_0= 2.25$: $p_{\rm S}^{\ \rm (coherent)}\approx 6.68\%$ and $p_{\rm S}^{\ \rm (non–coherent)}\approx 12.25\%$.
- The simpler realization of the incoherent demodulator (no clock synchronization) causes a loss of quality ⇒ greater error probability.
Applet Manual
(A) Theme (veränderbare grafische Oberflächengestaltung)
- Dark: schwarzer Hintergrund (wird von den Autoren empfohlen)
- Bright: weißer Hintergrund (empfohlen für Beamer und Ausdrucke)
- Deuteranopia: für Nutzer mit ausgeprägter Grün–Sehschwäche
- Protanopia: für Nutzer mit ausgeprägter Rot–Sehschwäche
(B) Vorauswahl für die Impulsform $x_1(t)$ (rote Kurve)
(C) Parameterfestlegung für $x_1(t)$
(D) Numerikausgabe für $x_1(t_*)$ und $X_1(f_*)$
(E) Vorauswahl für die Impulsform $x_2(t)$ (blaue Kurve)
(F) Parameterfestlegung für $x_2(t)$
(G) Numerikausgabe für $x_2(t_*)$ und $X_2(f_*)$
(H) Einstellung der Zeit $t_*$ für die Numerikausgabe
(I) Einstellung der Frequenz $f_*$ für die Numerikausgabe
(J) Bereich der graphischen Darstellung im Zeitbereich
(K) Bereich der graphischen Darstellung im Frequenzbereich
(L) Auswahl der Aufgabe entsprechend der Aufgabennummer
(M) Aufgabenbeschreibung und Fragestellung
(N) Musterlösung anzeigen und verbergen
Details zu den obigen Punkten (J ) und (K)
Zoom–Funktionen:
"$+$" (Vergrößern), "$-$" (Verkleinern), "$\rm o$" (Zurücksetzen)
Verschiebe–Funktionen: "$\leftarrow$" "$\uparrow$" "$\downarrow$" "$\rightarrow$"
"$\leftarrow$" bedeutet: Bildausschnitt nach links, Ordinate nach rechts
Andere Möglichkeiten:
- Bei gedrückter Shifttaste und Scrollen kann im Koordinatensystem gezoomt werden.
- Bei gedrückter Shifttaste und gedrückter linker Maustaste kann das Koordinatensystem verschoben werden.
About the Authors
This interactive calculation tool was designed and implemented at the Institute for Communications Engineering at the Technical University of Munich.
- The first version was created in 2011 by Martin Völkl as part of his diploma thesis with “FlashMX – Actionscript” (Supervisor: Günter Söder and Klaus Eichin).
- In 2020 the program was redesigned via HTML5/JavaScript by Carolin Mirschina in the context of a working student activity (Supervisor: Tasnád Kernetzky ).
- Last revision and English version 2021 by Carolin Mirschina. Translation using DEEPL.com (free version).
- The conversion of this applet was financially supported by "Studienzuschüsse" (TUM Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering). We thank.